Home>Politics and Government>NATO Vs BRICS: Unveiling The Surprising Similarities And Striking Differences In Military Organizations

Politics and Government
NATO Vs BRICS: Unveiling The Surprising Similarities And Striking Differences In Military Organizations
Published: February 20, 2024
Discover the intriguing parallels and disparities between NATO and BRICS military entities. Explore the intricate dynamics of global politics and government.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background of NATO
- Historical Background of BRICS
- Mission and Objectives of NATO
- Mission and Objectives of BRICS
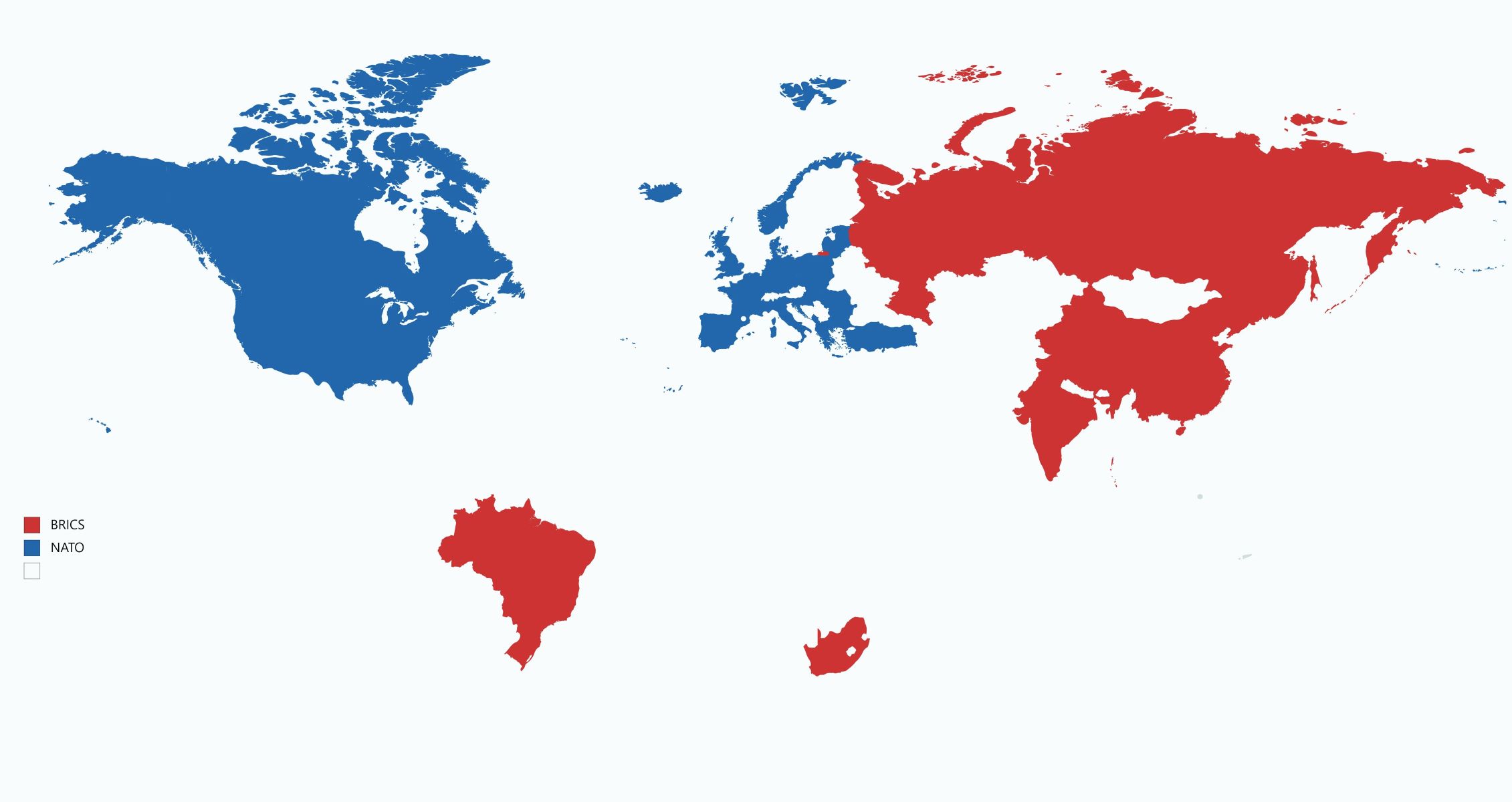
- Member Countries of NATO
- Member Countries of BRICS
- Military Capabilities of NATO
- Military Capabilities of BRICS
- Decision-making Process in NATO
- Decision-making Process in BRICS
- Relationship with Non-member Countries
- Conclusion
Introduction
The global geopolitical landscape is shaped by the presence and actions of various military organizations, each with its own unique history, mission, and capabilities. Two prominent entities that command attention on the world stage are the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) alliance. While these organizations may appear to serve different purposes, a closer examination reveals surprising similarities and striking differences in their structures, missions, and member compositions.
