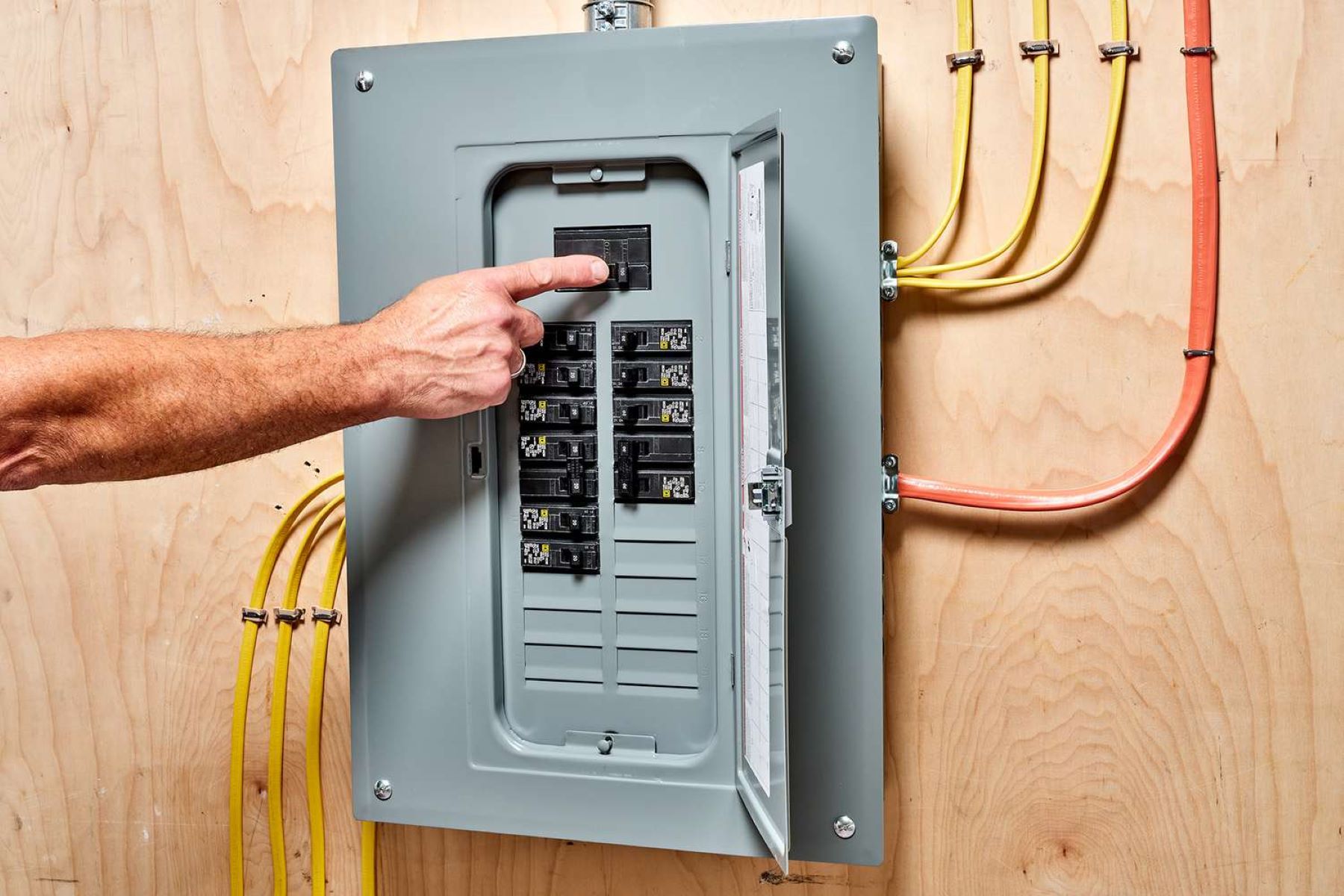
Home>Home and Garden>Choosing The Correct Wire Gauge For A 30-Amp Breaker: Is 12 Gauge Wire Suitable?

