Home>Automotive>The Shocking Truth: How Reversing A Car Battery Can Destroy Your Alternator


Automotive
The Shocking Truth: How Reversing A Car Battery Can Destroy Your Alternator
Published: January 8, 2024
Learn the shocking truth about how reversing a car battery can lead to the destruction of your alternator. Discover essential automotive insights now.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Car batteries and alternators are essential components of a vehicle's electrical system, working together to power the various electrical components and ensure the smooth operation of the vehicle. While many drivers are aware of the importance of maintaining their car battery, there is a lesser-known danger that can have serious repercussions: reversing a car battery. This seemingly innocent mistake can lead to catastrophic consequences, particularly for the alternator.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between car batteries and alternators, shedding light on the potential dangers of reversing a car battery. Understanding the implications of this error is crucial for every vehicle owner, as it can save them from costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns. So, let's embark on this eye-opening journey to uncover the shocking truth about how reversing a car battery can spell disaster for your alternator.
Understanding Car Batteries and Alternators
Car batteries and alternators are integral components of a vehicle's electrical system, working in tandem to provide the necessary power for starting the engine, running electrical systems, and charging the battery. Understanding the functions of these two components is crucial for every vehicle owner, as it enables them to grasp the potential risks associated with mishandling their car's electrical system.
Car Batteries:
Car batteries serve as the electrical storage unit of a vehicle, providing the initial power required to start the engine. They also supply power to the vehicle's electrical systems when the engine is not running. Most car batteries are lead-acid batteries, consisting of lead plates submerged in an electrolyte solution. When the battery is charged, a chemical reaction occurs, storing electrical energy within the battery. This stored energy is then released to power the starter motor and ignite the engine.
Alternators:
On the other hand, alternators are responsible for generating electrical power while the engine is running. They convert mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, which is used to recharge the battery and power the vehicle's electrical systems. Alternators produce alternating current (AC), which is then converted to direct current (DC) by the vehicle's electrical system for use in charging the battery and operating electrical components.
The Symbiotic Relationship:
Car batteries and alternators work symbiotically to ensure a continuous and reliable power supply for the vehicle. While the battery provides the initial power to start the engine and supports electrical systems when the engine is off, the alternator takes over once the engine is running, supplying power to the vehicle's electrical components and recharging the battery. This seamless coordination between the two components is essential for the proper functioning of the vehicle's electrical system.
Understanding the roles of car batteries and alternators is vital for maintaining the overall health of a vehicle's electrical system. Any mishandling or incorrect connections can disrupt this delicate balance, potentially leading to severe consequences for both the battery and the alternator. Therefore, being aware of the intricacies of these components is crucial for every vehicle owner to avoid costly repairs and prevent unexpected electrical failures.
The Dangers of Reversing a Car Battery
Reversing a car battery, also known as connecting the positive terminal to the vehicle's chassis and the negative terminal to the starter or ground, poses significant risks that can have detrimental effects on the vehicle's electrical system. This error can occur inadvertently during maintenance or when jump-starting a vehicle, making it crucial for every vehicle owner to understand the potential dangers associated with this mistake.
When a car battery is reversed, the flow of electrical current is disrupted, leading to a series of damaging consequences. One of the immediate risks is the potential for the battery to overheat and generate hydrogen gas at an accelerated rate. This buildup of hydrogen gas within the battery enclosure poses a severe safety hazard, as it increases the risk of an explosion or leakage of corrosive electrolyte, endangering the vehicle and its occupants.
Furthermore, reversing a car battery can result in the malfunctioning of the vehicle's electrical components and systems. The reversed polarity can cause irreversible damage to sensitive electronic components, including the vehicle's onboard computer, sensors, and entertainment systems. This can lead to a myriad of electrical malfunctions, such as erratic behavior of the dashboard instruments, malfunctioning of the audio system, and disruption of the vehicle's communication network.
