Home>Automotive>The Surprising Consequences Of A Stuck Open PCV Valve


Automotive
The Surprising Consequences Of A Stuck Open PCV Valve
Published: January 23, 2024
Learn about the surprising consequences of a stuck open PCV valve in automotive systems and how it can impact engine performance. Discover the importance of regular maintenance to prevent potential issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is a crucial component in modern automotive engines, playing a pivotal role in maintaining engine performance and longevity. The PCV valve, a small but vital part of this system, is responsible for regulating the flow of gases between the crankcase and the intake manifold. While the PCV valve is designed to function seamlessly, a common issue that can arise is a stuck open PCV valve.
When a PCV valve becomes stuck in the open position, it can lead to a cascade of unexpected and potentially damaging consequences for the vehicle. From increased oil consumption to compromised engine performance, the effects of a malfunctioning PCV valve can be far-reaching and costly if left unaddressed.
Understanding the function of the PCV valve, the implications of a stuck open valve, and the associated symptoms and repair processes is essential for every vehicle owner and enthusiast. In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of the PCV system, explore the repercussions of a stuck open PCV valve, and shed light on the telltale signs and solutions for this common automotive issue.
What is a PCV Valve?
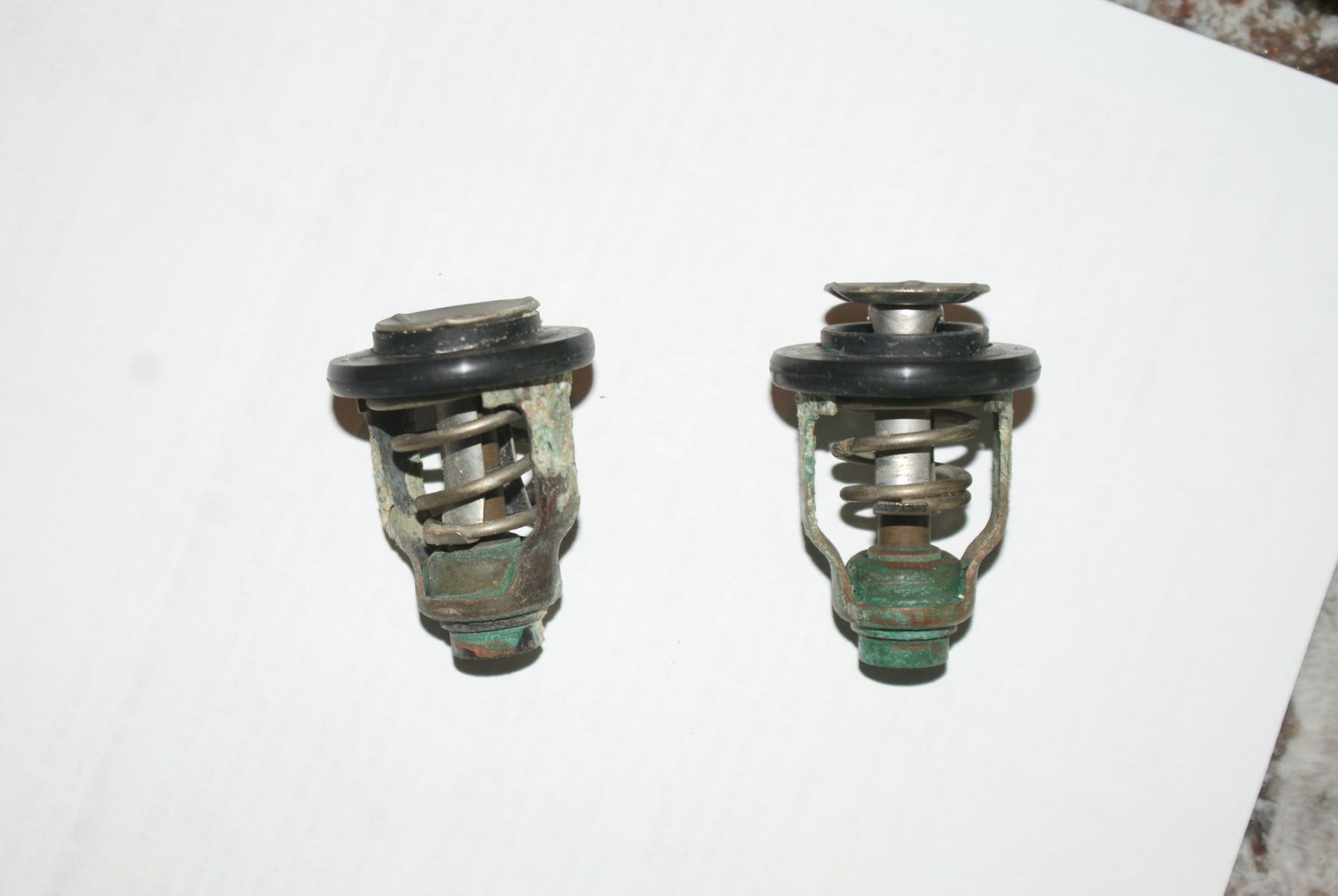
The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve is a fundamental component of the PCV system, which is designed to regulate and redirect harmful vapors and gases generated within the engine's crankcase. This small but critical valve serves as a gateway for the circulation of these gases, ensuring that the engine operates efficiently while minimizing environmental impact.