NATO, established in 1949, emerged in the aftermath of World War II as a collective defense alliance aimed at safeguarding the security and territorial integrity of its member states. In contrast, the BRICS alliance, formed in 2006, represents a coalition of emerging economies seeking to foster cooperation and influence on the global stage. Despite their differing origins and primary objectives, both NATO and BRICS play pivotal roles in shaping international relations and security dynamics.
As we delve into the historical backgrounds, missions, member countries, military capabilities, and decision-making processes of NATO and BRICS, a comprehensive understanding of these organizations will emerge. By examining their relationships with non-member countries, we can gain insights into the broader impact and influence of these military organizations on the global stage. Through this exploration, we will uncover the nuanced complexities and strategic implications inherent in the operations of NATO and BRICS, shedding light on their roles in shaping the contemporary geopolitical landscape.
Historical Background of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) traces its origins to the tumultuous aftermath of World War II. In 1949, against the backdrop of escalating Cold War tensions between the Western powers and the Soviet Union, NATO was established as a collective defense alliance. The pivotal catalyst for its formation was the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C., by twelve founding member countries, including the United States, Canada, and several European nations.
The primary impetus behind the creation of NATO was to counter the perceived threat posed by the expansionist policies of the Soviet Union and its influence over Eastern Europe. The alliance sought to provide a unified defense against potential aggression, thereby promoting stability and deterring the spread of communism. This marked a significant departure from traditional security arrangements, as NATO represented a collective commitment to mutual defense and solidarity among its member states.
The formation of NATO also reflected a broader shift in international relations, signaling the emergence of a bipolar world order characterized by the ideological and military standoff between the Western bloc and the Eastern bloc led by the Soviet Union. As such, NATO served as a cornerstone of Western security architecture, embodying a commitment to upholding democratic values and safeguarding the territorial integrity of its member states.
Throughout its history, NATO has adapted to evolving geopolitical dynamics, expanding its membership and refining its strategic focus to address new security challenges. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 prompted a reevaluation of NATO's role, leading to the organization's engagement in peacekeeping operations, crisis management, and counterterrorism efforts. Subsequent enlargement initiatives welcomed former Eastern bloc countries into the alliance, further solidifying NATO's role as a key player in shaping European security.
In essence, the historical trajectory of NATO underscores its enduring significance as a linchpin of transatlantic security cooperation. The alliance's evolution from a Cold War-era defense pact to a multifaceted security organization reflects its adaptive capacity and enduring relevance in an ever-changing global security landscape. As NATO continues to navigate contemporary challenges, its historical legacy remains integral to understanding its pivotal role in shaping international security dynamics.
Historical Background of BRICS
The BRICS alliance, comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, emerged as a significant geopolitical force in the early 21st century. The historical background of BRICS is rooted in the collective aspirations of its member countries to assert their influence on the global stage and foster cooperation among emerging economies.
The concept of BRICS first gained traction in 2001, when economist Jim O'Neill coined the acronym to represent the collective potential of Brazil, Russia, India, and China as major emerging economies. This initial conceptualization laid the groundwork for the formalization of the alliance, which culminated in the first BRIC summit held in 2009 in Yekaterinburg, Russia. At this historic meeting, the leaders of Brazil, Russia, India, and China convened to deliberate on issues of mutual interest and explore avenues for collaboration.
