Home>Automotive>Loud Acceleration: Is Your Car’s Engine In Trouble?

Automotive
Loud Acceleration: Is Your Car’s Engine In Trouble?
Published: January 11, 2024
Experience loud acceleration? Your car's engine might be in trouble. Get expert automotive advice to diagnose and fix the issue.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Loud Acceleration
When you press down on the accelerator pedal, you expect your car to respond with a smooth and consistent increase in speed. However, if you notice that the acceleration is accompanied by an unusually loud noise, it could be a sign of underlying engine trouble. Understanding the potential causes of loud acceleration is crucial for maintaining the health of your vehicle.
Loud acceleration can manifest in various ways, from a deep rumbling sound to a high-pitched whine. These noises can be indicative of different issues within the engine and its surrounding components. It's essential to pay attention to the specific characteristics of the sound, as this can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
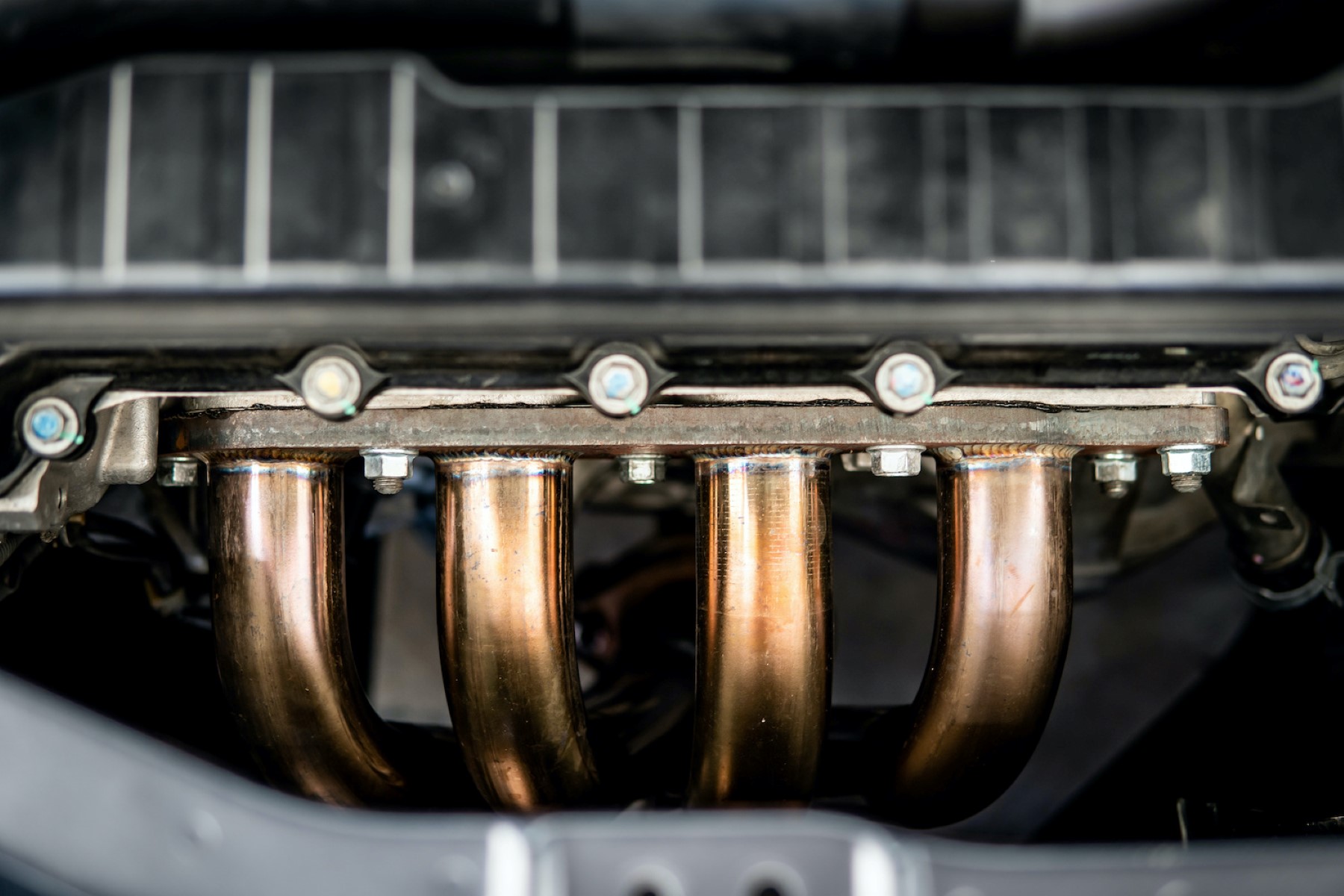
In some cases, a loud acceleration noise may stem from issues related to the exhaust system. A failing or damaged exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, or muffler can result in increased noise during acceleration. These components are vital for reducing engine noise and directing exhaust gases away from the vehicle, so any malfunction can lead to a noticeable increase in sound.
