Home>Health and Wellness>The Surprising Difference Between Military And Overhead Press Revealed!


Health and Wellness
The Surprising Difference Between Military And Overhead Press Revealed!
Published: January 16, 2024
Discover the key distinctions between military and overhead press techniques to optimize your health and wellness. Unlock the secrets to achieving your fitness goals!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The military press and the overhead press are two popular strength training exercises that are often used interchangeably. While they may appear similar at first glance, there are subtle yet significant differences between these two movements. Understanding these disparities can help individuals make informed decisions about which exercise to incorporate into their fitness routines.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the distinct characteristics of the military press and the overhead press, shedding light on their unique attributes, benefits, and considerations. By exploring the nuances of these exercises, readers will gain a deeper understanding of how each movement targets specific muscle groups and contributes to overall strength and fitness.
Join us as we uncover the surprising disparities between the military press and the overhead press, providing valuable insights for fitness enthusiasts, athletes, and anyone seeking to optimize their strength training regimen.
The Military Press
The military press, also known as the strict press, is a classic strength training exercise that has stood the test of time. This compound movement primarily targets the shoulders, specifically the deltoid muscles, while also engaging the triceps and upper chest. The military press is performed in a standing position, emphasizing strict form and controlled movements to effectively challenge the upper body musculature.
To execute the military press, an individual begins by standing with their feet shoulder-width apart, grasping a barbell at shoulder level with an overhand grip. The elbows are positioned slightly in front of the bar, creating a stable foundation for the lift. With a strong core and engaged glutes, the individual then presses the barbell overhead in a vertical trajectory, extending the arms fully without locking the elbows. The bar is then lowered back to the starting position with control, maintaining proper alignment and stability throughout the movement.
One of the defining characteristics of the military press is the absence of leg drive or momentum. Unlike the push press or jerk, which involve utilizing the legs to generate upward force, the military press relies solely on the strength of the upper body. This strict and controlled approach places a significant emphasis on shoulder strength and stability, making it an effective exercise for developing muscular endurance and promoting shoulder health.
Furthermore, the military press is renowned for its ability to enhance overall upper body strength and functional shoulder mobility. By targeting the deltoids, triceps, and stabilizing muscles, this exercise contributes to improved posture, shoulder stability, and overhead pressing capabilities. Additionally, the strict nature of the military press fosters greater muscle engagement and control, promoting muscular development and strength gains over time.
Incorporating the military press into a well-rounded strength training routine can yield numerous benefits, including enhanced shoulder strength, improved upper body muscular development, and increased stability for overhead movements. However, it is important to approach this exercise with proper form and caution, as the strict nature of the military press requires attention to detail and mindful execution to minimize the risk of injury.
In the next section, we will explore the intricacies of the overhead press, providing a comprehensive comparison to further illuminate the unique attributes of these two fundamental strength training exercises.