The inclusion of South Africa in 2010 expanded the alliance's scope, leading to the formal establishment of BRICS as a multilateral platform for dialogue and cooperation. The historical backdrop of BRICS is characterized by a shared commitment to promoting economic development, enhancing global governance, and advocating for a more equitable international order.
The formation of BRICS represented a departure from traditional Western-dominated institutions, signaling a concerted effort by its member countries to assert their collective influence and amplify their voices on the global stage. This strategic alignment aimed to address common developmental challenges, promote South-South cooperation, and foster a multipolar world order.
The historical trajectory of BRICS reflects the evolving dynamics of global economic and geopolitical power, as well as the collective aspirations of its member countries to shape the contours of international relations. As BRICS continues to evolve, its historical background serves as a testament to the enduring commitment of its member countries to foster cooperation, advance common interests, and contribute to the reshaping of the global economic and political landscape.
In essence, the historical background of BRICS underscores its emergence as a pivotal force in international relations, embodying a shared vision of promoting inclusive development, enhancing global governance, and advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order.
Mission and Objectives of NATO
The mission and objectives of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) are deeply rooted in its founding principles and have evolved in response to shifting global security dynamics. At its core, NATO is committed to safeguarding the freedom, security, and common values of its member states through collective defense and cooperative security measures.
NATO's primary mission is to ensure the security and territorial integrity of its member countries by deterring aggression and promoting stability in the Euro-Atlantic area. This mission is underpinned by the collective defense clause enshrined in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which stipulates that an armed attack against one or more NATO members shall be considered an attack against all, triggering a collective response. This commitment to mutual defense serves as a cornerstone of NATO's mission, fostering a sense of solidarity and shared responsibility among its member states.
In addition to its core mission of collective defense, NATO has expanded its objectives to encompass a broader spectrum of security challenges. The alliance is dedicated to crisis management, conflict prevention, and cooperative security efforts, reflecting its commitment to promoting peace and stability beyond its immediate borders. NATO's missions extend to areas such as counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and maritime security, reflecting its adaptability in addressing contemporary security threats.
Furthermore, NATO is actively engaged in partnerships with other countries and international organizations, seeking to promote dialogue, cooperation, and capacity-building in support of shared security objectives. Through its partnerships, NATO aims to enhance global security by fostering interoperability, promoting democratic values, and contributing to international security and stability.
NATO's mission and objectives are also aligned with its role as a forum for transatlantic consultation and cooperation, serving as a platform for political dialogue and strategic coordination among its member states. The alliance seeks to promote transatlantic unity, strengthen the bonds of solidarity, and advance shared values and interests across the Euro-Atlantic area.
In essence, the mission and objectives of NATO reflect its enduring commitment to collective defense, cooperative security, and the promotion of peace and stability. As NATO continues to adapt to evolving security challenges, its mission remains integral to shaping the contemporary security landscape and upholding the principles of international peace and security.
Mission and Objectives of BRICS
The mission and objectives of the BRICS alliance are deeply rooted in the collective aspirations of its member countries to assert their influence on the global stage and foster cooperation among emerging economies. At its core, BRICS is committed to promoting inclusive development, enhancing global governance, and advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order.
One of the primary missions of BRICS is to facilitate cooperation and dialogue among its member countries to address common developmental challenges and promote sustainable economic growth. The alliance seeks to leverage the collective potential of its member countries to advance shared interests, foster economic resilience, and enhance the welfare of their respective populations. This mission is underpinned by a commitment to promoting inclusive development and addressing socioeconomic disparities, reflecting the alliance's dedication to advancing the well-being of its member countries and contributing to global prosperity.
In addition to its core mission of economic cooperation, BRICS has expanded its objectives to encompass a broader spectrum of global governance and geopolitical issues. The alliance is dedicated to advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order, challenging traditional power structures, and promoting greater representation of emerging economies in global decision-making processes. BRICS seeks to amplify the voices of its member countries on the international stage, advocating for reforms in global governance institutions and fostering a more balanced and inclusive approach to addressing global challenges.
