Home>Science>The Secret Way Baby Birds Stay Hydrated In Their Nests
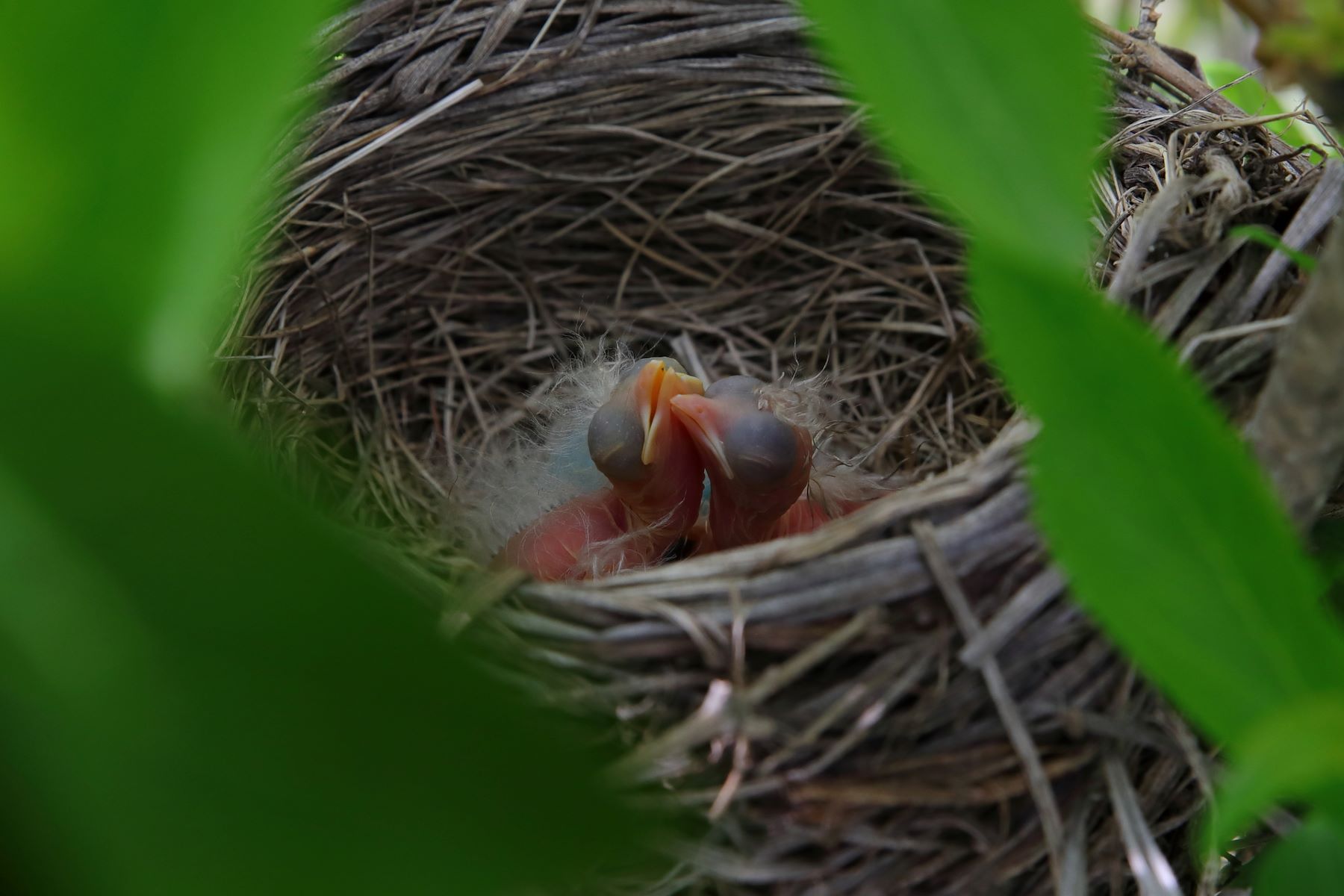


Science
The Secret Way Baby Birds Stay Hydrated In Their Nests
Published: January 26, 2024
Discover the fascinating science behind how baby birds stay hydrated in their nests. Explore the secret way nature ensures their survival.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Baby birds, with their delicate features and endearing chirps, captivate our hearts as they nestle in their cozy homes, awaiting the care of their devoted parents. While their fluffy appearance and playful antics may steal the show, there's a fascinating aspect of their survival that often goes unnoticed – their unique method of staying hydrated in the confines of their nests. The ability of baby birds to maintain proper hydration is a critical factor in their growth and development, and it's a marvel of nature that deserves our attention and admiration.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of baby birds and explore the secret mechanisms they employ to remain hydrated in their nests. From the importance of hydration for their well-being to the remarkable adaptations that enable them to thrive, we'll uncover the intricate web of nature's design. Furthermore, we'll unravel the role of parent birds in ensuring the hydration of their offspring and shed light on the challenges that baby birds face in maintaining adequate moisture levels within their nest environments. Prepare to embark on a journey of discovery as we unveil the hidden wonders of how baby birds quench their thirst amidst the confines of their nests.
