Home>Health and Wellness>The Surprising Truth About Surgical Steel And Titanium

Health and Wellness
The Surprising Truth About Surgical Steel And Titanium
Published: January 19, 2024
Discover the surprising benefits of surgical steel and titanium for your health and wellness. Learn why these materials are essential for your well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to health and wellness, the materials used in medical devices and implants play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of patients. Among the various materials utilized in the healthcare industry, surgical steel and titanium stand out as popular choices due to their exceptional properties and versatility. These materials are not only renowned for their durability and resistance to corrosion but also for their biocompatibility, making them ideal for a wide range of medical applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of surgical steel and titanium, uncovering their unique characteristics, exploring their common uses in the medical field, and weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each material. By the end of this exploration, you will gain a deeper understanding of the surprising truths behind these remarkable substances and their significant impact on the health and wellness landscape. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of surgical steel and titanium, and discover how these extraordinary materials contribute to the advancement of modern healthcare.
Properties of Surgical Steel
Surgical steel, also known as stainless steel, is a remarkable alloy celebrated for its exceptional properties, making it a preferred choice in the medical field. Let's delve into the distinctive characteristics that make surgical steel a standout material:
Corrosion Resistance
One of the most notable properties of surgical steel is its remarkable resistance to corrosion. This attribute is attributed to the presence of chromium in the alloy, which forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, shielding it from rust and corrosion. As a result, surgical steel remains unaffected by exposure to bodily fluids and various sterilization processes, ensuring its longevity and reliability in medical applications.
Biocompatibility
Surgical steel possesses excellent biocompatibility, meaning it is well-tolerated by the human body without triggering adverse reactions. This property is of utmost importance in medical implants and surgical instruments, as it minimizes the risk of allergic responses or tissue rejection, thereby promoting successful surgical outcomes and patient well-being.
Strength and Durability
Another key attribute of surgical steel is its impressive strength and durability. This material exhibits high tensile strength, allowing it to withstand mechanical stress and deformation without compromising its structural integrity. Moreover, its resilience against wear and tear makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing medical devices that require long-term reliability and performance.
Read more: The Surprising Truth About Sweating In Suits
Ease of Sterilization
Surgical steel is highly conducive to sterilization processes, a critical requirement in the medical setting. Whether through autoclaving, gamma irradiation, or chemical sterilants, this material can undergo rigorous sterilization methods without degrading its properties. This ensures that medical instruments and implants made from surgical steel maintain their hygienic integrity, contributing to infection control and patient safety.
Aesthetic Appeal
In addition to its functional properties, surgical steel also boasts an aesthetically pleasing appearance. Its lustrous and polished surface not only enhances the visual appeal of medical instruments but also facilitates easy cleaning and maintenance, further emphasizing its suitability for healthcare environments.
In summary, the exceptional properties of surgical steel, including corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, strength, ease of sterilization, and aesthetic appeal, underscore its pivotal role in the medical industry. As we continue our exploration, we will uncover the equally intriguing properties of titanium, paving the way for a comprehensive comparison between these two exceptional materials.
Properties of Titanium
Titanium, often hailed as the "wonder metal," possesses a remarkable set of properties that have earned it a prominent status in various industries, including healthcare. Let's unravel the exceptional characteristics that define titanium and make it a coveted material in medical applications.
Lightweight Strength
One of the most striking attributes of titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Despite being incredibly lightweight, titanium exhibits remarkable strength comparable to that of steel. This unique combination of strength and low density makes titanium an ideal choice for medical implants, as it offers the necessary structural integrity without adding excessive weight to the patient's body. This is particularly advantageous in orthopedic implants, where the material's strength and biocompatibility are crucial for long-term implant success.
Biocompatibility
Similar to surgical steel, titanium is renowned for its outstanding biocompatibility. When used in medical implants, titanium integrates seamlessly with the human body, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or implant rejection. This biocompatibility is attributed to the formation of a stable oxide layer on the metal's surface, which enables it to interact harmoniously with biological tissues. As a result, titanium implants promote favorable healing responses and long-term stability within the body.
Corrosion Resistance
Another noteworthy property of titanium is its exceptional resistance to corrosion, particularly in physiological environments. The formation of a protective oxide layer on the metal's surface confers remarkable resistance to corrosion, ensuring the longevity and reliability of titanium implants. This resistance to degradation in the presence of bodily fluids is pivotal in ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices and implants over extended periods.
Flexibility and Ductility
Despite its robust nature, titanium also exhibits a degree of flexibility and ductility, allowing it to be shaped and customized for specific medical applications. This malleability enables the fabrication of intricate implant designs tailored to the unique anatomical requirements of patients, thereby enhancing the precision and effectiveness of medical interventions.
Thermal and Biological Inertness
Titanium's exceptional thermal and biological inertness further contributes to its suitability for medical use. This property ensures that titanium implants do not react adversely to the body's natural processes and remain stable within various temperature ranges, providing assurance of their reliability and safety in clinical settings.