Furthermore, BRICS is actively engaged in promoting South-South cooperation and fostering partnerships with other developing countries and regions. The alliance aims to enhance solidarity among emerging economies, promote mutual understanding, and strengthen cooperation in areas such as trade, investment, and sustainable development. Through its partnerships, BRICS seeks to contribute to the advancement of a more inclusive and interconnected global community, reflecting its commitment to fostering a multipolar world order based on mutual respect and cooperation.
In essence, the mission and objectives of BRICS underscore its commitment to promoting inclusive development, enhancing global governance, and advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order. As BRICS continues to evolve, its mission remains integral to shaping the contemporary global landscape and advancing the collective interests of its member countries.
Member Countries of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) comprises a diverse array of member countries that collectively contribute to the alliance's mission of safeguarding security and promoting stability in the Euro-Atlantic area. As of 2021, NATO consists of 30 member countries, each bringing unique capabilities and strategic significance to the alliance. The member countries of NATO span North America and Europe, reflecting the transatlantic nature of the alliance and its commitment to fostering cooperation and mutual defense.
The founding members of NATO, including the United States, Canada, and several European nations, laid the groundwork for the alliance's collective defense framework. Over the years, NATO has expanded its membership through a series of enlargement initiatives, welcoming new member countries into the alliance. The inclusion of former Eastern bloc countries, such as Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, following the end of the Cold War, marked a significant expansion of NATO's reach and influence.
Subsequent rounds of enlargement saw the accession of countries from the Baltic region, including Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, further solidifying NATO's presence in Northern Europe. The alliance's commitment to integrating new member countries reflects its dedication to promoting stability and security across the Euro-Atlantic area, extending the benefits of collective defense to a broader spectrum of nations.
In addition to its European members, NATO includes Turkey as a key transcontinental member, bridging the alliance's presence between Europe and the Middle East. The strategic significance of Turkey underscores NATO's role in addressing security challenges that transcend traditional geographic boundaries, reflecting the alliance's adaptability in addressing diverse security dynamics.
Furthermore, the inclusion of countries such as Norway, Denmark, and Iceland underscores NATO's reach into the Arctic region, highlighting the alliance's commitment to addressing emerging security concerns in the High North. The diverse geographic representation of NATO's member countries underscores the alliance's role as a transatlantic security organization with a broad spectrum of capabilities and strategic interests.
In essence, the member countries of NATO collectively contribute to the alliance's mission of promoting security, stability, and cooperation across the Euro-Atlantic area. The diverse composition of NATO's membership reflects the alliance's enduring commitment to collective defense and solidarity among nations, shaping the contemporary security landscape and upholding the principles of international peace and security.
Member Countries of BRICS
The BRICS alliance is composed of five member countries, each representing major emerging economies with significant global influence. The acronym "BRICS" encompasses Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, collectively shaping the geopolitical landscape and contributing to the discourse on global governance and economic cooperation.
Brazil, as the largest country in South America, brings to the alliance its rich cultural diversity, vast natural resources, and a burgeoning economy. With a focus on sustainable development and regional leadership, Brazil plays a pivotal role in advancing the collective interests of BRICS on the global stage.
Russia, as a major Eurasian power, contributes its geopolitical influence, technological prowess, and strategic resources to the alliance. With a strong emphasis on fostering multilateral cooperation and advocating for a multipolar world order, Russia's participation in BRICS amplifies the alliance's global impact.
India, as a rapidly growing economy and a vibrant democracy, brings to BRICS its demographic dividend, technological innovation, and a commitment to inclusive growth. India's active engagement in the alliance underscores its role in shaping the narrative on global economic governance and South-South cooperation.
China, as the world's second-largest economy and a global manufacturing hub, wields significant economic influence and technological advancement within BRICS. With a focus on promoting trade, investment, and infrastructure development, China's participation in the alliance underscores its commitment to fostering mutually beneficial partnerships among emerging economies.
South Africa, as the most industrialized economy in Africa, brings to BRICS its regional leadership, diverse economic sectors, and a commitment to sustainable development. South Africa's active involvement in the alliance amplifies the voice of the African continent and underscores the importance of inclusive growth and global representation within BRICS.
The collective representation of these diverse member countries within BRICS reflects a shared commitment to fostering economic cooperation, advocating for global governance reforms, and promoting inclusive development. As the alliance continues to evolve, the member countries of BRICS remain integral to shaping the contemporary global landscape and advancing the collective interests of major emerging economies.