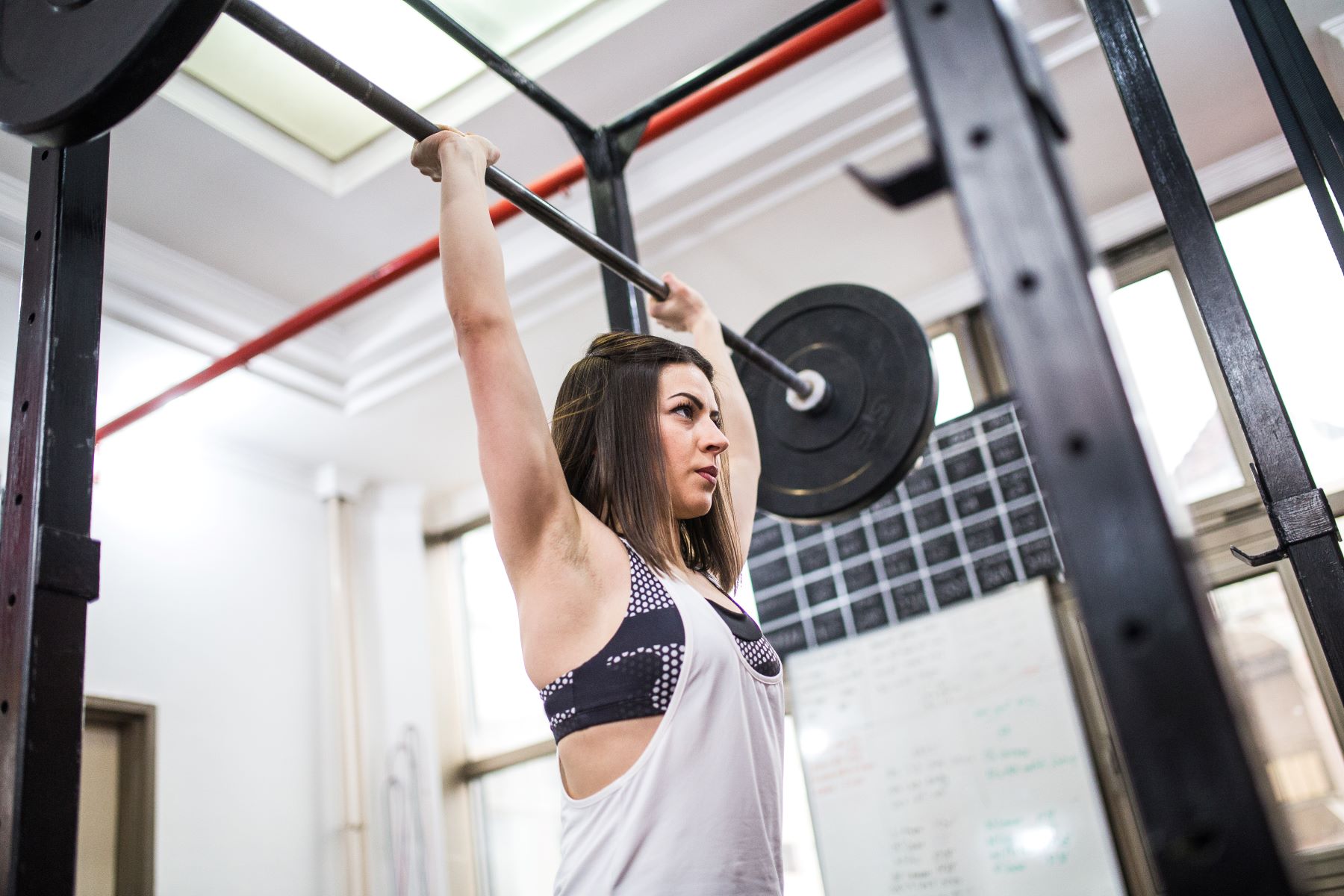
The Overhead Press
The overhead press, also referred to as the shoulder press, is a fundamental compound exercise that targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest. This versatile movement can be performed using various equipment, including barbells, dumbbells, or kettlebells, offering individuals the flexibility to adapt the exercise to their specific training preferences and available resources.
To execute the overhead press with a barbell, an individual typically begins by standing with their feet shoulder-width apart, gripping the barbell slightly wider than shoulder width. With the barbell positioned at shoulder level, the individual engages their core and glutes to stabilize the body before pressing the weight overhead in a controlled manner. Throughout the movement, emphasis is placed on maintaining proper form, with the elbows positioned slightly in front of the bar to optimize shoulder mechanics and stability. Once the arms are fully extended overhead, the barbell is lowered back to the starting position with controlled descent, completing one repetition of the overhead press.
In contrast to the military press, the overhead press allows for a degree of leg drive and momentum, enabling individuals to generate additional force by utilizing the lower body to assist in lifting the weight. This dynamic aspect of the overhead press can result in greater overall power output, making it a valuable exercise for developing full-body strength and coordination. Furthermore, the overhead press promotes functional shoulder mobility and stability, contributing to improved performance in various upper body movements and activities.