The PCV valve is typically a spring-loaded device, often housed within a rubber grommet and connected to the crankcase or valve cover. Its primary function is to control the flow of gases between the crankcase and the intake manifold. As the engine operates, a mixture of air, fuel, and combustion by-products enters the crankcase, leading to the formation of harmful gases, including hydrocarbons and moisture. Without the PCV system, these gases would accumulate, leading to increased pressure and potential damage to engine seals and gaskets.
By incorporating the PCV valve into the system, these harmful gases are drawn into the intake manifold, where they are reintroduced into the combustion chamber for re-burning. This process not only reduces emissions but also prevents the buildup of pressure within the crankcase, safeguarding the engine against potential damage.
The PCV valve operates based on the engine's vacuum, adjusting the flow of gases according to the engine's demands. When the engine is idling or operating at low speeds, the PCV valve restricts the flow of gases to maintain optimal air-fuel ratios. Conversely, during high-speed or high-load conditions, the valve opens wider to facilitate the evacuation of gases from the crankcase.
In essence, the PCV valve serves as a crucial safeguard, preventing the accumulation of harmful gases within the engine while promoting efficient combustion and minimizing environmental pollution. Its seamless operation is integral to the overall performance and longevity of the engine, making it a component of significant importance in the realm of automotive engineering and maintenance.
The Function of a PCV Valve
The PCV valve, short for Positive Crankcase Ventilation valve, is a critical component within the PCV system of modern automotive engines. Its primary function is to regulate the flow of gases between the crankcase and the intake manifold, thereby preventing the accumulation of harmful vapors and maintaining optimal engine performance.
At the core of its operation, the PCV valve acts as a gateway for the circulation of gases generated within the engine's crankcase. As the engine operates, a mixture of air, fuel, and combustion by-products enters the crankcase, leading to the formation of harmful gases, including hydrocarbons and moisture. Without the PCV system, these gases would accumulate, leading to increased pressure and potential damage to engine seals and gaskets.
The PCV valve plays a pivotal role in mitigating these issues by facilitating the controlled flow of gases. It achieves this through a spring-loaded mechanism, often housed within a rubber grommet and connected to the crankcase or valve cover. This design allows the PCV valve to adjust the flow of gases based on the engine's vacuum, ensuring that the system responds dynamically to the engine's demands.
During idle or low-speed operation, the PCV valve restricts the flow of gases, maintaining optimal air-fuel ratios and preventing the buildup of pressure within the crankcase. Conversely, during high-speed or high-load conditions, the valve opens wider to facilitate the evacuation of gases from the crankcase, thereby preventing potential damage to engine components.
By incorporating the PCV valve into the system, harmful gases are drawn into the intake manifold, where they are reintroduced into the combustion chamber for re-burning. This process not only reduces emissions but also prevents the buildup of pressure within the crankcase, safeguarding the engine against potential damage.
In essence, the PCV valve serves as a crucial safeguard, preventing the accumulation of harmful gases within the engine while promoting efficient combustion and minimizing environmental pollution. Its seamless operation is integral to the overall performance and longevity of the engine, making it a component of significant importance in the realm of automotive engineering and maintenance.
The Consequences of a Stuck Open PCV Valve
When a PCV valve becomes stuck in the open position, the repercussions can be far-reaching and impactful, affecting various aspects of the vehicle's performance and longevity. The consequences of a stuck open PCV valve can manifest in several critical areas, ultimately leading to potential engine damage and increased operational costs.
