Home>Home and Garden>The Ultimate Guide To Choosing The Perfect Plywood For Your Subfloor


Home and Garden
The Ultimate Guide To Choosing The Perfect Plywood For Your Subfloor
Published: January 4, 2024
Discover the best plywood for your subfloor with our comprehensive guide. Make the right choice for your home and garden projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to home improvement projects, ensuring a strong and reliable foundation is crucial. Whether you're renovating, building a new home, or addressing a flooring issue, the choice of subflooring material plays a pivotal role in the structural integrity and longevity of your floors. Among the various subflooring options available, plywood stands out as a popular and versatile choice for its durability, strength, and ease of installation.
The subfloor serves as the sturdy layer that supports the finished flooring material, such as hardwood, laminate, or tile. It provides stability, insulation, and a level surface for the top flooring to rest upon. Plywood, a engineered wood product made from thin layers of wood veneer, is renowned for its exceptional strength and dimensional stability, making it an ideal candidate for subflooring applications.
Understanding the nuances of plywood, the different types available, and the factors to consider when choosing the right plywood for your subfloor is essential for a successful home improvement project. Whether you're a seasoned DIY enthusiast or a homeowner embarking on your first subflooring endeavor, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights needed to make informed decisions and achieve a robust, long-lasting subfloor.
As we delve into the intricacies of plywood subflooring, you'll discover the diverse options at your disposal, the key considerations that influence your choice, and invaluable tips for proper installation and maintenance. By the end of this guide, you'll be well-prepared to select the perfect plywood for your subfloor, ensuring a solid foundation that withstands the test of time.
Let's embark on this journey to unravel the world of plywood subflooring, empowering you to make informed choices and embark on your home improvement endeavors with confidence.
Understanding Plywood
Plywood is a versatile and widely used building material that has earned its reputation for strength, durability, and adaptability. Composed of thin layers of wood veneer, known as plies, plywood is manufactured by bonding these layers together with adhesive under high pressure and heat. This construction method results in a strong and dimensionally stable sheet material that exhibits remarkable resistance to warping, cracking, and twisting.
The composition of plywood contributes to its exceptional strength and stability. Each layer of wood veneer is placed with the grain perpendicular to the adjacent layers, creating a cross-grain pattern that enhances the structural integrity of the material. This cross-grain configuration mitigates the natural tendency of wood to expand and contract with changes in humidity and temperature, making plywood an ideal choice for subflooring applications where stability and resilience are paramount.
Plywood is available in various grades, with each grade indicating the quality and appearance of the material. These grades range from A to D, with A being the highest quality and D being the lowest. The grading system considers factors such as the number of blemishes, knots, and voids present on the surface of the plywood, providing consumers with clear distinctions to suit their specific project requirements.
In addition to its structural attributes, plywood offers versatility in terms of thickness and size. Standard plywood sheets come in 4-foot by 8-foot dimensions, with thickness options ranging from 1/4 inch to 3/4 inch. This variability in thickness allows for tailored subflooring solutions based on the load-bearing requirements and structural considerations of the project.
Furthermore, plywood is available in different wood species, including pine, fir, and cedar, each offering unique characteristics in terms of strength, appearance, and suitability for specific environments. The choice of wood species can impact the overall performance and aesthetics of the subfloor, making it important to consider the environmental conditions and intended use of the space when selecting the plywood material.
In essence, understanding plywood involves recognizing its composition, structural advantages, grading system, and the array of options available. This knowledge serves as the foundation for informed decision-making when choosing the perfect plywood for your subfloor, ensuring a robust and enduring base for your flooring endeavors.
Types of Plywood
1. Structural Plywood
Structural plywood, also known as sheathing plywood, is engineered for structural applications that require strength and stability. It is commonly used in subflooring, wall and roof sheathing, and other construction projects where load-bearing capacity is essential. This type of plywood is manufactured to meet specific standards and is graded based on its structural performance, making it a reliable choice for supporting heavy loads and withstanding the rigors of construction.
2. Exterior Plywood
Exterior plywood is designed to withstand moisture, weather, and humidity, making it suitable for outdoor applications such as exterior cladding, roofing, and subflooring in areas prone to moisture exposure. It is constructed using water-resistant adhesives and is manufactured with veneers treated to enhance its resistance to the elements. The durability and weather-resistant properties of exterior plywood make it a preferred choice for subflooring in outdoor structures and areas with high moisture levels.