The diverse composition of BRICS member countries underscores the alliance's role in fostering cooperation, promoting inclusive development, and advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order.
Military Capabilities of NATO
The military capabilities of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) represent a formidable force, underpinned by the collective strength and interoperability of its member countries. NATO's military capabilities encompass a wide spectrum of assets, ranging from advanced weaponry and cutting-edge technology to highly trained personnel and strategic infrastructure. The alliance's commitment to maintaining a credible deterrence posture and the ability to respond to diverse security challenges underscores its pivotal role in shaping the contemporary security landscape.
NATO's military capabilities are anchored in its integrated command structure, which enables seamless coordination and rapid deployment of forces across member countries. The alliance's emphasis on interoperability and joint training exercises enhances its readiness to address a wide range of security scenarios, including conventional warfare, hybrid threats, and emerging challenges in the cyber and space domains.
Furthermore, NATO's military capabilities extend to its robust air and maritime forces, which play a critical role in ensuring security and stability across the Euro-Atlantic area. The alliance's air power, comprising advanced fighter aircraft and aerial surveillance assets, serves as a deterrent against potential airborne threats and provides vital support for crisis response and peacekeeping operations. Additionally, NATO's maritime capabilities, including naval task forces and maritime patrol aircraft, contribute to safeguarding vital sea lanes and conducting maritime security operations.
NATO's land forces, equipped with modern armored vehicles, artillery systems, and specialized infantry units, bolster the alliance's ability to respond to potential land-based threats and provide support for stability operations and humanitarian assistance. The alliance's commitment to maintaining a credible and agile land force posture reflects its dedication to promoting security and deterring aggression in the Euro-Atlantic region.
Moreover, NATO's investment in cutting-edge capabilities, such as missile defense systems, cyber defense capabilities, and intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance assets, underscores its adaptability in addressing evolving security challenges. The alliance's commitment to enhancing its resilience against emerging threats and disruptive technologies reflects its proactive approach to safeguarding member countries from diverse security risks.
In essence, NATO's military capabilities embody a robust and adaptable force, underpinned by the collective strength and commitment of its member countries. The alliance's readiness to address diverse security challenges, promote stability, and uphold the principles of collective defense underscores its pivotal role in shaping the contemporary security landscape and fostering international peace and security.
Military Capabilities of BRICS
The military capabilities of the BRICS alliance reflect the collective strength and strategic significance of its member countries, each contributing unique assets and expertise to the global security landscape. While BRICS is primarily an economic and political alliance, the military capabilities of its member countries play a pivotal role in shaping the alliance's influence and capacity to address regional and global security challenges.
Russia, as a key member of BRICS, boasts a formidable military arsenal, including advanced weaponry, sophisticated air defense systems, and a robust nuclear deterrent. With a legacy of military innovation and strategic capabilities, Russia's military prowess contributes to the alliance's overall deterrence posture and its ability to address complex security dynamics.
China, as the world's most populous country and a rising military power, wields significant influence through its modernized military forces, advanced missile systems, and a growing naval presence. China's military capabilities underscore its role in shaping regional security dynamics and contributing to the alliance's collective defense posture.
India, as a major South Asian power, brings to BRICS its diverse military capabilities, including a well-equipped army, air force, and navy. With a focus on indigenous defense production and technological innovation, India's military strength contributes to the alliance's strategic depth and its ability to address diverse security challenges.
Brazil, as the largest country in South America, possesses a capable military force, including a well-trained army, air force, and navy. Brazil's military capabilities underscore its role in promoting regional stability and contributing to the alliance's efforts to address security dynamics in the Latin American region.
South Africa, as the most industrialized economy in Africa, brings to BRICS its military expertise and a commitment to regional peacekeeping and stability operations. South Africa's military capabilities contribute to the alliance's efforts to address security challenges on the African continent and promote cooperative security initiatives.
In essence, the military capabilities of BRICS member countries collectively contribute to the alliance's strategic influence and capacity to address regional and global security challenges. While BRICS is primarily focused on economic cooperation and political dialogue, the military capabilities of its member countries underscore the alliance's role in shaping the contemporary security landscape and fostering cooperative security initiatives.
