Home>Technology and Computers>The Ultimate Guide To Wiring A Three-Prong Plug: Unveiling The Secrets Of Wire Colors!


Technology and Computers
The Ultimate Guide To Wiring A Three-Prong Plug: Unveiling The Secrets Of Wire Colors!
Published: January 26, 2024
Learn the secrets of wire colors and the art of wiring a three-prong plug with our ultimate guide. Get expert tips and insights on technology and computers.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Wiring a three-prong plug may seem like a daunting task, especially for those new to the world of electrical work. However, with the right guidance and understanding of wire colors, this process can be demystified. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of wiring a three-prong plug, shedding light on the significance of wire colors and providing a step-by-step walkthrough. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle this essential task.
Understanding the fundamentals of wiring is crucial for anyone venturing into electrical work. It not only ensures the safe and efficient functioning of electrical devices but also minimizes the risk of hazards such as electrical shocks and fires. At the heart of this understanding lies the significance of wire colors, which serve as a universal language in the realm of electrical wiring. By unraveling the mysteries behind wire colors and their roles in electrical circuits, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the importance of precision and accuracy in wiring processes.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the intricacies of wire colors and their specific roles in electrical circuits. From identifying the hot, neutral, and ground wires to executing the wiring process with precision, each step is essential for ensuring the safety and functionality of the electrical connection. By breaking down the process into manageable steps and providing clear explanations, this guide aims to demystify the complexities of wiring a three-prong plug, making it accessible to individuals with varying levels of technical expertise.
Whether you're embarking on a home improvement project or seeking to expand your knowledge of electrical systems, mastering the art of wiring a three-prong plug is a valuable skill. With the insights and guidance offered in this guide, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the world of wire colors and confidently undertake the wiring process. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of electrical wiring, where the secrets of wire colors await discovery!
Understanding the Basics of Wiring
Wiring serves as the circulatory system of electrical devices, facilitating the seamless flow of power to enable their operation. At its core, the process of wiring involves connecting electrical components using conductive materials, typically copper or aluminum wires, to establish a complete electrical circuit. Understanding the basics of wiring is essential for anyone engaging with electrical systems, as it forms the foundation for safe and efficient electrical connections.
The primary objective of wiring is to establish a pathway for electrical current to travel from its source to the intended destination, such as a light fixture, appliance, or power outlet. This pathway is meticulously designed to ensure the unimpeded flow of electricity, minimizing resistance and heat generation that could compromise the system's integrity. By comprehending the fundamental principles of wiring, individuals can navigate the intricacies of electrical circuits with confidence and precision.
One of the fundamental concepts in wiring is the distinction between various types of electrical connections, including series and parallel circuits. In a series circuit, electrical components are arranged sequentially, forming a single pathway for current to flow. This configuration is commonly found in decorative lighting and holiday light strings. In contrast, parallel circuits feature multiple pathways for current, offering redundancy and independent operation of electrical devices. Understanding these circuit configurations is crucial for designing and implementing wiring systems tailored to specific electrical requirements.
Furthermore, the concept of voltage, current, and resistance lies at the heart of electrical wiring. Voltage represents the electrical potential difference that drives current flow, while current denotes the rate of flow of electric charge. Resistance, measured in ohms, impedes the flow of current and plays a pivotal role in determining the behavior of electrical circuits. By grasping these fundamental electrical principles, individuals can make informed decisions when selecting wiring materials and configuring electrical connections.
In essence, understanding the basics of wiring empowers individuals to navigate the intricate web of electrical systems with confidence and proficiency. Whether it involves installing a new lighting fixture, troubleshooting electrical issues, or undertaking home improvement projects, a solid grasp of wiring fundamentals forms the bedrock of safe and effective electrical work. As we delve deeper into the realm of wiring, we will unravel the significance of wire colors and their pivotal role in electrical circuits, paving the way for a comprehensive understanding of wiring a three-prong plug.
The Importance of Wire Colors
Wire colors play a pivotal role in electrical systems, serving as a visual language that conveys essential information about the function and purpose of individual wires. Understanding the significance of wire colors is paramount in ensuring the safe and accurate installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of electrical circuits. By adhering to standardized color codes, individuals can interpret the roles of wires within a circuit, thereby minimizing the risk of errors and enhancing overall safety.
In the realm of electrical wiring, wire colors are not arbitrary; they adhere to established conventions that are universally recognized and standardized. These color codes vary across regions and countries, but they are consistently applied within specific jurisdictions to maintain consistency and clarity in electrical installations. The adherence to these color codes is essential for promoting interoperability and facilitating seamless communication among electricians, technicians, and individuals working with electrical systems.