3. Hardwood Plywood
Hardwood plywood is crafted from hardwood veneers, offering superior strength, durability, and an attractive appearance. It is prized for its smooth and consistent surface, making it well-suited for visible applications such as cabinetry, furniture, and decorative paneling. While it is not commonly used for subflooring due to its higher cost, hardwood plywood can be a viable option for specialty flooring projects that require a refined finish and exceptional strength.
4. Marine Plywood
Marine plywood is engineered for marine applications and is designed to withstand exposure to water, making it ideal for boat building, docks, and other water-centric projects. It is constructed using waterproof adhesive and durable wood species, ensuring its resilience in wet environments. While marine plywood is not typically used for standard subflooring, its exceptional moisture resistance and structural integrity make it a valuable choice for subflooring in areas prone to water intrusion or high humidity levels.
5. Underlayment Plywood
Underlayment plywood is specifically designed as a smooth, flat base for resilient flooring materials such as vinyl, linoleum, and carpet. It provides a level surface for the installation of finished flooring and offers enhanced support and impact resistance. While underlayment plywood is not intended for structural subflooring, its role in providing a stable foundation for resilient flooring makes it an essential component of many flooring projects.
Understanding the diverse types of plywood empowers homeowners and builders to select the most suitable option for their subflooring needs, considering factors such as environmental conditions, intended use, and project requirements. Each type of plywood offers distinct characteristics and advantages, catering to a wide range of applications and ensuring a solid foundation for various construction and flooring endeavors.
Factors to Consider
When choosing the perfect plywood for your subfloor, several key factors come into play, each influencing the performance, longevity, and suitability of the material for your specific project. By carefully considering these factors, you can make informed decisions that align with your structural requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term goals.
1. Subflooring Application
The intended use of the subfloor is a crucial consideration when selecting plywood. For instance, if the subfloor will be exposed to moisture or high humidity levels, such as in bathrooms or basements, opting for moisture-resistant plywood, such as exterior or marine plywood, is essential to prevent warping, delamination, and structural compromise over time. Understanding the environmental demands placed on the subfloor allows you to choose a plywood type that can withstand the specific challenges posed by the application.
2. Load-Bearing Capacity
Assessing the load-bearing requirements of the subfloor is paramount in ensuring structural integrity and safety. Heavy furniture, appliances, or high foot traffic areas necessitate plywood with sufficient strength and stiffness to support the anticipated loads without flexing or sagging. Structural plywood, engineered to withstand heavy loads, is an ideal choice for subflooring applications where load-bearing capacity is a primary concern.
3. Environmental Conditions
The environmental conditions in the installation area, including temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and exposure to moisture, profoundly impact the performance and longevity of the subfloor. It is crucial to select plywood that can withstand the prevailing environmental factors to prevent issues such as swelling, warping, or decay. Considering the climate, location within the home, and potential exposure to moisture guides the choice of plywood with the appropriate moisture resistance and dimensional stability.
4. Subfloor Thickness
The thickness of the plywood directly influences its load-bearing capacity, rigidity, and suitability for the intended application. Thicker plywood is better equipped to handle heavier loads and provides enhanced stability, making it well-suited for areas with increased demands on the subfloor. Understanding the load requirements and structural considerations of the project aids in determining the optimal plywood thickness for a robust and durable subfloor.
5. Budget and Cost Considerations
Budgetary constraints play a significant role in the selection process, as plywood prices vary based on type, grade, and quality. Balancing the desired performance attributes with budget considerations ensures that you choose plywood that meets your structural needs without overspending. While high-quality plywood may entail a higher initial investment, it can yield long-term cost savings by minimizing the need for premature replacements or repairs.
6. Compatibility with Finished Flooring
Considering the type of finished flooring material that will be installed over the plywood subfloor is essential for ensuring compatibility and a seamless installation process. Different finished flooring materials, such as hardwood, laminate, or tile, may have specific subfloor requirements in terms of smoothness, flatness, and moisture resistance. Selecting plywood that aligns with the compatibility needs of the finished flooring material contributes to a successful and enduring flooring system.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make informed decisions when choosing the perfect plywood for your subfloor, aligning the material's attributes with the specific demands of your project. This thoughtful approach sets the stage for a robust and reliable subfloor that forms the foundation for a durable and aesthetically pleasing flooring system.