One of the key distinctions between the military press and the overhead press lies in the range of motion and muscle recruitment. The overhead press typically involves a slightly longer range of motion, allowing for increased activation of the upper chest and triceps in addition to the primary emphasis on the shoulders. This comprehensive engagement of multiple muscle groups makes the overhead press a highly effective exercise for promoting overall upper body strength and muscular development.
In addition to its physical benefits, the overhead press offers individuals the opportunity to enhance their coordination and balance, as the exercise demands controlled movements and stability throughout the entire range of motion. By incorporating the overhead press into a well-rounded strength training routine, individuals can cultivate greater shoulder strength, upper body stability, and functional pressing capabilities.
As we compare and contrast the military press and the overhead press, it becomes evident that both exercises offer unique advantages and considerations. By understanding the nuances of each movement, individuals can make informed decisions about how to integrate these exercises into their training regimens, ultimately optimizing their strength, muscular development, and overall fitness.
The Overhead Press is a fundamental exercise that targets the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest. This versatile movement can be performed using various equipment, including barbells, dumbbells, or kettlebells, offering individuals the flexibility to adapt the exercise to their specific training preferences and available resources.
To execute the overhead press with a barbell, an individual typically begins by standing with their feet shoulder-width apart, gripping the barbell slightly wider than shoulder width. With the barbell positioned at shoulder level, the individual engages their core and glutes to stabilize the body before pressing the weight overhead in a controlled manner. Throughout the movement, emphasis is placed on maintaining proper form, with the elbows positioned slightly in front of the bar to optimize shoulder mechanics and stability. Once the arms are fully extended overhead, the barbell is lowered back to the starting position with controlled descent, completing one repetition of the overhead press.
In contrast to the military press, the overhead press allows for a degree of leg drive and momentum, enabling individuals to generate additional force by utilizing the lower body to assist in lifting the weight. This dynamic aspect of the overhead press can result in greater overall power output, making it a valuable exercise for developing full-body strength and coordination. Furthermore, the overhead press promotes functional shoulder mobility and stability, contributing to improved performance in various upper body movements and activities.
One of the key distinctions between the military press and the overhead press lies in the range of motion and muscle recruitment. The overhead press typically involves a slightly longer range of motion, allowing for increased activation of the upper chest and triceps in addition to the primary emphasis on the shoulders. This comprehensive engagement of multiple muscle groups makes the overhead press a highly effective exercise for promoting overall upper body strength and muscular development.
In addition to its physical benefits, the overhead press offers individuals the opportunity to enhance their coordination and balance, as the exercise demands controlled movements and stability throughout the entire range of motion. By incorporating the overhead press into a well-rounded strength training routine, individuals can cultivate greater shoulder strength, upper body stability, and functional pressing capabilities.
As we compare and contrast the military press and the overhead press, it becomes evident that both exercises offer unique advantages and considerations. By understanding the nuances of each movement, individuals can make informed decisions about how to integrate these exercises into their training regimens, ultimately optimizing their strength, muscular development, and overall fitness.
Muscles Worked
The military press and the overhead press are both compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups, particularly focusing on the upper body. Understanding the specific muscles targeted by each exercise is crucial for tailoring strength training programs and maximizing the benefits of these movements.
Military Press:
The military press primarily targets the deltoid muscles, which are located in the shoulders. This exercise places significant emphasis on the anterior (front) and lateral (side) deltoid heads, contributing to overall shoulder strength and development. Additionally, the triceps brachii, located at the back of the upper arm, are actively engaged during the military press, serving as synergistic muscles to assist in the pressing movement. The upper chest muscles, including the pectoralis major and minor, also play a supportive role in stabilizing the shoulders and arms throughout the exercise. Furthermore, the core muscles, particularly the rectus abdominis and obliques, are activated to maintain stability and posture during the standing military press, promoting overall core strength and engagement.