The Importance of Hydration for Baby Birds
Proper hydration is paramount for the growth, development, and overall well-being of baby birds. Just like any other living organism, water is essential for their survival. The significance of hydration for baby birds extends beyond mere sustenance; it is intricately linked to their physiological processes and plays a pivotal role in their ability to thrive in their delicate early stages of life.
Water is a fundamental component of a bird's body, constituting a substantial portion of their overall mass. It serves as a medium for vital biological processes, including nutrient transport, temperature regulation, and waste removal. For baby birds, whose bodies are rapidly developing and undergoing significant metabolic activity, the presence of adequate water is indispensable for supporting these essential functions.
Furthermore, hydration is closely tied to the thermoregulation of baby birds. As ectothermic creatures, they rely on external sources of heat to maintain their body temperature. During periods of high temperatures, water serves as a cooling agent, enabling baby birds to dissipate excess heat through evaporative cooling, thereby preventing overheating and heat stress. Conversely, in colder conditions, proper hydration aids in maintaining the necessary body temperature for their physiological processes to function optimally.
In the realm of nutrition, water is indispensable for the digestion and absorption of food. It facilitates the breakdown of nutrients and the transport of essential substances throughout the body, ensuring that baby birds can derive the necessary nourishment from their diet. Additionally, adequate hydration supports the development of healthy tissues and organs, contributing to the overall growth and vitality of the young avian individuals.
Beyond these physiological aspects, hydration also holds implications for the behavioral and cognitive facets of baby birds. Proper hydration is integral to their mental acuity and alertness, influencing their ability to learn, interact with their environment, and exhibit natural behaviors. In essence, water is not merely a source of sustenance for baby birds; it is an indispensable element that underpins their very existence and empowers them to flourish in their early stages of life.
As we unravel the intricacies of how baby birds stay hydrated in their nests, it is crucial to recognize the profound significance of hydration in shaping their journey from fragile hatchlings to robust fledglings. The secret mechanisms that enable them to quench their thirst within the confines of their nests are not just a matter of survival; they are a testament to the remarkable adaptations that have evolved to safeguard the future of these captivating creatures.
The Unique Adaptations of Baby Birds for Hydration
From the moment they break through their shells into the world, baby birds embark on a remarkable journey of adaptation, equipped with innate mechanisms that enable them to thrive in their unique environments. Their ability to stay hydrated within the confines of their nests is a testament to the extraordinary adaptations that have evolved over millennia, shaping them into resilient and resourceful beings.
One of the most striking adaptations of baby birds for hydration lies in the composition of their diet. Unlike adult birds, whose diet may encompass a diverse array of foods, baby birds primarily rely on a diet of regurgitated food provided by their parent birds. This regurgitated food, often referred to as "crop milk," is a specialized substance rich in water, proteins, fats, and essential nutrients. It serves as a vital source of hydration for the growing nestlings, ensuring that they receive the necessary moisture to support their physiological processes and development.