Furthermore, problems with the engine itself can also contribute to loud acceleration. Issues such as a worn-out timing belt, malfunctioning fuel injectors, or damaged pistons can generate abnormal sounds when the car is speeding up. Additionally, a lack of proper lubrication in the engine's moving parts can lead to increased friction and noise during acceleration.
Understanding the nuances of loud acceleration is not only essential for identifying potential problems but also for taking preemptive measures to prevent further damage. By recognizing the distinct characteristics of the noise and its possible sources, you can equip yourself with the knowledge needed to address the issue effectively.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the common causes of loud acceleration, the symptoms of engine trouble, steps to diagnose engine issues, and practical tips for preventing engine problems. Armed with this information, you will be better prepared to tackle any issues related to loud acceleration and ensure the optimal performance of your vehicle.
Read more: How To Determine The Engine Type Of Your Car
Common Causes of Loud Acceleration
Loud acceleration in a vehicle can be attributed to a variety of underlying issues, each with its own distinct characteristics and potential repercussions. Understanding these common causes is crucial for identifying and addressing engine trouble effectively.
-
Exhaust System Malfunction: A failing exhaust system, including components such as the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, or muffler, can lead to increased noise during acceleration. These components play a vital role in reducing engine noise and directing exhaust gases away from the vehicle. Any malfunction in these parts can result in a noticeable increase in sound, often characterized by a deep rumbling or hissing noise.
-
Engine Component Wear: As a vehicle's engine ages, various components may experience wear and tear, leading to increased noise during acceleration. A worn-out timing belt, malfunctioning fuel injectors, or damaged pistons can all contribute to abnormal sounds when the car is speeding up. Additionally, insufficient lubrication in the engine's moving parts can result in increased friction and noise during acceleration.
-
Transmission Issues: Problems within the transmission system can also cause loud acceleration. Issues such as worn-out gears, low transmission fluid levels, or a malfunctioning torque converter can lead to unusual noise when the vehicle is accelerating. This noise may be characterized by a high-pitched whine or grinding sound, indicating potential issues within the transmission assembly.
-
Air Intake Problems: An improperly functioning air intake system can result in loud acceleration noise. Any blockages or damage within the air intake components, such as the air filter or intake manifold, can disrupt the airflow into the engine, leading to irregular combustion and increased noise during acceleration. This can manifest as a distinctive sucking or wheezing sound.
-
Ignition System Irregularities: Faulty ignition components, including spark plugs, ignition coils, or the ignition timing, can contribute to loud acceleration noise. When these components fail to function optimally, the combustion process within the engine may become irregular, leading to increased noise during acceleration. This noise may be characterized by sputtering or popping sounds.
Understanding these common causes of loud acceleration is essential for diagnosing potential engine issues. By recognizing the specific characteristics of the noise and its likely sources, vehicle owners can take proactive measures to address these issues and maintain the optimal performance of their vehicles.
Symptoms of Engine Trouble
Recognizing the symptoms of engine trouble is crucial for identifying potential issues early and taking proactive measures to address them. Several distinct signs can indicate underlying problems within a vehicle's engine, serving as red flags for drivers to be mindful of. Here are the key symptoms that may signify engine trouble:
-
Unusual Noises: A significant indicator of engine trouble is the presence of unusual noises during operation. These may include knocking, tapping, or hissing sounds emanating from the engine compartment. Such noises can signify issues with the internal components, such as worn-out bearings, damaged pistons, or malfunctioning valves. Additionally, a loud acceleration noise, as discussed earlier, can also be a symptom of engine trouble.
-
Decreased Performance: A noticeable decline in the vehicle's overall performance, including reduced power, sluggish acceleration, or difficulty maintaining consistent speed, can point towards underlying engine issues. This decrease in performance may be attributed to problems such as fuel system irregularities, ignition component malfunctions, or inefficient combustion processes within the engine.
-
Increased Exhaust Emissions: An increase in visible exhaust emissions, such as dark smoke or unusual odors, can indicate potential engine trouble. These emissions may be indicative of issues with the combustion process, fuel system inefficiencies, or exhaust system malfunctions. Monitoring the color, consistency, and odor of the exhaust emissions can provide valuable insights into the health of the engine.
-
Abnormal Vibrations: Unusual vibrations or shaking felt within the vehicle, especially during idling or acceleration, can signal underlying engine irregularities. These vibrations may be indicative of misfiring cylinders, engine misalignment, or worn-out engine mounts. Detecting and addressing these vibrations early can prevent further damage to the engine and surrounding components.
-
Warning Lights: The illumination of the check engine light or other dashboard warning indicators is a clear indication of potential engine trouble. Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostic systems that can detect and signal various engine irregularities. When these warning lights appear, it is essential to promptly diagnose the underlying issues to prevent further damage.
Recognizing these symptoms of engine trouble empowers vehicle owners to take timely action and seek professional assistance when necessary. By remaining vigilant and attentive to these signs, drivers can maintain the optimal performance and longevity of their vehicles while minimizing the risk of extensive engine damage.