In summary, the remarkable properties of titanium, including its lightweight strength, biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, flexibility, and inertness, position it as a highly sought-after material in the healthcare industry. As we transition to the next segment, we will embark on a detailed comparison of the properties of surgical steel and titanium, shedding light on their respective advantages and applications in the medical field.
Read more: The Surprising Truth About Airline Food
Comparison of Surgical Steel and Titanium
Both surgical steel and titanium exhibit exceptional properties that render them invaluable in medical applications. However, a detailed comparison reveals distinct characteristics that differentiate these materials, influencing their suitability for specific healthcare needs.
Strength and Weight: Surgical steel is renowned for its robustness and durability, making it an ideal choice for surgical instruments and medical devices requiring high tensile strength. On the other hand, titanium boasts a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, offering comparable strength to steel while being significantly lighter. This lightweight nature makes titanium particularly advantageous in orthopedic implants, where minimizing the burden on the patient's body is crucial.
Biocompatibility: Both materials demonstrate excellent biocompatibility, ensuring minimal risk of adverse reactions within the body. Surgical steel's biocompatibility is attributed to its hypoallergenic nature and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of medical devices. Similarly, titanium's biocompatibility is enhanced by its ability to integrate seamlessly with biological tissues, promoting favorable healing responses and long-term stability in the body.
Corrosion Resistance: Surgical steel's chromium content provides exceptional resistance to corrosion, ensuring its longevity and reliability in medical settings. Titanium, with its stable oxide layer, exhibits remarkable resistance to corrosion in physiological environments, making it an ideal choice for long-term implants.
Aesthetic Appeal: Surgical steel's lustrous and polished surface enhances the visual appeal of medical instruments, contributing to easy cleaning and maintenance. Titanium's natural metallic luster, combined with its lightweight nature, adds an aesthetic advantage, particularly in the fabrication of implants where minimal weight and visual appeal are desired.
Cost and Availability: Surgical steel is widely available and cost-effective, making it a practical choice for a range of medical instruments and devices. Titanium, while more expensive, offers a unique combination of properties that justify its use in critical medical implants and devices, where its benefits outweigh the cost considerations.
In essence, while both materials exhibit remarkable qualities, the choice between surgical steel and titanium depends on the specific requirements of the medical application. Surgical steel's strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness make it a versatile option for various medical instruments and devices. Conversely, titanium's lightweight strength, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance position it as an exceptional choice for long-term implants and devices where reduced weight and biocompatibility are paramount. Understanding the nuanced differences between these materials is essential in selecting the most suitable material for diverse healthcare needs.
Common Uses of Surgical Steel and Titanium
Surgical steel and titanium, with their exceptional properties, find extensive utilization across various medical domains, contributing to advancements in healthcare technology and patient care. Let's explore the common uses of these remarkable materials, shedding light on their diverse applications in the medical field.