Decision-making Process in NATO
The decision-making process in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is characterized by a commitment to consensus-based decision-making, reflecting the alliance's dedication to fostering unity and solidarity among its member countries. At the core of NATO's decision-making framework is the principle of collective consultation and cooperation, which underpins the alliance's ability to address diverse security challenges and strategic priorities.
NATO's decision-making process is structured around a framework of political and military consultations, providing a platform for member countries to deliberate on key security issues and strategic initiatives. The alliance's decision-making mechanisms encompass a range of forums, including ministerial meetings, summits, and specialized committees, where member countries engage in dialogue and exchange perspectives on matters of mutual interest.
The North Atlantic Council (NAC), as NATO's principal political decision-making body, serves as a forum for ambassadors from member countries to engage in regular consultations and decision-making processes. The NAC provides a platform for member countries to address security challenges, assess strategic developments, and coordinate collective responses to emerging threats. The consensus-based approach within the NAC underscores NATO's commitment to fostering unity and ensuring that decisions reflect the shared interests and concerns of all member countries.
Furthermore, NATO's decision-making process extends to its military dimension, where the Military Committee plays a pivotal role in providing military advice and contributing to the alliance's strategic decision-making. The Military Committee, composed of senior military representatives from member countries, offers expertise and recommendations on military matters, contributing to the alliance's ability to formulate effective defense and deterrence strategies.
In addition to formal decision-making structures, NATO emphasizes the importance of political dialogue and strategic coordination among member countries, reflecting a commitment to transparency and inclusivity in the decision-making process. The alliance's dedication to fostering open and constructive dialogue underscores its ability to address diverse perspectives and ensure that decisions reflect the collective interests of all member countries.
In essence, the decision-making process in NATO embodies a commitment to consensus, consultation, and cooperation, reflecting the alliance's enduring dedication to fostering unity and solidarity among its member countries. By upholding the principles of collective consultation and inclusive decision-making, NATO remains agile and responsive in addressing evolving security challenges and shaping the contemporary security landscape.
Decision-making Process in BRICS
The decision-making process within the BRICS alliance is characterized by a commitment to consensus-building and multilateral dialogue, reflecting the collective approach of its member countries in addressing global challenges and advancing common objectives. At the core of BRICS' decision-making framework lies the principle of inclusivity and mutual respect, which underpins the alliance's ability to foster cooperation and strategic coordination.
BRICS' decision-making process is structured around a framework of regular summits, ministerial meetings, and working groups, providing a platform for member countries to engage in substantive discussions and deliberations on a wide range of economic, political, and security issues. These forums serve as avenues for member countries to exchange perspectives, share expertise, and collectively address challenges of mutual interest, reflecting the alliance's commitment to fostering a collaborative and inclusive decision-making environment.
The BRICS summits, held annually, represent a key forum for leaders of member countries to engage in high-level discussions and strategic decision-making. These summits provide a platform for leaders to articulate shared priorities, set strategic objectives, and endorse initiatives aimed at advancing cooperation in areas such as trade, investment, sustainable development, and global governance reform. The consensus-driven approach within the BRICS summits underscores the alliance's commitment to ensuring that decisions reflect the collective aspirations and interests of all member countries.
In addition to the summits, ministerial meetings and working groups within BRICS play a crucial role in facilitating specialized discussions and policy coordination in specific areas such as finance, foreign affairs, and security. These platforms enable member countries to engage in in-depth consultations, exchange best practices, and formulate joint initiatives, contributing to the alliance's ability to address complex global challenges and promote cooperation in diverse domains.
Furthermore, the decision-making process within BRICS emphasizes the importance of fostering partnerships with other developing countries and international organizations, reflecting the alliance's commitment to promoting South-South cooperation and amplifying the voices of emerging economies on the global stage. By engaging in inclusive dialogue and strategic coordination, BRICS remains dedicated to advancing its collective interests and contributing to the reshaping of the global economic and political landscape.
In essence, the decision-making process in BRICS embodies a commitment to consensus-building, inclusivity, and strategic coordination, reflecting the alliance's enduring dedication to fostering cooperation and advancing common objectives. Through its multilateral approach to decision-making, BRICS remains agile and responsive in addressing global challenges and shaping the contemporary global landscape.