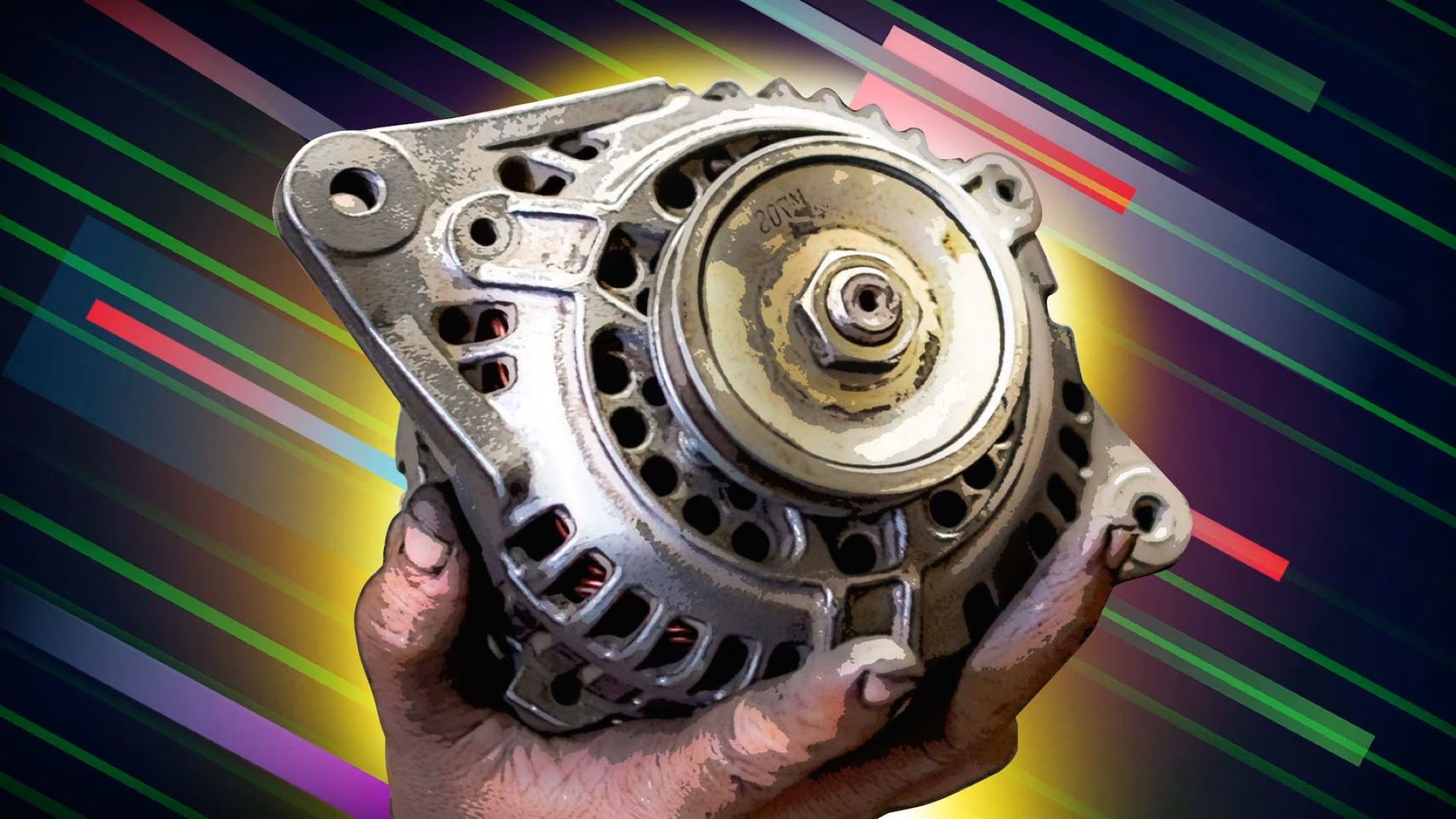
In addition to the immediate risks, the most significant danger of reversing a car battery lies in its potential to damage the alternator. The alternator, designed to produce electrical power in a specific direction, is highly sensitive to changes in polarity. When a car battery is reversed, the alternator is subjected to an abnormal electrical load, causing it to work in reverse and generate electricity in the opposite direction. This abnormal operation places immense strain on the alternator, leading to overheating, increased wear and tear, and ultimately, irreversible damage to its internal components.
The repercussions of a damaged alternator extend beyond the electrical system, affecting the vehicle's overall performance and reliability. A compromised alternator can lead to frequent battery failures, dimming or flickering headlights, and erratic electrical behavior, ultimately resulting in unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Understanding the dangers of reversing a car battery is pivotal for every vehicle owner, as it underscores the critical importance of handling the vehicle's electrical system with care and precision. By being mindful of the potential risks and taking proactive measures to prevent this error, vehicle owners can safeguard their alternator, preserve the integrity of their electrical system, and avoid the costly consequences of a seemingly innocuous mistake.
How Reversing a Car Battery Can Destroy Your Alternator
Reversing a car battery, a seemingly innocuous mistake, can have catastrophic consequences for the alternator, the very heart of a vehicle's electrical system. The alternator, designed to produce electrical power in a specific direction, is highly sensitive to changes in polarity. When a car battery is reversed, the alternator is subjected to an abnormal electrical load, causing it to work in reverse and generate electricity in the opposite direction.
This abnormal operation places immense strain on the alternator, leading to a cascade of damaging effects. The first and most immediate impact is the overheating of the alternator. The abnormal flow of electrical current within the alternator results in increased resistance and heat generation, exceeding the component's designed capacity. This excessive heat not only compromises the alternator's internal components but also accelerates wear and tear, significantly reducing its operational lifespan.
Furthermore, the reversed polarity places the alternator's diodes under immense stress. Diodes are crucial components within the alternator responsible for converting the alternating current (AC) produced by the alternator into direct current (DC) to charge the battery and power the vehicle's electrical systems. When the car battery is reversed, the diodes are forced to function in a manner contrary to their design, leading to rapid deterioration and potential failure. This compromised functionality not only impedes the charging of the battery but also disrupts the supply of stable electrical power to the vehicle's systems, leading to erratic behavior and potential malfunctions.