In the context of wiring a three-prong plug, the significance of wire colors becomes particularly pronounced. The three primary wire colors – black, white, and green (or bare copper) – each carry distinct meanings that are integral to the safe and effective operation of electrical devices. The black wire typically represents the "hot" wire, carrying the electrical current from the power source to the connected device. Conversely, the white wire serves as the "neutral" wire, providing a return path for the current to complete the circuit. Lastly, the green or bare copper wire is designated as the "ground" wire, safeguarding against electrical faults and providing a path for fault currents to safely dissipate.
By adhering to these standardized wire colors and understanding their respective roles, individuals can confidently navigate the wiring process, ensuring that each wire is correctly identified and connected according to its designated function. This adherence to wire color conventions not only enhances the efficiency of electrical installations but also mitigates the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits and electrical shocks.
In essence, wire colors serve as a visual roadmap, guiding individuals through the intricate network of electrical connections. By recognizing the importance of wire colors and the valuable information they convey, individuals can approach electrical wiring with heightened precision and confidence, ultimately fostering a safer and more reliable electrical infrastructure.
Identifying the Hot, Neutral, and Ground Wires
When embarking on the task of wiring a three-prong plug, the ability to accurately identify the hot, neutral, and ground wires is of paramount importance. Each wire plays a distinct role in facilitating the safe and efficient operation of electrical devices, and understanding how to differentiate between them is crucial for ensuring a successful electrical connection.
The hot wire, typically colored black, carries the electrical current from the power source to the connected device. It is essential to exercise caution when handling the hot wire, as it is the conduit through which electrical energy flows. Identifying the hot wire is the first step in the wiring process, and its proper connection is fundamental to the functionality and safety of the electrical circuit.
In contrast, the neutral wire, often colored white, serves as the return path for the electrical current to complete the circuit. It provides a crucial link between the connected device and the power source, ensuring the smooth and uninterrupted flow of electricity. While the neutral wire may not carry the same level of electrical potential as the hot wire, its role in completing the circuit is indispensable.
Furthermore, the ground wire, typically green or bare copper, acts as a vital safety feature within electrical systems. In the event of a fault or electrical surge, the ground wire provides a pathway for fault currents to safely dissipate, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and mitigating potential damage to connected devices. Properly identifying and connecting the ground wire is essential for safeguarding against electrical hazards and ensuring the overall integrity of the electrical circuit.
To accurately identify these wires, it is crucial to adhere to standardized wire color codes and to exercise diligence when examining the wiring. In situations where the color-coding may not be readily visible or available, the use of a voltage tester or multimeter can aid in confirming the identity of each wire. Additionally, referencing wiring diagrams and consulting relevant electrical codes and standards can provide valuable guidance in the process of identifying the hot, neutral, and ground wires.
By mastering the skill of identifying these essential wires, individuals can approach the task of wiring a three-prong plug with confidence and precision. This foundational knowledge forms the cornerstone of safe and effective electrical work, ensuring that electrical connections are established in a manner that prioritizes both functionality and safety.
Wiring a Three-Prong Plug Step by Step
-
Prepare the Plug: Begin by carefully inspecting the three-prong plug and ensuring that it is free from any defects or damage. This includes checking for cracks, frayed wires, or loose connections. It is crucial to work with a plug that is in optimal condition to guarantee a safe and reliable electrical connection.
-
Strip the Insulation: Using wire strippers, carefully strip off approximately 3/4 inch of insulation from the end of the power cord to expose the individual wires. Exercise caution to avoid damaging the underlying wires during this process, as their integrity is essential for the effectiveness of the electrical connection.