Steps to Diagnose Engine Issues
-
Listen Carefully: When experiencing loud acceleration or other unusual engine noises, start by listening carefully to the sound. Note the specific characteristics, such as the type, intensity, and location of the noise. Is it a knocking, whining, or hissing sound? Does it originate from the engine compartment, exhaust system, or transmission? This initial assessment can provide valuable clues about the potential source of the issue.
-
Check Fluid Levels: Inspect the levels and condition of essential fluids, including engine oil, transmission fluid, and coolant. Low oil levels or contaminated fluids can contribute to engine irregularities and increased noise during operation. Additionally, look for any signs of leaks or unusual fluid discoloration, which may indicate underlying issues within the engine or its associated systems.
-
Examine the Exhaust System: A thorough inspection of the exhaust system can reveal potential causes of loud acceleration noise. Check for visible damage or corrosion in the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler. Any leaks, dents, or loose components within the exhaust system can lead to increased noise and should be addressed promptly.
-
Scan for Error Codes: Utilize an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle's onboard computer. These codes can provide specific insights into potential engine irregularities, such as misfires, sensor malfunctions, or fuel system issues. By interpreting the error codes, you can narrow down the possible causes of the loud acceleration noise.
-
Inspect Ignition Components: Examine the condition of ignition components, including spark plugs, ignition coils, and the ignition timing. Worn-out or malfunctioning ignition parts can contribute to irregular combustion and increased noise during acceleration. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, and replace any components showing signs of deterioration.
-
Evaluate Air Intake System: Assess the air intake components, such as the air filter, intake manifold, and associated ducting, for any blockages or damage. A restricted airflow into the engine can lead to irregular combustion and noisy acceleration. Ensure that the air intake system is clean, free from debris, and functioning optimally to support efficient engine operation.
-
Seek Professional Inspection: If the above steps do not pinpoint the source of the loud acceleration noise, or if you are uncertain about diagnosing the issue, it is advisable to seek professional inspection from a qualified mechanic or automotive technician. They can perform comprehensive diagnostic tests, including compression tests, leak-down tests, and visual inspections, to identify and address underlying engine issues effectively.
By following these steps to diagnose engine issues, vehicle owners can gain valuable insights into the root cause of loud acceleration noise and take appropriate measures to address the problem. Proactive diagnosis and timely intervention can help prevent further damage to the engine and ensure the continued reliability of the vehicle.
Tips for Preventing Engine Problems
Preventing engine problems is essential for maintaining the longevity and performance of your vehicle. By implementing proactive measures and adhering to regular maintenance practices, you can minimize the risk of engine-related issues and ensure the optimal functioning of your car. Here are valuable tips for preventing engine problems:
-
Routine Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle. Regular oil changes, filter replacements, and fluid checks are vital for preserving the health of the engine and its associated components. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to accelerated wear and potential malfunctions within the engine.
-
Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel from reputable sources. Poor-quality or contaminated fuel can lead to fuel system irregularities and engine damage. Opt for fuel that meets the recommended octane rating for your vehicle, and consider using fuel additives to maintain fuel system cleanliness.
-
Cooling System Care: Monitor the condition of your vehicle's cooling system, including the radiator, coolant levels, and hoses. Overheating can cause severe damage to the engine, so it's crucial to ensure proper cooling system function. Regularly inspect and replace coolant as recommended by the manufacturer.
-
Air Filter Maintenance: Regularly inspect and replace the air filter as per the manufacturer's guidelines. A clean air filter is essential for maintaining optimal air intake into the engine, supporting efficient combustion, and preventing contaminants from entering the engine.
-
Driving Habits: Practice smooth and considerate driving habits to reduce strain on the engine. Avoid aggressive acceleration, excessive idling, and over-revving the engine. Consistent and gentle driving can contribute to prolonged engine life and reduced wear on internal components.
-
Timely Repairs: Address any identified issues promptly to prevent them from escalating into more significant engine problems. Whether it's unusual noises, warning lights, or performance irregularities, seeking professional diagnosis and repairs can prevent minor issues from causing extensive damage to the engine.
-
Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Allow the engine to warm up for a few minutes before driving, especially in cold weather. Similarly, avoid turning off the engine immediately after high-speed or strenuous driving. Allowing the engine to cool down gradually can prevent thermal stress and potential damage.
-
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of the engine compartment, checking for leaks, worn-out belts, or loose components. Additionally, monitor fluid levels, including engine oil, transmission fluid, and coolant, to ensure they are at the appropriate levels.
-
Professional Maintenance: Entrust complex engine maintenance tasks to qualified automotive professionals. Regular tune-ups, timing belt replacements, and comprehensive engine inspections by experienced technicians can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
By incorporating these tips into your vehicle maintenance routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of engine problems and enjoy a reliable and efficient driving experience. Prioritizing engine health through proactive maintenance and attentive care can contribute to the long-term performance and durability of your vehicle.