Choosing the Right Plywood for Your Subfloor
Selecting the right plywood for your subfloor is a pivotal decision that directly impacts the structural integrity, longevity, and performance of your flooring system. By carefully assessing your project requirements and considering the key factors outlined earlier, you can navigate the diverse options available and make an informed choice that aligns with your specific needs.
Begin by evaluating the application and environmental demands placed on the subfloor. If your project involves areas prone to moisture exposure, such as bathrooms or basements, opting for moisture-resistant plywood, such as exterior or marine plywood, is imperative to safeguard against potential damage and deterioration due to water intrusion. Understanding the environmental challenges allows you to prioritize plywood types that offer enhanced moisture resistance and durability.
Assessing the load-bearing requirements of the subfloor is equally critical. Areas with heavy furniture, appliances, or high foot traffic necessitate plywood with robust load-bearing capacity to prevent flexing or sagging. Structural plywood, engineered to withstand substantial loads, emerges as the ideal choice for subflooring applications where strength and stiffness are paramount.
Consider the thickness of the plywood in relation to the anticipated loads and structural demands of the project. Thicker plywood provides greater stability and load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for areas with heightened subfloor requirements. By aligning the plywood thickness with the specific load considerations, you can ensure a sturdy and resilient subfloor that meets the demands of the space.
Budget and cost considerations play a significant role in the decision-making process. Balancing the desired performance attributes with budget constraints enables you to choose plywood that meets your structural needs without exceeding your financial limits. While high-quality plywood may entail a higher initial investment, it offers long-term benefits by minimizing the risk of premature replacements or repairs, ultimately contributing to cost savings over time.
Furthermore, ensuring the compatibility of the chosen plywood with the finished flooring material is essential for a seamless and successful installation. Different flooring materials may have distinct subfloor requirements, such as smoothness, flatness, and moisture resistance. By selecting plywood that aligns with the compatibility needs of the finished flooring material, you pave the way for a harmonious and durable flooring system.
By carefully considering these factors and aligning them with your project's specific requirements, you can confidently choose the perfect plywood for your subfloor. This thoughtful selection process sets the stage for a robust and reliable subfloor, laying the groundwork for a resilient, long-lasting, and visually appealing flooring system.