-
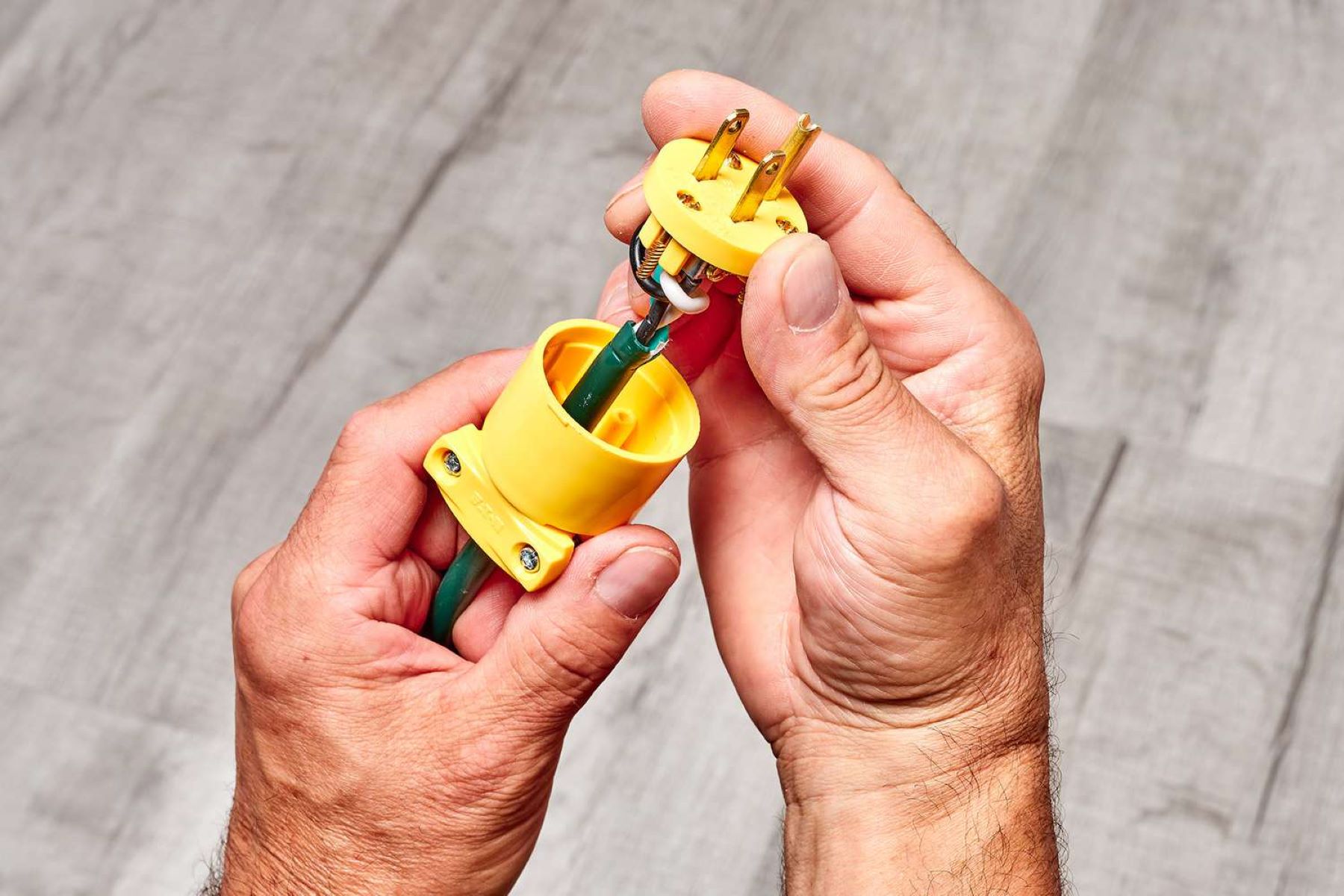
Identify the Wires: Once the insulation is removed, identify the hot, neutral, and ground wires within the power cord. The hot wire is typically black, the neutral wire is white, and the ground wire is green or bare copper. Ensuring the accurate identification of these wires is fundamental to the success of the wiring process.
-
Connect the Wires: With the wires identified, proceed to connect them to the corresponding terminals within the plug. The hot wire should be connected to the brass or gold-colored terminal, the neutral wire to the silver-colored terminal, and the ground wire to the green terminal. It is essential to secure the connections firmly to guarantee a reliable electrical contact.
-
Secure the Strain Relief: After the wires are connected, insert the power cord into the plug housing, ensuring that the outer insulation is secured within the strain relief mechanism. This serves to protect the wires from excessive tension or pulling, enhancing the overall durability of the electrical connection.
-
Assemble the Plug: Carefully assemble the plug housing, ensuring that all components fit together snugly. Verify that there are no exposed wires or loose connections within the plug, as these could pose safety hazards and compromise the effectiveness of the electrical connection.
-
Test the Plug: Before putting the plug into use, it is crucial to conduct a thorough testing process. Utilize a voltage tester or multimeter to verify that the wiring is correctly configured and that there are no faults or inconsistencies. This step is essential for ensuring the safety and functionality of the wired plug.
