Home>Technology and Computers>Unveiling The Secrets Of The Zinc Lined Coffin


Technology and Computers
Unveiling The Secrets Of The Zinc Lined Coffin
Published: January 8, 2024
Discover the intersection of technology and computers in the fascinating world of the zinc lined coffin. Uncover the secrets and innovations that define this unique technological marvel.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the final resting place for our loved ones, we often seek a solution that not only honors their memory but also provides long-lasting preservation. In this quest, the concept of zinc-lined coffins has emerged as a topic of fascination and intrigue. The utilization of zinc in coffin construction has sparked curiosity due to its potential to enhance the longevity of the burial vessel and protect the deceased within. As we delve into the world of zinc-lined coffins, we will unravel the historical background, the scientific principles governing their efficacy, and the environmental implications associated with their usage. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the secrets and significance of zinc-lined coffins, shedding light on an aspect of funerary practices that intertwines tradition with modern innovation.
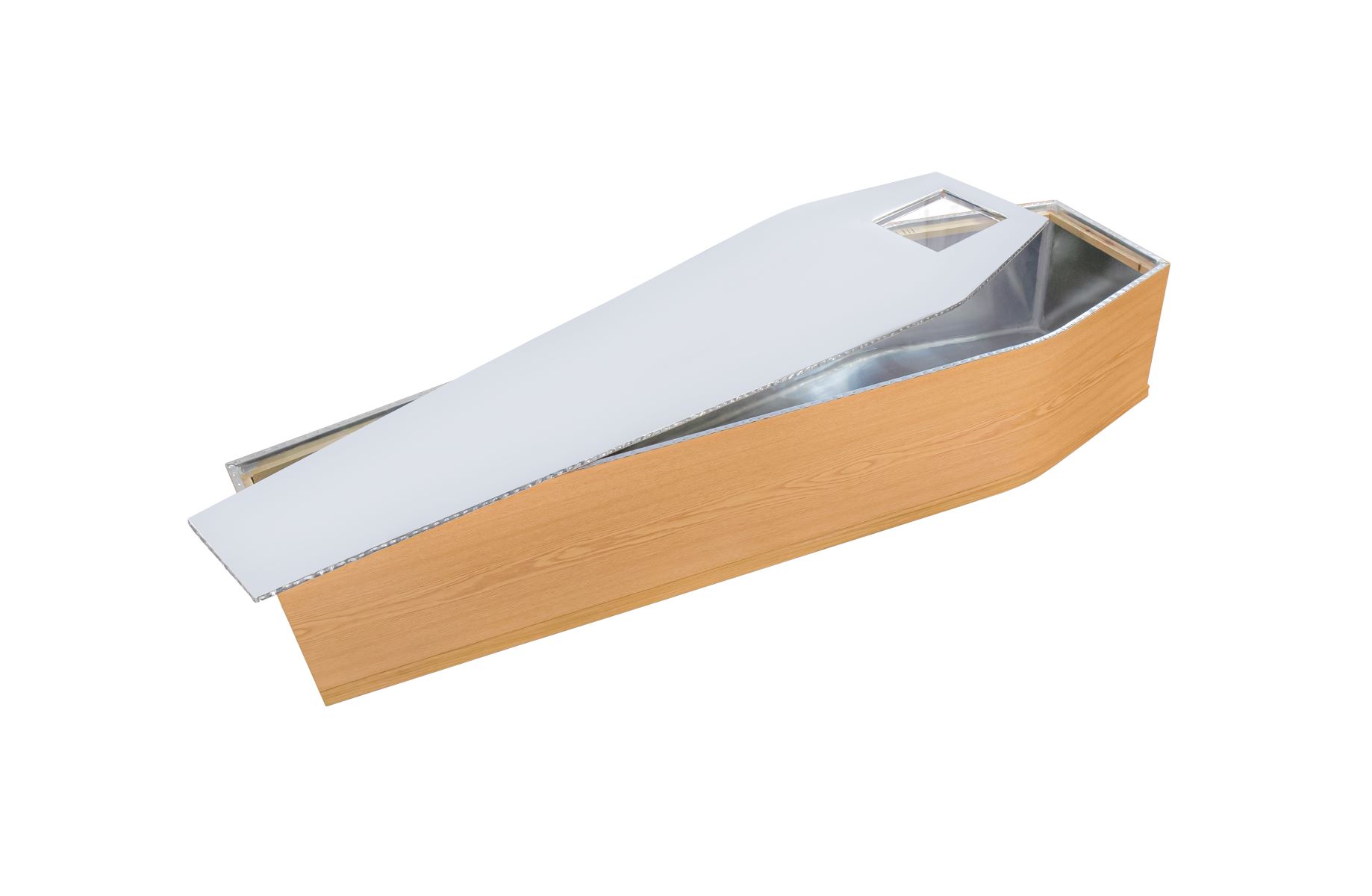
Historical Background of Zinc Lined Coffins
The concept of utilizing zinc-lined coffins traces its origins back to the 19th century. During this period, the understanding of the chemical and physical properties of zinc led to its application in various industries, including the production of burial caskets. The incorporation of zinc in coffin construction was primarily driven by the desire to mitigate the effects of decomposition and ensure the long-term preservation of the deceased.