Relationship with Non-member Countries
NATO, as a cornerstone of transatlantic security cooperation, maintains a multifaceted relationship with non-member countries, reflecting its commitment to promoting stability and security beyond its immediate membership. The alliance actively engages in partnerships and dialogue with non-member countries, seeking to foster cooperation, enhance global security, and contribute to international stability.
NATO's partnerships with non-member countries are structured around the framework of the Partnership for Peace (PfP) program, which provides a platform for cooperation and dialogue with countries across Europe and beyond. Through the PfP program, NATO engages in military-to-military cooperation, defense reform initiatives, and capacity-building efforts, reflecting the alliance's commitment to promoting regional stability and enhancing interoperability with partner countries.
Furthermore, NATO maintains a network of partnerships with countries in the broader Euro-Atlantic area, the Mediterranean region, and the Middle East, reflecting its dedication to addressing security challenges that transcend traditional geographic boundaries. These partnerships encompass a range of activities, including joint exercises, training programs, and crisis management initiatives, underscoring NATO's role in promoting dialogue and cooperation with non-member countries.
In addition to its regional partnerships, NATO actively engages in dialogue and cooperation with global partners, including countries in Asia, the Pacific, and Latin America. The alliance seeks to foster strategic dialogue, promote transparency, and address common security concerns with non-member countries, reflecting its commitment to enhancing global security and stability.
BRICS, as an alliance of major emerging economies, maintains a dynamic relationship with non-member countries, reflecting its commitment to promoting inclusive development and fostering cooperation on the global stage. The alliance actively engages in dialogue and partnerships with non-member countries, seeking to enhance South-South cooperation, promote economic development, and advocate for a more equitable international order.
BRICS' engagement with non-member countries extends to regions such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, reflecting its commitment to fostering partnerships and promoting mutual understanding. The alliance seeks to leverage its collective influence to address common developmental challenges, enhance trade and investment cooperation, and contribute to the advancement of a more inclusive and interconnected global community.
In essence, both NATO and BRICS maintain dynamic relationships with non-member countries, reflecting their respective commitments to promoting stability, fostering cooperation, and contributing to global security and development. Through their engagement with non-member countries, both alliances underscore their roles as key players in shaping the contemporary global landscape and advancing shared interests on the international stage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparison of NATO and BRICS reveals the nuanced complexities and strategic implications inherent in the operations of these two prominent military organizations. Despite their differing historical backgrounds, missions, and member compositions, both NATO and BRICS play pivotal roles in shaping international relations and security dynamics.
NATO, with its origins rooted in the aftermath of World War II, remains committed to safeguarding the freedom, security, and common values of its member states through collective defense and cooperative security measures. The alliance's military capabilities, decision-making process, and relationships with non-member countries underscore its enduring significance as a linchpin of transatlantic security cooperation.
On the other hand, BRICS, comprising major emerging economies, is dedicated to promoting inclusive development, enhancing global governance, and advocating for a more equitable and multipolar world order. The alliance's historical background, mission, and member countries reflect its emergence as a pivotal force in international relations, embodying a shared vision of fostering economic cooperation and advocating for global governance reforms.
The diverse composition of member countries within NATO and BRICS underscores their respective commitments to collective defense, solidarity, and strategic coordination. While NATO's military capabilities emphasize its readiness to address diverse security challenges and promote stability, BRICS' military capabilities reflect the collective strength and strategic significance of its member countries in shaping the global security landscape.
Furthermore, both alliances maintain dynamic relationships with non-member countries, reflecting their commitments to promoting stability, fostering cooperation, and contributing to global security and development. Through their engagement with non-member countries, both NATO and BRICS underscore their roles as key players in shaping the contemporary global landscape and advancing shared interests on the international stage.
In essence, the comparison of NATO and BRICS illuminates the multifaceted nature of contemporary military organizations, highlighting their roles in shaping the geopolitical landscape and fostering international cooperation. As NATO and BRICS continue to navigate evolving security challenges and global dynamics, their enduring significance remains integral to understanding the complexities of international security and the pursuit of collective peace and stability.