Overhead Press:
Similar to the military press, the overhead press targets the deltoid muscles, particularly the anterior and lateral heads, to promote shoulder strength and development. In addition, the triceps brachii are actively involved in extending the elbows during the pressing motion, contributing to the overall power and stability of the lift. The upper chest muscles, including the pectoralis major, are also engaged to a lesser extent, providing support and stability throughout the movement. Furthermore, the serratus anterior, a muscle located on the side of the chest, is activated during the overhead press to assist in scapular protraction and stabilization, enhancing shoulder mobility and stability.
Key Differences:
While both the military press and the overhead press target similar muscle groups, the military press places a greater emphasis on strict shoulder strength and stability, with minimal involvement of lower body momentum. In contrast, the overhead press allows for a degree of leg drive and full-body coordination, resulting in additional activation of the lower body muscles, including the quadriceps, glutes, and core stabilizers. This distinction highlights the nuanced differences in muscle recruitment and overall engagement between these two fundamental strength training exercises.
Understanding the specific muscles worked during the military press and the overhead press is essential for tailoring training programs to individual fitness goals and optimizing overall upper body strength and development. By recognizing the unique contributions of each exercise to muscular engagement and functional movement patterns, individuals can make informed decisions about incorporating these movements into their strength training routines, ultimately promoting balanced muscular development and enhanced performance in various upper body activities.
Equipment and Form
When it comes to the military press and the overhead press, understanding the equipment and proper form is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these exercises and minimizing the risk of injury. Both movements can be performed using various types of equipment, each offering unique advantages and considerations. Additionally, maintaining proper form is crucial for optimizing muscle engagement and promoting safe and efficient execution of the exercises.
Military Press:
The military press is traditionally performed using a barbell, which provides a stable and balanced platform for pressing movements. When selecting a barbell for the military press, it is important to choose an appropriate weight that allows for controlled and strict execution of the exercise. Additionally, ensuring that the barbell is positioned securely on the shoulders before initiating the press is vital for maintaining stability and minimizing unnecessary strain on the wrists and elbows.
Proper form is paramount during the military press, as the exercise emphasizes strict shoulder strength and stability. To execute the military press with optimal form, individuals should stand with their feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining a strong and stable base. Gripping the barbell at shoulder level with an overhand grip, the elbows are positioned slightly in front of the bar to establish a solid foundation for the lift. Throughout the movement, the core should be engaged, and the glutes activated to promote overall stability and alignment. As the barbell is pressed overhead, the arms extend fully without locking the elbows, emphasizing controlled and deliberate movements. Lowering the barbell back to the starting position with precision and control completes one repetition of the military press.
Overhead Press:
Similar to the military press, the overhead press can be performed using a barbell, dumbbells, or kettlebells, offering individuals the flexibility to adapt the exercise to their specific training preferences and available resources. When utilizing a barbell for the overhead press, individuals should ensure that the weight is distributed evenly and that the grip width allows for comfortable and secure handling of the barbell.
Maintaining proper form during the overhead press is essential for optimizing muscle engagement and promoting safe execution. Individuals should stand with their feet shoulder-width apart, gripping the barbell slightly wider than shoulder width. Core engagement and glute activation are crucial for stabilizing the body throughout the movement. As the barbell is pressed overhead, emphasis should be placed on maintaining a straight bar path and controlled upward movement, utilizing the legs to generate upward force if desired. Lowering the barbell back to the starting position with controlled descent completes one repetition of the overhead press.
By understanding the equipment and proper form associated with the military press and the overhead press, individuals can optimize their training routines and minimize the risk of injury. Whether utilizing a barbell, dumbbells, or kettlebells, selecting appropriate weights and maintaining strict form are fundamental for reaping the full benefits of these foundational strength training exercises.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The military press and overhead press offer a myriad of benefits for individuals seeking to enhance their strength, muscular development, and overall fitness. However, it is important to recognize that each exercise also presents unique considerations and potential drawbacks that warrant careful attention.