The historical significance of zinc-lined coffins can be attributed to the emergence of concerns regarding the durability and protective capabilities of traditional wooden coffins. It was recognized that wooden caskets, while serving as a dignified vessel for the deceased, were susceptible to decay and environmental factors that could compromise their structural integrity over time. This realization prompted the exploration of alternative materials that could offer enhanced resistance to deterioration and contribute to the overall preservation of the deceased.
The introduction of zinc-lined coffins represented a pivotal advancement in the evolution of funerary practices, signifying a transition towards more robust and enduring burial solutions. The utilization of zinc, renowned for its corrosion-resistant properties, offered a compelling solution to the challenges associated with traditional coffin materials. This marked a significant shift in the approach to burial customs, as the incorporation of zinc represented a deliberate effort to extend the longevity of the burial vessel and safeguard the remains of the departed.
As the funeral industry continued to evolve, the adoption of zinc-lined coffins gained momentum, with an increasing recognition of the benefits they offered in terms of preservation and protection. This historical progression underscores the enduring relevance of zinc-lined coffins, reflecting a convergence of tradition and innovation in the pursuit of dignified and enduring memorialization for the departed.
The historical background of zinc-lined coffins serves as a testament to the enduring quest for solutions that honor the memory of the deceased while addressing the practical considerations of long-term preservation. This evolution reflects a deep-seated commitment to upholding the sanctity of funerary practices and ensuring that the final resting place of our loved ones endures as a timeless tribute to their legacy.
The Science Behind Zinc Lined Coffins
The efficacy of zinc-lined coffins is rooted in the fundamental principles of corrosion resistance and protective encapsulation. Zinc, renowned for its exceptional resistance to corrosion, serves as a formidable barrier against the natural processes of decay and deterioration. When integrated into the construction of coffins, zinc functions as a shield, safeguarding the interior environment from external elements and preserving the structural integrity of the vessel.
At the core of the science behind zinc-lined coffins lies the phenomenon of galvanic protection, wherein zinc acts as a sacrificial anode, offering itself as a protective barrier to prevent corrosion of the underlying materials. This process, known as cathodic protection, effectively shields the coffin from the corrosive effects of moisture, soil, and other environmental factors that could compromise its longevity.
Furthermore, the utilization of zinc in coffin construction aligns with the principles of biosecurity and containment. By encapsulating the deceased within a zinc-lined environment, the coffin serves as a barrier that impedes the intrusion of external elements, thereby contributing to the preservation of the remains. This protective enclosure minimizes the impact of external factors, such as microbial activity and environmental exposure, thereby fostering an environment conducive to long-term preservation.
Moreover, the science behind zinc-lined coffins extends beyond corrosion resistance to encompass the thermal conductivity of zinc. This property plays a crucial role in regulating the internal temperature of the coffin, thereby mitigating the effects of temperature fluctuations and maintaining a more stable microclimate within the burial vessel. This aspect is particularly significant in regions characterized by diverse climatic conditions, where the thermal conductivity of zinc contributes to the preservation of the deceased by minimizing the impact of external temperature variations.
In essence, the science behind zinc-lined coffins embodies a harmonious fusion of material properties and protective mechanisms, culminating in a burial solution that harmonizes preservation with durability. The utilization of zinc as a foundational component of coffin construction exemplifies a meticulous consideration of scientific principles to ensure the enduring protection and preservation of the deceased, thereby upholding the sanctity of the final resting place.
This section is a testament to the intricate scientific underpinnings that underlie the utilization of zinc in coffin construction, underscoring its role as a guardian of preservation and a testament to the enduring commitment to honoring the memory of the departed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc Lined Coffins
The utilization of zinc-lined coffins presents a myriad of advantages and disadvantages that warrant careful consideration in the context of funerary practices and burial solutions.
Advantages
-
Corrosion Resistance: One of the primary advantages of zinc-lined coffins lies in their exceptional resistance to corrosion. The inherent properties of zinc render the coffin impervious to the detrimental effects of moisture and environmental factors, thereby ensuring prolonged structural integrity and preservation.
-
Longevity and Preservation: Zinc-lined coffins are renowned for their ability to facilitate long-term preservation of the deceased. By creating a protective enclosure that mitigates the impact of external elements, these coffins contribute to the sustained integrity of the remains, thereby honoring the memory of the departed over an extended period.
-
Biosecurity and Containment: The encapsulating nature of zinc-lined coffins serves as a barrier that impedes the intrusion of external elements, such as microbial activity and environmental contaminants. This containment fosters an environment conducive to preservation, thereby upholding the sanctity of the final resting place.
-
Thermal Conductivity: The thermal conductivity of zinc contributes to the regulation of internal temperature within the coffin, thereby minimizing the effects of temperature variations and maintaining a more stable microclimate. This aspect is particularly significant in diverse climatic conditions, where it enhances the preservation of the deceased.