Home and Garden
Choosing The Correct Wire Gauge For A 30-Amp Breaker: Is 12 Gauge Wire Suitable?
Modified: February 28, 2024
Learn how to choose the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker and find out if 12 gauge wire is suitable. Get expert advice for your home and garden projects.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Choosing the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems in homes and gardens. The wire gauge directly impacts the flow of electricity and must be carefully selected to match the specific amperage requirements of the circuit. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of wire gauge selection, focusing on the suitability of 12 gauge wire for a 30-amp breaker.
Understanding the relationship between wire gauge and amperage is essential for homeowners, DIY enthusiasts, and professionals alike. By gaining insights into the principles of electrical wiring, individuals can make informed decisions when it comes to selecting the appropriate wire gauge for various applications. In the following sections, we will explore the concept of wire gauge and ampacity, discuss the factors that influence the choice of wire gauge, and address the question of whether 12 gauge wire is suitable for a 30-amp breaker.
As we embark on this journey through the realm of electrical systems and wiring, it is important to approach the topic with a keen sense of curiosity and a commitment to understanding the underlying principles. By the end of this guide, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the considerations involved in choosing the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker, empowering them to make well-informed decisions when working with electrical circuits.
The next section will delve into the fundamentals of wire gauge and ampacity, laying the groundwork for a deeper exploration of the topic. Let's embark on this enlightening journey into the world of electrical wiring and discover the intricacies of selecting the right wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker.
Understanding Wire Gauge and Ampacity
Wire gauge, also known as the American Wire Gauge (AWG), is a standardized system used to measure the diameter of electrical wire. In the context of electrical wiring, the gauge of the wire plays a critical role in determining its ampacity, which refers to the maximum current-carrying capacity of the wire. Understanding the relationship between wire gauge and ampacity is fundamental to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical circuits.
The wire gauge system is based on a numerical scale, with lower gauge numbers representing thicker wires and higher gauge numbers representing thinner wires. For instance, a 10-gauge wire is thicker and has a higher ampacity than a 14-gauge wire. As the gauge number decreases, the diameter of the wire increases, allowing it to carry more current without overheating.
Ampacity, on the other hand, is the maximum current that a wire can safely carry without exceeding its temperature rating. This is crucial because if a wire is subjected to a current higher than its ampacity, it can overheat, potentially leading to insulation damage, electrical fires, or other hazardous situations.
When selecting the appropriate wire gauge for a specific application, it is essential to consider the ampacity requirements of the circuit. The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides guidelines and standards for determining the correct wire gauge based on the anticipated load and the type of circuit. By adhering to these standards, individuals can ensure compliance with safety regulations and minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
In summary, wire gauge and ampacity are integral aspects of electrical wiring, influencing the safe and efficient transmission of electrical current. By understanding the relationship between wire gauge, ampacity, and current-carrying capacity, individuals can make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate wire gauge for various electrical applications. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for delving deeper into the considerations involved in choosing the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker.
Determining the Correct Wire Gauge for a 30-Amp Breaker
When it comes to determining the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker, precision and adherence to safety standards are paramount. The ampacity of the wire must align with the specific amperage rating of the circuit to ensure safe and efficient electrical operation. In the case of a 30-amp breaker, the wire gauge selection is critical in preventing overheating and maintaining the integrity of the electrical system.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides clear guidelines for selecting the appropriate wire gauge based on the ampacity requirements of the circuit. For a 30-amp circuit, the NEC specifies that a wire with a minimum ampacity of 10-gauge should be used. This standard is designed to safeguard against the potential hazards associated with inadequate wire size, such as overheating, voltage drop, and increased resistance.