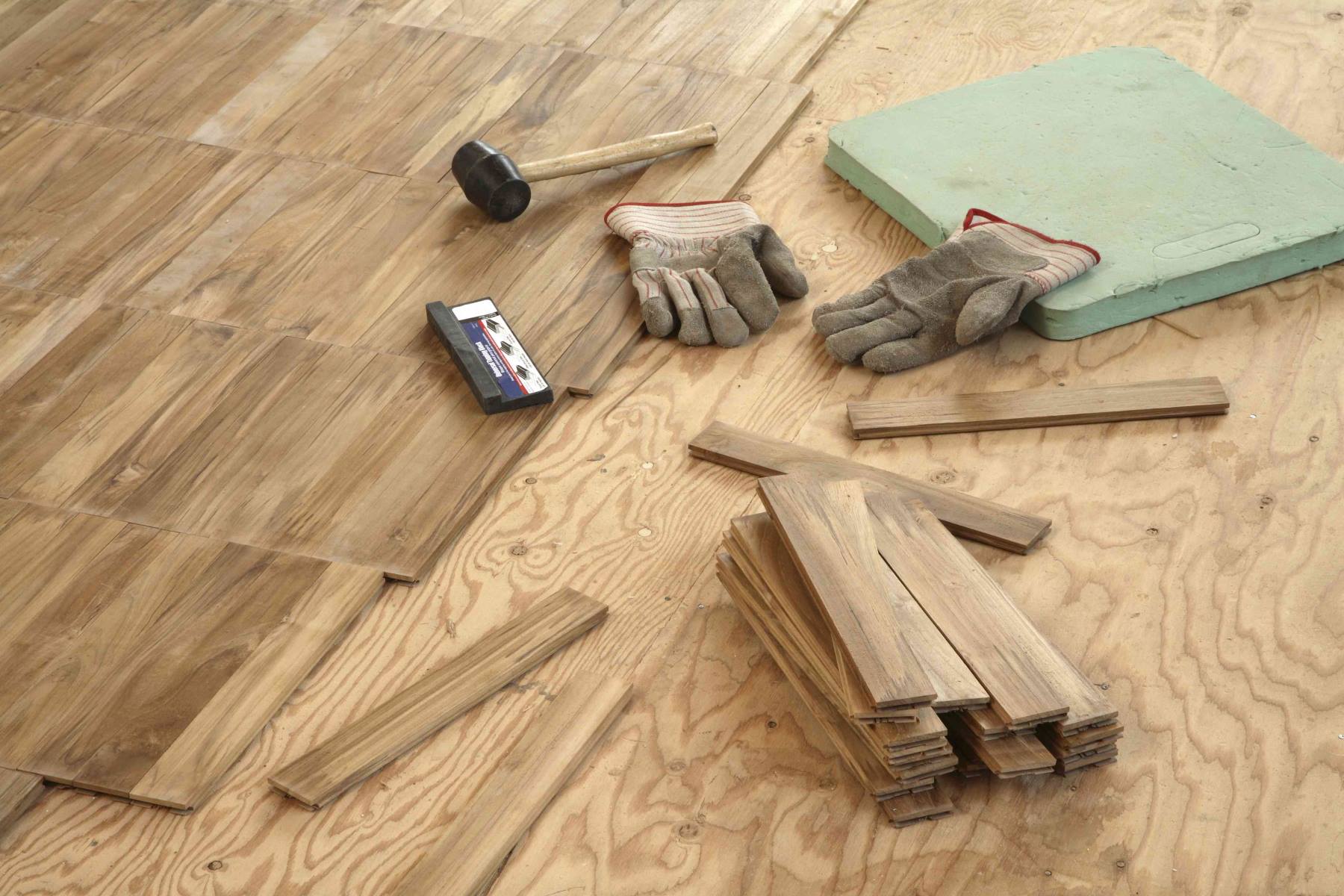
Installation Tips
Proper installation is paramount to the performance and longevity of your plywood subfloor. By adhering to best practices and employing meticulous techniques, you can ensure a sturdy and reliable foundation for your finished flooring. Here are essential installation tips to guide you through the process:
-
Subfloor Preparation: Before laying the plywood, thoroughly inspect the subfloor for any structural issues, moisture damage, or unevenness. Address any underlying problems and ensure the subfloor is clean, dry, and level to provide a sound base for the plywood installation.
-
Acclimatization: Allow the plywood sheets to acclimate to the ambient conditions of the installation area for a minimum of 48 hours. This acclimatization period minimizes the risk of dimensional changes after installation, promoting stability and reducing the potential for warping or buckling.
-
Fastening and Spacing: Utilize appropriate fasteners, such as screws or nails, to secure the plywood to the subfloor, ensuring a tight and uniform attachment. Follow the recommended fastening pattern and spacing guidelines provided by the plywood manufacturer to achieve optimal structural integrity and load distribution.
-
Seam Placement and Staggering: Plan the placement of plywood seams to minimize the concentration of joints in high-traffic areas. Stagger the seams of adjacent plywood sheets to distribute loads evenly and prevent weak points in the subfloor.
-
Adhesive Application: When installing plywood over concrete subfloors, apply a suitable adhesive to ensure proper bonding and minimize the risk of delamination. Follow the adhesive manufacturer's guidelines for application and curing to achieve a secure and durable bond between the plywood and the concrete subfloor.
-
Moisture Barrier Installation: In areas prone to moisture, such as basements or bathrooms, consider installing a moisture barrier between the subfloor and the finished flooring material. This barrier helps mitigate moisture-related issues and enhances the long-term durability of the subfloor.
-
Edge Sealing: Apply edge sealant to the exposed edges of the plywood sheets to protect against moisture infiltration and enhance the overall moisture resistance of the subfloor. Proper edge sealing contributes to the longevity and dimensional stability of the plywood subfloor.
-
Quality Control and Inspection: Throughout the installation process, conduct quality control checks to ensure the plywood is installed according to the specified guidelines and industry standards. Inspect for proper fastening, seam alignment, and overall subfloor integrity before proceeding with the installation of finished flooring.