In addition to overheating and diode stress, the abnormal operation of the alternator due to reversed battery polarity can cause voltage irregularities. The alternator's voltage regulator, responsible for maintaining a steady output voltage, is unable to effectively control the electrical output under these abnormal conditions. This results in fluctuating voltage levels, which can damage sensitive electronic components within the vehicle's electrical system, including the onboard computer, sensors, and entertainment systems.
The cumulative effect of these damaging consequences is the irreversible destruction of the alternator. Once compromised, the alternator's ability to generate electrical power and maintain a stable electrical system is severely diminished. This not only jeopardizes the vehicle's performance and reliability but also leads to the need for costly repairs or replacement, adding to the already substantial repercussions of reversing a car battery.
Understanding how reversing a car battery can destroy the alternator underscores the critical importance of handling the vehicle's electrical system with precision and care. By being mindful of the potential risks and taking proactive measures to prevent this error, vehicle owners can safeguard their alternator, preserve the integrity of their electrical system, and avoid the costly consequences of a seemingly innocuous mistake.
Preventing Damage to Your Alternator
Preventing damage to your alternator starts with a fundamental understanding of the risks associated with mishandling a car's electrical system. By being mindful of the potential dangers and taking proactive measures, vehicle owners can effectively safeguard their alternator and preserve the overall health of the vehicle's electrical system.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of the car's electrical components are crucial for identifying any potential issues that could lead to alternator damage. This includes checking the battery terminals for corrosion, ensuring secure connections, and inspecting the alternator for signs of wear or damage. Additionally, monitoring the vehicle's electrical performance, such as the battery charging rate and the behavior of electrical systems, can provide early indications of potential problems.
Correct Battery Installation
When replacing or installing a new battery, it is essential to ensure the correct polarity and connections. Double-checking the positive and negative terminals and following the manufacturer's guidelines for installation can prevent the risk of reversing the battery and safeguard the alternator from potential damage.
Safe Jump-Starting Practices
During jump-starting procedures, it is critical to follow the correct sequence of connections to avoid reversing the battery. Always connect the positive (+) terminal of the charged battery to the positive terminal of the dead battery and the negative (-) terminal of the charged battery to a solid, unpainted metal part of the vehicle's engine, ensuring a secure ground connection. This practice prevents the risk of inadvertently reversing the battery and protects the alternator from potential harm.
Utilize Surge Protection Devices
Installing surge protection devices, such as diode isolators or surge protectors, can provide an additional layer of defense against electrical mishaps. These devices help prevent voltage spikes and reverse polarity situations, safeguarding the alternator and other sensitive electrical components from potential damage.
Professional Installation and Repairs
When replacing the alternator or conducting electrical system repairs, entrusting the task to qualified professionals ensures that the components are installed correctly and the electrical system is properly configured. Professional installation and repairs minimize the risk of errors that could lead to alternator damage and ensure the optimal functioning of the vehicle's electrical system.
By implementing these preventive measures and maintaining a vigilant approach to the vehicle's electrical system, car owners can effectively protect their alternator from potential damage and uphold the reliability and performance of their vehicle's electrical components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between car batteries and alternators underscores the critical importance of understanding the potential dangers associated with mishandling the vehicle's electrical system. Reversing a car battery, a seemingly innocent mistake, can have far-reaching and devastating consequences, particularly for the alternator. The alternator, designed to produce electrical power in a specific direction, is highly sensitive to changes in polarity. When a car battery is reversed, the alternator is subjected to abnormal electrical loads, leading to overheating, diode stress, voltage irregularities, and ultimately, irreversible damage.
The shocking truth about how reversing a car battery can destroy the alternator serves as a stark reminder of the need for vigilance and precision when dealing with the vehicle's electrical components. The potential risks, including overheating, diode stress, and voltage irregularities, highlight the delicate balance within the vehicle's electrical system and the catastrophic repercussions that can arise from a simple error.
However, by understanding the dangers and taking proactive measures, vehicle owners can effectively safeguard their alternator and preserve the overall health of the vehicle's electrical system. Regular maintenance and inspection, correct battery installation, safe jump-starting practices, utilization of surge protection devices, and professional installation and repairs are vital strategies for preventing damage to the alternator.
Ultimately, the prevention of alternator damage lies in the hands of vehicle owners, who must prioritize the proper handling of the vehicle's electrical system. By adhering to best practices and remaining vigilant, vehicle owners can mitigate the risks associated with reversing a car battery and ensure the reliable performance of their vehicle's electrical components.
In essence, the shocking truth about how reversing a car battery can destroy the alternator serves as a compelling call to action for every vehicle owner. By embracing a proactive and informed approach to the maintenance and handling of their vehicle's electrical system, they can protect their alternator, avoid costly repairs, and uphold the reliability and performance of their vehicle's electrical components.