In practical terms, the selection of the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker involves a meticulous assessment of the anticipated load, the length of the circuit, and the type of wiring method employed. Factors such as ambient temperature, insulation type, and the presence of other conductors in the same raceway or cable must also be taken into account to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
It is important to note that using a wire gauge that is too small for a 30-amp circuit can lead to excessive heat generation, posing a significant fire risk. Conversely, employing a wire gauge that exceeds the ampacity requirements may result in unnecessary costs and installation complexities without providing tangible benefits in terms of electrical performance.
In essence, determining the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker involves a meticulous evaluation of the specific requirements of the electrical circuit, coupled with a thorough understanding of the NEC guidelines. By adhering to these standards and exercising diligence in the selection process, individuals can ensure the safe and reliable operation of 30-amp circuits, thereby mitigating the potential risks associated with inadequate wire sizing.
This foundational understanding sets the stage for addressing the question of whether 12 gauge wire is suitable for a 30-amp breaker, a topic that will be explored in the subsequent section.
Is 12 Gauge Wire Suitable for a 30-Amp Breaker?
The suitability of 12 gauge wire for a 30-amp breaker is a topic that sparks considerable debate and scrutiny within the realm of electrical wiring. As per the National Electrical Code (NEC) guidelines, a 30-amp circuit necessitates a minimum wire gauge of 10, raising questions about the compatibility of 12 gauge wire with such a circuit.
In the context of electrical systems, the ampacity of a wire, which denotes its current-carrying capacity, is a critical factor in determining its suitability for a specific amperage rating. When considering 12 gauge wire for a 30-amp breaker, it is essential to evaluate its ampacity and compare it against the requirements of the circuit.
According to the NEC, 12 gauge wire is typically rated with an ampacity of 20 amperes for general-purpose circuits. This ampacity rating aligns with the standard usage scenarios for 12 gauge wire, where it is commonly employed in 15- and 20-amp circuits. However, when confronted with the prospect of accommodating a 30-amp load, the ampacity of 12 gauge wire falls short of the prescribed minimum for a 30-amp circuit.
The disparity between the ampacity of 12 gauge wire and the requirements of a 30-amp breaker raises concerns regarding safety, efficiency, and compliance with electrical codes. Employing 12 gauge wire in a 30-amp circuit poses inherent risks, including the potential for overheating, increased resistance, and compromised electrical performance. Such deviations from the recommended wire gauge standards can compromise the integrity of the electrical system and may lead to hazardous conditions.
In essence, while 12 gauge wire exhibits sufficient ampacity for lower amperage circuits, its compatibility with a 30-amp breaker is not in alignment with established safety standards and regulatory guidelines. As such, adhering to the NEC requirements for wire gauge selection is imperative to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical circuits, particularly those associated with higher amperage ratings.
The considerations surrounding the suitability of 12 gauge wire for a 30-amp breaker underscore the significance of meticulous wire gauge selection in upholding electrical safety and performance standards. By aligning wire gauge choices with the specific ampacity requirements of circuits, individuals can mitigate potential hazards and uphold the integrity of electrical systems.
This analysis sheds light on the nuanced intricacies of wire gauge selection and its implications for electrical safety, underscoring the importance of adhering to established standards in the pursuit of safe and efficient electrical installations.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Wire Gauge
When it comes to choosing the appropriate wire gauge for electrical installations, several critical factors must be carefully evaluated to ensure the safe and efficient operation of circuits. These factors play a pivotal role in determining the suitability of a specific wire gauge for a given application, guiding individuals in making informed decisions that align with safety standards and regulatory requirements.
-
Ampacity Requirements: The primary consideration when selecting a wire gauge is the ampacity requirements of the circuit. Understanding the anticipated load and the corresponding ampacity rating is essential for choosing a wire gauge that can safely accommodate the electrical current without exceeding its capacity. Adhering to the prescribed ampacity guidelines minimizes the risk of overheating and ensures the integrity of the electrical system.