Increased Oil Consumption
One of the primary consequences of a stuck open PCV valve is increased oil consumption. When the valve is stuck open, excessive amounts of air are drawn into the crankcase, creating a higher level of internal pressure. This increased pressure can force oil past the piston rings and valve seals, leading to oil consumption at an accelerated rate. As a result, the vehicle may experience low oil levels and require more frequent oil top-ups, potentially causing long-term engine damage if left unaddressed.
Engine Contamination
A stuck open PCV valve can also result in the contamination of engine components. The continuous flow of air through the valve can carry excess oil vapors and moisture into the intake manifold, leading to the accumulation of sludge and deposits within the engine. This contamination can impede the proper functioning of critical engine parts, potentially leading to reduced performance, increased wear, and compromised longevity of engine components.
Reduced Fuel Efficiency
In addition to increased oil consumption, a stuck open PCV valve can contribute to reduced fuel efficiency. The influx of excessive air into the crankcase can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to suboptimal combustion within the engine. As a result, the vehicle may experience decreased fuel efficiency, requiring more frequent refueling and leading to higher operational costs for the owner.
Potential Engine Damage
Perhaps the most severe consequence of a stuck open PCV valve is the potential for engine damage. The combination of increased oil consumption, engine contamination, and reduced fuel efficiency can place undue stress on critical engine components, leading to accelerated wear and potential mechanical failures. Over time, this can result in costly repairs and the need for extensive engine maintenance, significantly impacting the vehicle's overall reliability and performance.
In essence, a stuck open PCV valve can have a domino effect on various aspects of the vehicle's operation, ranging from increased oil consumption and reduced fuel efficiency to potential engine damage. Recognizing the signs of a malfunctioning PCV valve and addressing the issue promptly is crucial in safeguarding the engine's health and preserving the vehicle's long-term performance and reliability.
Symptoms of a Stuck Open PCV Valve
Identifying the symptoms of a stuck open PCV valve is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of the vehicle's engine. While the consequences of this issue can be significant, recognizing the early warning signs can prompt timely intervention, mitigating potential damage and operational disruptions. Here are the key symptoms to watch for:
-
Increased Oil Consumption: A noticeable uptick in oil consumption is a common indicator of a stuck open PCV valve. As excessive air enters the crankcase due to the valve malfunction, it can lead to increased pressure, forcing oil past the piston rings and valve seals. This results in higher oil consumption, often evidenced by the need for more frequent oil top-ups between scheduled maintenance intervals.
-
Poor Engine Performance: A stuck open PCV valve can adversely impact engine performance. This may manifest as rough idling, misfiring, or a noticeable decrease in power and acceleration. The influx of unregulated air into the crankcase can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to suboptimal combustion and compromised engine operation.
-
Elevated Levels of Exhaust Smoke: An observable increase in exhaust smoke, particularly blue or grayish in color, can be indicative of a stuck open PCV valve. The excess oil vapor and contaminants drawn into the intake manifold due to the valve malfunction can contribute to abnormal exhaust emissions, signaling potential issues with the PCV system.
-
Contaminated Air Filter: A clogged or saturated air filter can point to a malfunctioning PCV valve. When the valve is stuck open, it can lead to the accumulation of oil and moisture in the air filter, causing it to become dirty or saturated more quickly than usual. Regular inspection of the air filter can help in identifying this symptom.
-
Check Engine Light: The vehicle's onboard diagnostics system may illuminate the check engine light in response to a malfunctioning PCV valve. The system can detect irregularities in engine performance and emissions, signaling the need for diagnostic assessment to pinpoint the underlying issue.
-
Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A decrease in fuel efficiency, evidenced by the need for more frequent refueling or a noticeable decrease in miles per gallon, can be a symptom of a stuck open PCV valve. The disruption in the air-fuel mixture due to the valve malfunction can lead to inefficient combustion, impacting overall fuel economy.
-
Audible Air Leaks: An audible hissing or whistling sound, particularly from the engine bay, can indicate the presence of air leaks associated with a malfunctioning PCV valve. These leaks can stem from the excessive airflow caused by the stuck open valve, warranting thorough inspection and diagnosis.
By remaining vigilant for these symptoms, vehicle owners and enthusiasts can proactively address a stuck open PCV valve, safeguarding the engine's health and optimizing overall performance. Timely diagnosis and corrective measures can mitigate the potential consequences of this issue, ensuring the vehicle operates at its best while minimizing operational costs and unexpected repairs.