Moreover, the unique anatomy of baby birds contributes to their efficient utilization of the available moisture. Their digestive systems are adept at extracting and absorbing water from the ingested food, maximizing the uptake of hydration from their diet. This adaptive trait allows baby birds to derive optimal benefit from the limited resources present within their nest environments, enabling them to thrive even in arid or challenging conditions.
In addition to their dietary adaptations, baby birds exhibit behavioral strategies that contribute to their hydration. Nestlings often have a lower rate of water loss through excretion compared to adult birds, allowing them to conserve the precious moisture within their bodies. Furthermore, their behavior, such as minimizing physical activity and maintaining a relatively sedentary lifestyle within the nest, helps to reduce unnecessary water expenditure, ensuring that the available hydration is utilized judiciously.
The remarkable adaptations of baby birds for hydration extend beyond their physical and behavioral attributes to encompass their developmental timeline. Many species of baby birds have a relatively short nestling period, during which they undergo rapid growth and maturation. This abbreviated timeframe is a strategic adaptation that minimizes the duration for which they are dependent on external sources of hydration, reducing their vulnerability and reliance on the nest environment for an extended period.
As we unravel the intricacies of these unique adaptations, we gain a profound appreciation for the resilience and ingenuity of baby birds. Their ability to navigate the challenges of hydration within the confines of their nests is a testament to the wondrous mechanisms that have evolved to safeguard their well-being and ensure their successful transition from vulnerable hatchlings to independent fledglings.
The Role of Parent Birds in Keeping Baby Birds Hydrated
The nurturing care provided by parent birds plays a pivotal role in ensuring the hydration of their offspring within the confines of the nest. From diligently sourcing water to delivering it in a readily consumable form, the dedication of parent birds to maintaining the hydration of their nestlings is a testament to their unwavering commitment to the well-being of their progeny.
One of the primary responsibilities of parent birds in keeping their offspring hydrated is the procurement and preparation of nourishing food. The regurgitated food, often referred to as "crop milk," serves as a vital source of hydration for the growing nestlings. This specialized substance, rich in water, proteins, fats, and essential nutrients, is meticulously crafted by the parent birds to meet the specific needs of their offspring. Through their foraging efforts and metabolic processes, parent birds ensure the provision of this nourishing sustenance, which not only satiates the hunger of their young but also fulfills their essential hydration requirements.
Furthermore, the attentive behavior of parent birds is instrumental in directly facilitating the hydration of their nestlings. They meticulously monitor the condition of their offspring, assessing their nutritional and hydration needs with keen precision. Through their keen observations, parent birds are adept at discerning the cues that indicate the thirst or hunger of their young, promptly responding to their needs with nourishment and hydration. This vigilant care is a testament to the profound bond between parent and offspring, as well as the instinctual drive of parent birds to safeguard the well-being of their vulnerable nestlings.
Additionally, the role of parent birds in regulating the microclimate of the nest environment contributes to the hydration of their offspring. During hot weather, parent birds may employ strategies to shield their nestlings from excessive heat, thereby reducing the risk of dehydration. Conversely, in cooler conditions, they may employ methods to maintain an optimal temperature within the nest, ensuring that their young can effectively regulate their hydration and thermoregulatory needs.
In essence, the role of parent birds in keeping their offspring hydrated is a multifaceted and intricate endeavor that encompasses the provision of nourishing food, vigilant care, and environmental regulation. Their unwavering dedication and nurturing instincts are integral to the survival and thriving of baby birds, exemplifying the profound bond between parent and offspring in the intricate tapestry of avian life.
The Challenges of Staying Hydrated in the Nest
The nest, while serving as a sanctuary for the young avian individuals, presents a myriad of challenges when it comes to maintaining adequate hydration. The confined space, coupled with the dependency on external sources of nourishment and moisture, creates a delicate balancing act for baby birds as they navigate the complexities of staying hydrated within their cozy abode.