By following these step-by-step instructions with meticulous attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols, individuals can successfully wire a three-prong plug with confidence and precision. This process not only contributes to the safe and reliable operation of electrical devices but also reinforces the foundational principles of effective electrical work.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing and troubleshooting are critical phases in the process of wiring a three-prong plug, as they serve to validate the integrity of the electrical connection and identify any potential issues that may compromise its safety and functionality. By conducting thorough testing and implementing effective troubleshooting techniques, individuals can ensure that the wired plug meets the necessary standards for safe operation, thereby minimizing the risk of electrical hazards and optimizing the performance of connected devices.
Voltage Testing
One of the primary methods for testing the wired plug involves utilizing a voltage tester or multimeter to verify the presence of electrical potential at the plug terminals. This involves carefully inserting the voltage tester probes into the plug's receptacles to measure the voltage across the hot, neutral, and ground terminals. By confirming the presence of the expected voltage levels, individuals can ascertain that the wiring has been correctly configured and that the electrical circuit is functioning as intended.
Continuity Testing
Continuity testing is instrumental in ensuring the integrity of the electrical connections within the wired plug. By using a multimeter set to the continuity or resistance mode, individuals can verify the continuity of the hot, neutral, and ground wires from the plug terminals to their respective points of connection within the plug housing. This process aids in identifying any breaks or discontinuities in the wiring, allowing for prompt corrective action to be taken to rectify the issues.
Insulation Resistance Testing
To safeguard against electrical faults and potential short circuits, insulation resistance testing is employed to assess the effectiveness of the insulation surrounding the wired plug's conductors. By subjecting the plug to insulation resistance testing using a megohmmeter or insulation resistance tester, individuals can evaluate the insulation's ability to withstand the applied voltage and identify any weaknesses or defects that may compromise its insulating properties.
Ground Fault Testing
Given the critical role of the ground wire in mitigating electrical hazards, ground fault testing is essential to ensure its effectiveness in diverting fault currents safely. This involves simulating ground fault conditions and measuring the response of the ground wire to effectively dissipate fault currents. By conducting comprehensive ground fault testing, individuals can verify the reliability of the ground wire and address any deficiencies that may compromise its protective function.
Troubleshooting
In the event of any discrepancies or irregularities identified during the testing process, effective troubleshooting techniques must be employed to diagnose and rectify the underlying issues. This may involve inspecting the wiring for loose connections, damaged insulation, or incorrect terminations and taking corrective measures to address these issues. Additionally, referencing wiring diagrams and consulting relevant electrical codes and standards can provide valuable guidance in troubleshooting and resolving wiring-related concerns.
By meticulously conducting testing and implementing systematic troubleshooting procedures, individuals can ensure that the wired plug meets the necessary safety and performance criteria. These measures not only validate the integrity of the electrical connection but also reinforce the commitment to upholding the highest standards of electrical safety and reliability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of wiring a three-prong plug is a fundamental aspect of electrical work that demands precision, adherence to safety protocols, and a comprehensive understanding of wire colors. Throughout this guide, we have unraveled the intricacies of wire colors and their pivotal role in electrical circuits, shedding light on the significance of identifying the hot, neutral, and ground wires. By delving into the step-by-step process of wiring a three-prong plug and emphasizing the importance of testing and troubleshooting, we have equipped individuals with the knowledge and confidence to undertake this essential task.
Mastering the art of wiring a three-prong plug not only contributes to the safe and reliable operation of electrical devices but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the principles of effective electrical work. The adherence to standardized wire color codes, the accurate identification of wires, and the meticulous execution of the wiring process are essential for ensuring the integrity and safety of electrical connections. By recognizing the visual language of wire colors and interpreting their meanings within electrical circuits, individuals can navigate the complexities of wiring with precision and confidence.
The thorough testing and troubleshooting processes outlined in this guide serve as critical measures to validate the integrity of the wired plug and identify any potential issues that may compromise its safety and functionality. From voltage testing and continuity testing to insulation resistance testing and ground fault testing, these procedures underscore the commitment to upholding the highest standards of electrical safety and reliability.
As individuals venture into the realm of electrical work, whether for personal projects or professional endeavors, the knowledge and insights gained from this guide will serve as a valuable foundation for approaching wiring tasks with confidence and proficiency. By embracing the principles of safe and effective electrical work, individuals contribute to the creation of a secure and resilient electrical infrastructure, fostering a culture of excellence and reliability in electrical installations.
In essence, the journey into the world of wiring a three-prong plug unveils the intricate interplay of wire colors, electrical principles, and safety considerations. By embracing these principles and integrating them into practice, individuals can embark on electrical endeavors with the assurance that their contributions uphold the highest standards of safety, functionality, and reliability in electrical systems.