Read more: How To Remove A Stuck Hose From A Spigot
Diagnosis and Repair of a Stuck Open PCV Valve
Diagnosing and repairing a stuck open PCV valve is essential to maintain the optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle's engine. When confronted with symptoms indicative of a malfunctioning PCV valve, a systematic approach to diagnosis and repair is crucial in addressing the issue effectively.
Diagnosis
The diagnostic process for a stuck open PCV valve typically begins with a thorough visual inspection of the PCV valve and associated components. This involves locating the valve, which is often situated on the valve cover or within the engine's crankcase ventilation system. Visual cues such as oil accumulation around the valve or signs of physical damage can provide initial insights into the valve's condition.
Subsequent diagnostic steps may involve testing the PCV valve's functionality using specialized diagnostic tools. This can include measuring the valve's vacuum and airflow characteristics to assess its responsiveness to engine demands. Additionally, a compression test may be conducted to evaluate the engine's internal pressure and identify any irregularities associated with a malfunctioning PCV valve.
In some cases, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle's onboard diagnostics system can provide valuable information regarding the PCV system's performance, aiding in pinpointing the root cause of the issue.
Repair
Once the stuck open PCV valve has been diagnosed, the repair process typically involves replacing the faulty valve with a new, OEM-approved component. This entails locating the specific PCV valve for the vehicle's make and model, ensuring compatibility and optimal functionality.
Before replacing the PCV valve, it is imperative to conduct a comprehensive inspection of associated components, such as hoses, grommets, and the intake manifold, to identify potential damage or contamination. Addressing any underlying issues in these components is crucial to prevent future malfunctions and ensure the seamless operation of the PCV system.
After the replacement, it is essential to verify the proper installation and functionality of the new PCV valve. This may involve conducting a vacuum test to ensure the valve responds appropriately to changes in engine vacuum and airflow, validating its effectiveness in regulating crankcase gases.
Prevention and Maintenance
To prevent future occurrences of a stuck open PCV valve, regular maintenance and inspection of the PCV system are paramount. This includes adhering to the manufacturer's recommended service intervals for PCV valve inspection and replacement, as well as monitoring engine oil consumption and quality to detect potential issues early on.
Additionally, maintaining clean air filters and ensuring the integrity of hoses and grommets within the PCV system can contribute to its longevity and optimal performance.
By diligently diagnosing, repairing, and implementing preventive measures for a stuck open PCV valve, vehicle owners can uphold the health and efficiency of their engines, mitigating potential consequences and ensuring a reliable and enduring driving experience.
Read more: Unlock The Possibilities: Open The Door
Conclusion
In conclusion, the PCV valve, an unassuming yet indispensable component of the Positive Crankcase Ventilation system, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the health and performance of modern automotive engines. Its function, intricately tied to regulating the flow of harmful gases and vapors, is essential for preventing the accumulation of pressure within the crankcase and promoting efficient combustion.
The consequences of a stuck open PCV valve, as explored in this article, underscore the far-reaching impact of this common issue. From increased oil consumption and engine contamination to reduced fuel efficiency and potential mechanical damage, the implications of a malfunctioning PCV valve can significantly disrupt the vehicle's operation and lead to unexpected operational costs.
Recognizing the symptoms of a stuck open PCV valve is paramount for proactive intervention, safeguarding the engine's health and optimizing performance. By remaining vigilant for signs such as increased oil consumption, poor engine performance, and elevated exhaust smoke, vehicle owners can promptly address this issue, mitigating potential damage and preserving the engine's longevity.
Furthermore, the diagnostic and repair processes outlined in this article provide a roadmap for effectively addressing a stuck open PCV valve. From visual inspections and diagnostic tests to the meticulous replacement of the faulty valve, a systematic approach is essential for restoring the PCV system's functionality and preventing future malfunctions.
Ultimately, the proactive maintenance and vigilance in monitoring the PCV system are key to preventing the recurrence of a stuck open PCV valve. Adhering to manufacturer-recommended service intervals, maintaining clean air filters, and ensuring the integrity of associated components are crucial steps in preserving the PCV system's effectiveness and the engine's overall health.
By understanding the critical role of the PCV valve, recognizing its potential issues, and implementing proactive maintenance measures, vehicle owners can ensure that their engines operate at their best, minimizing unexpected repairs and optimizing long-term reliability.
In essence, the PCV valve, though often overlooked, stands as a testament to the intricate engineering and meticulous maintenance required in modern automotive systems. Its seamless operation is a testament to the harmonious interplay of components within the engine, underscoring the importance of every element, no matter how small, in ensuring the vehicle's enduring performance and reliability.