One of the foremost challenges arises from the limited availability of water within the nest environment. Unlike adult birds, who have the freedom to seek out water sources beyond the confines of the nest, baby birds are reliant on the provisions brought to them by their parent birds. This dependency on external sources of hydration necessitates a delicate coordination between the foraging efforts of the parent birds and the hydration needs of their offspring, creating a potential vulnerability in the face of fluctuating environmental conditions.
Furthermore, the nest environment itself poses challenges to the hydration of baby birds. In warm weather, the risk of dehydration looms as the confined space may trap heat, elevating the temperature within the nest and increasing the potential for water loss through evaporation. Conversely, in cooler conditions, the limited access to external water sources may pose challenges in maintaining optimal hydration levels, especially as the metabolic demands of the growing nestlings require a consistent supply of moisture.
The developmental stage of the nestlings also contributes to the challenges of staying hydrated within the nest. As they progress through their growth and maturation, their hydration needs evolve, necessitating a dynamic response from the parent birds to accommodate these changing requirements. The ability of parent birds to accurately gauge the hydration needs of their offspring and provide the appropriate nourishment in a timely manner is crucial in mitigating the challenges posed by the evolving demands of the nestlings.
Moreover, the vulnerability of the nestlings to environmental stressors further compounds the challenges of staying hydrated in the nest. Factors such as predation risk, inclement weather, and nest disturbances can disrupt the delicate balance of hydration within the nest, necessitating swift and adaptive responses from both the parent birds and the nestlings to ensure their well-being amidst the uncertainties of their microcosmic world.
As we unravel the intricacies of the challenges faced by baby birds in staying hydrated within their nests, we gain a profound appreciation for the resilience and adaptability that underpin their journey to independence. The delicate dance of hydration within the confines of the nest is a testament to the intricate web of life, where every aspect, no matter how seemingly small, plays a pivotal role in shaping the destiny of these captivating creatures.
Conclusion
The captivating world of baby birds and their unique mechanisms for staying hydrated within the confines of their nests unveils a tapestry of resilience, adaptation, and unwavering dedication. From the delicate interplay of hydration with their physiological, behavioral, and developmental facets to the nurturing care provided by their devoted parent birds, the journey of baby birds is a testament to the profound intricacies of nature's design.
As we reflect on the importance of hydration for the well-being and growth of baby birds, we gain a profound understanding of the indispensable role that water plays in shaping their journey from vulnerable hatchlings to robust fledglings. The significance of hydration extends far beyond mere sustenance; it permeates every aspect of their existence, influencing their thermoregulation, digestion, cognitive acuity, and overall vitality.
The unique adaptations of baby birds for hydration, encompassing their specialized diet, efficient utilization of moisture, and strategic developmental timeline, underscore the remarkable resilience and resourcefulness that have evolved to safeguard their well-being within the confines of their nests. These adaptations serve as a testament to the intricate balance of nature, where every facet of their being is finely tuned to thrive in their microcosmic world.
The role of parent birds in ensuring the hydration of their offspring is a poignant testament to the unwavering dedication and nurturing instincts that underpin the intricate tapestry of avian life. From the procurement and preparation of nourishing food to the vigilant care and environmental regulation, the commitment of parent birds to safeguarding the well-being of their young exemplifies the profound bond between parent and offspring in the intricate dance of life.
Amidst the challenges of staying hydrated in the nest, baby birds exhibit resilience, adaptability, and a remarkable capacity to thrive in the face of adversity. The delicate balancing act of maintaining adequate hydration within the confines of their nests underscores the intricate web of life, where every challenge is met with ingenuity and every vulnerability is countered with resilience.
In unraveling the hidden wonders of how baby birds stay hydrated in their nests, we are invited to marvel at the intricate web of life that unfolds within the cozy abodes of these captivating creatures. Their journey serves as a poignant reminder of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the remarkable adaptations that enable every creature, no matter how small, to flourish in their own unique way.