Benefits
Military Press:
- Shoulder Strength and Stability: The military press is renowned for its ability to target the deltoid muscles, promoting enhanced shoulder strength and stability. By engaging the shoulders in a strict and controlled manner, individuals can cultivate greater muscular endurance and functional shoulder mobility, contributing to improved posture and overall upper body strength.
- Upper Body Muscular Development: Incorporating the military press into a strength training routine can lead to significant muscular development in the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest. This comprehensive engagement of multiple muscle groups fosters balanced upper body strength and contributes to improved pressing capabilities in various movements and activities.
- Core Engagement: The military press necessitates core engagement and stability throughout the exercise, promoting greater overall core strength and functional stability. This aspect of the movement contributes to enhanced postural alignment and overall core strength, benefiting individuals in various athletic and functional endeavors.
Overhead Press:
- Full-Body Coordination: The overhead press, particularly when performed with a degree of leg drive, encourages full-body coordination and engagement. By integrating the lower body into the pressing movement, individuals can develop greater overall power output and coordination, contributing to improved athletic performance and functional strength.
- Muscular Balance and Stability: Engaging multiple muscle groups, including the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest, the overhead press promotes balanced muscular development and stability in the upper body. This comprehensive engagement of various muscle groups contributes to improved functional strength and stability in pressing movements and everyday activities.
- Versatility: The overhead press can be performed using different equipment, such as barbells, dumbbells, or kettlebells, offering individuals versatility in their training routines. This adaptability allows for variations in grip and movement patterns, catering to individual preferences and training objectives.
Drawbacks
Military Press:
- Shoulder Strain: The strict and controlled nature of the military press can potentially lead to shoulder strain or overuse injuries if proper form and caution are not observed. Individuals should be mindful of maintaining proper shoulder mechanics and avoiding excessive weight that may compromise shoulder health.
- Limited Lower Body Engagement: As the military press restricts lower body momentum, it may not fully capitalize on the benefits of full-body coordination and power generation, which are inherent in exercises involving leg drive.
Overhead Press:
- Risk of Lower Back Strain: When utilizing a significant degree of leg drive, individuals may be susceptible to lower back strain if proper bracing and core engagement are not prioritized. It is essential to maintain a stable and aligned posture throughout the movement to mitigate the risk of lower back discomfort or injury.
- Potential for Overreliance on Momentum: While the incorporation of leg drive can enhance power output, individuals must be cautious not to rely excessively on momentum, which may compromise the strict and controlled nature of the exercise.
Understanding the diverse benefits and potential drawbacks of the military press and overhead press is crucial for individuals aiming to optimize their strength training routines. By recognizing the unique advantages and considerations associated with each exercise, individuals can make informed decisions about their training approach, ultimately maximizing the benefits while mitigating potential risks.
Training Considerations
When incorporating the military press and overhead press into a strength training regimen, several essential considerations should be taken into account to optimize the effectiveness of these exercises and ensure safe and sustainable progress.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is a fundamental principle in strength training that involves gradually increasing the demands placed on the muscles to stimulate growth and adaptation. When performing the military press and overhead press, individuals should strive to progressively increase the resistance over time, whether through incremental weight additions, additional repetitions, or enhanced time under tension. This approach encourages continuous strength gains and muscular development, contributing to long-term progress and performance improvements.
Proper Form and Technique
Maintaining proper form and technique is paramount when executing the military press and overhead press. Emphasizing strict shoulder mechanics, controlled movements, and stable core engagement is essential for minimizing the risk of injury and maximizing muscle engagement. Individuals should focus on maintaining a neutral spine, avoiding excessive arching or leaning, and prioritizing smooth and deliberate lifting and lowering of the weights. Additionally, seeking guidance from a qualified fitness professional or coach can provide valuable insights into refining form and technique for these exercises.