By adhering to these installation tips and meticulous techniques, you can establish a robust and enduring plywood subfloor that provides a stable and reliable foundation for your finished flooring. These best practices contribute to the structural integrity, longevity, and performance of the subfloor, setting the stage for a successful and enduring flooring system.
Maintenance and Care
Maintaining and caring for your plywood subfloor is essential to preserve its structural integrity, longevity, and performance over time. By implementing routine maintenance practices and exercising diligent care, you can ensure that your subfloor remains resilient, stable, and capable of providing a solid foundation for your flooring system. Here are key considerations and best practices for maintaining and caring for your plywood subfloor:
1. Regular Inspection:
Periodically inspect the plywood subfloor for signs of wear, damage, or moisture-related issues. Look for any areas of delamination, warping, or discoloration that may indicate underlying problems. Addressing issues promptly can prevent further damage and preserve the structural stability of the subfloor.
2. Moisture Management:
Manage moisture levels in the environment to prevent potential damage to the plywood subfloor. Ensure that areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms or kitchens, are well-ventilated and properly sealed to minimize the risk of water intrusion. Address any leaks or spills promptly to prevent moisture from compromising the subfloor.
3. Cleaning and Maintenance:
Keep the plywood subfloor clean and free from debris, dust, and dirt accumulation. Regular sweeping, vacuuming, or mopping with a damp cloth can help maintain a clean and hygienic subfloor surface. Avoid using excessive water during cleaning to prevent moisture infiltration into the plywood.
4. Addressing Surface Damage:
If the plywood subfloor sustains surface damage, such as scratches or gouges, consider repairing the affected areas to prevent further deterioration. Utilize appropriate repair materials and techniques to restore the integrity and smoothness of the subfloor surface.
5. Preventative Measures:
Implement preventative measures to safeguard the plywood subfloor from potential harm. Use protective pads or coasters under heavy furniture to distribute the weight and minimize indentations. Avoid dragging sharp or heavy objects across the subfloor to prevent surface damage.
6. Professional Maintenance:
Consider engaging professional flooring or maintenance services for comprehensive inspections and maintenance. Professional assessment can identify underlying issues and provide expert recommendations for preserving the condition and performance of the plywood subfloor.
7. Addressing Subfloor Movement:
Monitor the subfloor for any signs of movement or shifting, especially in areas with frequent foot traffic or heavy loads. Address any noticeable movement promptly to prevent structural compromise and ensure the stability of the subfloor.
By incorporating these maintenance and care practices into your routine, you can uphold the strength, stability, and longevity of your plywood subfloor. Diligent maintenance not only preserves the subfloor's structural integrity but also contributes to the overall durability and performance of your flooring system, ensuring a solid foundation for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the selection and installation of plywood for your subfloor are pivotal steps in ensuring the strength, stability, and longevity of your flooring system. By understanding the diverse types of plywood, considering key factors such as subflooring application, load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and compatibility with finished flooring, and implementing best practices for installation, maintenance, and care, you can create a robust and reliable subfloor that forms the foundation for a durable and visually appealing flooring system.
The versatility and structural advantages of plywood make it a preferred choice for subflooring applications, offering exceptional strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to environmental challenges. Whether you opt for structural plywood for heavy-duty support, exterior plywood for moisture resistance, or underlayment plywood for resilient flooring installations, the diverse options available cater to a wide range of project requirements, ensuring that you can select the most suitable plywood for your specific needs.
Proper installation techniques, including subfloor preparation, fastening, seam placement, and moisture barrier installation, are essential for establishing a sturdy and uniform plywood subfloor. Adhering to these best practices minimizes the risk of structural issues and ensures that the subfloor provides a stable and reliable base for your finished flooring material.
Furthermore, ongoing maintenance and care, such as regular inspections, moisture management, and preventative measures, are vital for preserving the structural integrity and performance of the plywood subfloor. By implementing these maintenance practices, you can safeguard the subfloor against wear, damage, and moisture-related issues, contributing to its long-term durability and reliability.
In essence, the process of choosing, installing, and maintaining the plywood subfloor is a comprehensive endeavor that requires careful consideration, meticulous attention to detail, and a commitment to quality. By integrating the knowledge and insights gained from this guide into your subflooring endeavors, you can embark on your home improvement projects with confidence, knowing that you have equipped yourself with the tools and understanding needed to create a solid and enduring foundation for your flooring system.