Read more: How To Determine Whose Line It Is Anyway
Disadvantages
-
Environmental Impact: The production and eventual disposal of zinc-lined coffins may pose environmental concerns, particularly in terms of resource utilization and waste management. The extraction and processing of zinc entail environmental implications that warrant conscientious consideration in the broader context of sustainability.
-
Cost Considerations: Zinc-lined coffins may be associated with higher production costs compared to traditional burial vessels. This aspect necessitates a balanced assessment of the financial implications and accessibility, ensuring that the benefits of zinc-lined coffins align with the preferences and means of the individuals and families involved.
-
Regulatory Compliance: The utilization of zinc-lined coffins may be subject to regulatory standards and requirements, necessitating adherence to specific guidelines and protocols. This regulatory dimension adds a layer of consideration in the selection and utilization of zinc-lined coffins within the framework of funerary practices.
The exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of zinc-lined coffins underscores the multifaceted considerations that underpin the selection and utilization of burial vessels. By weighing these factors thoughtfully, individuals and families can make informed decisions that align with their values, preferences, and the enduring tribute they seek to create for their departed loved ones.
Environmental Impact of Zinc Lined Coffins
The environmental impact of zinc-lined coffins encompasses a complex interplay of considerations that extend from the production phase to the eventual disposition of these burial vessels. As the funeral industry gravitates towards sustainable practices and eco-conscious choices, it becomes imperative to scrutinize the ecological footprint associated with the utilization of zinc-lined coffins.
Production and Resource Utilization
The manufacturing process of zinc-lined coffins entails resource utilization and energy consumption, thereby contributing to the ecological footprint attributed to their production. The extraction and processing of zinc, a vital component of these coffins, necessitate the utilization of natural resources and energy, thereby warranting a conscientious assessment of the environmental implications associated with their fabrication.
Waste Management and Disposal
Upon fulfilling their intended purpose, zinc-lined coffins present challenges in terms of waste management and disposal. The eventual disposition of these burial vessels raises considerations regarding their impact on the environment, particularly in the context of burial practices that prioritize sustainability and environmental stewardship. The materials used in the construction of zinc-lined coffins, including zinc itself, necessitate thoughtful deliberation regarding their long-term environmental consequences.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
In light of the growing emphasis on sustainable funeral practices, the environmental impact of zinc-lined coffins prompts a reflection on the ethical dimensions of their utilization. As individuals and families navigate end-of-life arrangements, the ecological ramifications of their choices become intertwined with broader considerations of environmental responsibility and stewardship. This underscores the need for conscientious decision-making that aligns with sustainable principles while honoring the memory of the departed.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Standards
The selection and utilization of zinc-lined coffins intersect with regulatory frameworks and environmental standards that seek to mitigate the ecological impact of funeral practices. Adherence to these standards necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications associated with zinc-lined coffins, thereby fostering a conscientious approach to their utilization within the broader context of environmentally responsible funerary practices.
In essence, the environmental impact of zinc-lined coffins underscores the imperative of integrating ecological considerations into the fabric of funeral practices. By fostering an informed awareness of the environmental implications associated with these burial vessels, individuals and families can navigate end-of-life arrangements with a mindful appreciation for sustainability and environmental stewardship. This multifaceted perspective enriches the dialogue surrounding funeral practices, emphasizing the harmonious coexistence of commemoration and ecological mindfulness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of zinc-lined coffins unveils a tapestry of historical significance, scientific ingenuity, practical considerations, and environmental implications that converge to shape the landscape of funerary practices. The historical background of zinc-lined coffins reflects an enduring quest for burial solutions that honor the memory of the departed while addressing the imperative of long-term preservation. This evolution signifies a deliberate transition towards more durable and enduring burial vessels, embodying a harmonious blend of tradition and innovation.
The science behind zinc-lined coffins illuminates the meticulous integration of material properties and protective mechanisms, culminating in a burial solution that harmonizes preservation with durability. The utilization of zinc as a foundational component of coffin construction exemplifies a meticulous consideration of scientific principles to ensure the enduring protection and preservation of the deceased, thereby upholding the sanctity of the final resting place.
Furthermore, the examination of the advantages and disadvantages of zinc-lined coffins underscores the multifaceted considerations that underpin the selection and utilization of burial vessels. By weighing these factors thoughtfully, individuals and families can make informed decisions that align with their values, preferences, and the enduring tribute they seek to create for their departed loved ones.
The environmental impact of zinc-lined coffins prompts a reflection on the ethical dimensions of their utilization, intertwining ecological ramifications with broader considerations of environmental responsibility and stewardship. This underscores the need for conscientious decision-making that aligns with sustainable principles while honoring the memory of the departed.
In essence, the unveiling of the secrets and significance of zinc-lined coffins transcends the realm of funeral practices, encapsulating a narrative of reverence, preservation, and environmental mindfulness. It underscores the enduring commitment to honoring the memory of the departed while embracing sustainable principles that resonate with the broader ethos of environmental stewardship. As individuals and families navigate end-of-life arrangements, the multifaceted dimensions of zinc-lined coffins enrich the dialogue surrounding funeral practices, emphasizing the harmonious coexistence of commemoration and ecological mindfulness.