Variation and Periodization
Introducing variation and periodization into training routines can prevent plateaus and enhance overall progress. Individuals can incorporate variations of the military press and overhead press, such as using different equipment, adjusting grip widths, or modifying rep ranges, to stimulate muscle adaptation and prevent monotony. Furthermore, implementing periodization strategies, such as alternating between strength-focused phases and hypertrophy-focused phases, can optimize training outcomes and promote well-rounded muscular development.
Recovery and Rest
Allowing adequate time for recovery and rest is crucial for optimizing the benefits of strength training. The military press and overhead press place significant demands on the shoulders, triceps, and upper body musculature, necessitating sufficient recovery periods to facilitate muscle repair and growth. Integrating rest days into training schedules, prioritizing quality sleep, and adhering to proper nutrition and hydration are essential components of effective recovery strategies, promoting overall training sustainability and performance enhancement.
Injury Prevention and Mobility
Incorporating injury prevention strategies and mobility work into training considerations can safeguard against potential setbacks and enhance overall movement quality. Individuals should prioritize prehabilitation exercises, such as shoulder mobility drills and scapular stabilization movements, to promote shoulder health and reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Additionally, integrating dynamic warm-up routines and mobility exercises specific to the shoulders and upper body can enhance overall movement patterns and functional range of motion, contributing to improved exercise performance and injury resilience.
Individualized Programming
Tailoring training programs to individual fitness levels, goals, and capabilities is essential for optimizing training considerations. Recognizing individual strengths, limitations, and preferences allows for the development of personalized programming that aligns with specific objectives and promotes sustainable progress. Whether focusing on strength development, muscular endurance, or functional movement patterns, individualized programming fosters a tailored approach to training that maximizes results and minimizes the risk of burnout or injury.
By integrating these training considerations into strength training routines that incorporate the military press and overhead press, individuals can cultivate a holistic approach to exercise that prioritizes safety, progress, and long-term success. Embracing the principles of progressive overload, proper form, variation, recovery, injury prevention, and individualized programming empowers individuals to optimize their training experiences and achieve their fitness aspirations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the military press and the overhead press stand as foundational pillars of strength training, each offering unique benefits and considerations for individuals seeking to enhance their upper body strength, muscular development, and overall fitness. By delving into the distinct characteristics of these exercises, we have gained valuable insights into their nuanced differences and the impact they can have on strength training regimens.
The military press, characterized by its strict and controlled nature, places a significant emphasis on shoulder strength and stability. By targeting the deltoid muscles and engaging the triceps and upper chest, the military press fosters enhanced muscular endurance, functional shoulder mobility, and overall upper body strength. However, the strict form and limited lower body engagement of the military press necessitate careful attention to proper execution and caution to minimize the risk of shoulder strain and overuse injuries.
Conversely, the overhead press, with its versatility and potential for full-body coordination, offers individuals the opportunity to develop greater overall power output and balanced muscular development. By engaging the shoulders, triceps, and upper chest, the overhead press promotes functional strength and stability in pressing movements, while also encouraging dynamic movement patterns and coordination. However, individuals must be mindful of maintaining proper form and avoiding overreliance on momentum to mitigate the risk of lower back strain and compromised exercise integrity.
As individuals navigate their strength training journeys, it is essential to consider progressive overload, proper form and technique, variation and periodization, recovery and rest, injury prevention and mobility, and individualized programming. By integrating these training considerations, individuals can optimize the effectiveness of the military press and overhead press while promoting sustainable progress and overall well-being.
Ultimately, the nuanced differences between the military press and the overhead press underscore the importance of informed decision-making and tailored training approaches. By recognizing the distinct attributes of these exercises and embracing the principles of effective strength training, individuals can cultivate balanced muscular development, enhanced functional strength, and a resilient foundation for long-term fitness success. Whether striving for improved shoulder strength, muscular endurance, or full-body coordination, the military press and overhead press offer valuable avenues for individuals to pursue their fitness aspirations and elevate their strength training experiences.