-
Circuit Length and Voltage Drop: The length of the electrical circuit and the associated voltage drop must be taken into account when choosing the wire gauge. Longer circuits and higher voltage drops necessitate the use of thicker wire gauges to mitigate the impact of resistance and maintain the desired voltage levels at the load end. By considering these factors, individuals can optimize the performance and efficiency of the electrical system.
-
Ambient Temperature and Insulation Type: Environmental conditions, including ambient temperature and the type of insulation used, can influence the choice of wire gauge. Higher temperatures may necessitate the use of larger wire gauges to offset the effects of heat on the wire's ampacity. Additionally, the insulation type plays a crucial role in determining the wire's ability to withstand varying environmental conditions, impacting its suitability for specific applications.
-
Wire Type and Installation Method: The type of wire and the installation method employed are significant factors in wire gauge selection. Different wire types, such as copper and aluminum, have distinct ampacity ratings and installation requirements. Furthermore, the installation method, whether in conduit, cable, or open air, influences the heat dissipation and current-carrying capacity of the wire, guiding the choice of an appropriate wire gauge.
-
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards: Adhering to regulatory codes and safety standards, such as those outlined in the National Electrical Code (NEC), is imperative when selecting a wire gauge. Compliance with established guidelines ensures the safety, reliability, and longevity of electrical installations, mitigating potential hazards and ensuring consistency with industry best practices.
By meticulously evaluating these factors and integrating them into the decision-making process, individuals can make well-informed choices when selecting the correct wire gauge for various electrical applications. This comprehensive approach not only enhances the safety and efficiency of electrical systems but also fosters a deeper understanding of the intricate considerations involved in wire gauge selection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of choosing the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker is a critical undertaking that demands meticulous attention to detail, adherence to safety standards, and a comprehensive understanding of the principles governing electrical wiring. Throughout this guide, we have delved into the intricacies of wire gauge selection, explored the relationship between wire gauge and ampacity, and addressed the question of whether 12 gauge wire is suitable for a 30-amp breaker.
The significance of wire gauge selection cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the safety, efficiency, and reliability of electrical circuits in homes and gardens. By aligning the wire gauge with the specific ampacity requirements of the circuit, individuals can mitigate potential hazards, prevent overheating, and ensure the optimal performance of electrical systems.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) serves as a cornerstone for establishing guidelines and standards for wire gauge selection, providing a framework for safe and compliant electrical installations. Adhering to the NEC requirements, including the stipulated minimum wire gauge for 30-amp circuits, is essential for upholding electrical safety and mitigating the risks associated with inadequate wire sizing.
The question of whether 12 gauge wire is suitable for a 30-amp breaker underscores the nuanced considerations involved in wire gauge selection. While 12 gauge wire exhibits sufficient ampacity for lower amperage circuits, its compatibility with a 30-amp breaker is not in alignment with established safety standards and regulatory guidelines. This highlights the importance of precision and diligence in choosing the appropriate wire gauge to ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical circuits.
Furthermore, the factors to consider when choosing wire gauge, including ampacity requirements, circuit length, ambient temperature, wire type, and regulatory compliance, provide a comprehensive framework for informed decision-making. By evaluating these factors in conjunction with the specific needs of the electrical installation, individuals can make well-informed choices that prioritize safety, efficiency, and compliance with industry best practices.
In essence, the process of selecting the correct wire gauge for a 30-amp breaker demands a holistic approach that integrates technical knowledge, regulatory awareness, and a commitment to upholding electrical safety standards. By embracing these principles and guidelines, individuals can navigate the complexities of wire gauge selection with confidence, ensuring the integrity and performance of electrical systems in homes and gardens.
As individuals embark on electrical projects and installations, the insights gained from this guide will serve as a valuable resource, empowering them to make informed decisions and uphold the highest standards of electrical safety and performance. Through a steadfast commitment to precision and compliance, individuals can navigate the realm of wire gauge selection with proficiency and ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical circuits.