Surgical Steel
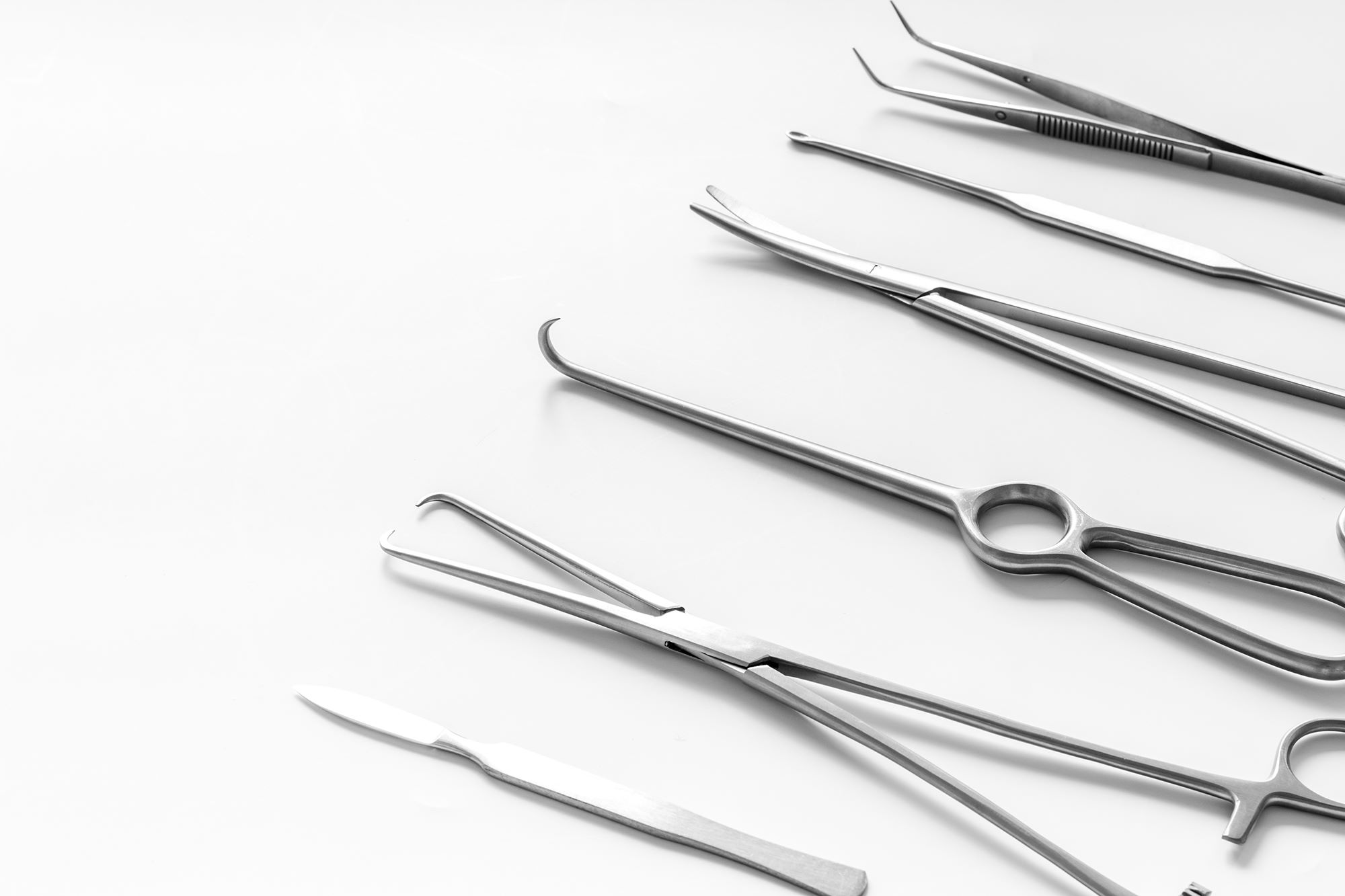
Surgical steel, celebrated for its strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, is widely employed in the manufacturing of surgical instruments such as scalpels, forceps, and scissors. The material's durability and ease of sterilization make it an ideal choice for instruments requiring precision, longevity, and hygienic integrity in surgical procedures. Additionally, surgical steel serves as a primary material for medical implants, including orthopedic plates, screws, and bone fixation devices, where its robustness and biocompatibility are essential for ensuring the stability and healing of fractures and orthopedic interventions. Furthermore, surgical steel's aesthetic appeal and resistance to staining make it a preferred option for the fabrication of dental instruments and equipment, contributing to the maintenance of aseptic conditions in dental practices.
Titanium
Titanium's lightweight strength and exceptional biocompatibility render it invaluable in the realm of medical implants, particularly in orthopedic and dental applications. Orthopedic implants, such as hip prostheses, bone plates, and spinal fixation devices, benefit from titanium's strength and corrosion resistance, providing patients with durable and biocompatible solutions for orthopedic interventions. In the field of dentistry, titanium implants offer a reliable and long-lasting alternative to natural teeth, restoring oral function and aesthetics while integrating seamlessly with the surrounding bone tissue. Moreover, titanium's inertness and resistance to bodily fluids make it an ideal material for the fabrication of surgical tools and equipment, ensuring reliable performance and durability in diverse surgical specialties.
By virtue of their unique properties, both surgical steel and titanium play pivotal roles in the development of medical devices, implants, and instruments, contributing to improved patient outcomes and the overall quality of healthcare delivery. Understanding the diverse applications of these materials underscores their significance in shaping the landscape of modern medicine, where innovation and reliability are paramount in addressing the evolving needs of patients and healthcare professionals.
Read more: The Surprising Truth About Manual Breathing
Advantages and Disadvantages of Surgical Steel and Titanium
Surgical steel and titanium each offer a unique set of advantages and disadvantages, influencing their suitability for specific medical applications. Understanding the distinct attributes of these materials is essential for informed decision-making in healthcare settings.
Advantages of Surgical Steel
1. Corrosion Resistance: Surgical steel's chromium content forms a protective oxide layer, rendering it highly resistant to corrosion in harsh environments, including exposure to bodily fluids and sterilization processes.
2. Biocompatibility: The hypoallergenic nature of surgical steel, coupled with its corrosion resistance, ensures excellent biocompatibility, making it suitable for a wide range of medical devices and implants without triggering adverse reactions in the body.
3. Strength and Durability: Surgical steel exhibits remarkable tensile strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing surgical instruments and medical devices requiring robustness and longevity.
4. Ease of Sterilization: The material's compatibility with various sterilization methods, including autoclaving and chemical sterilants, ensures that medical instruments and implants maintain their hygienic integrity, contributing to infection control and patient safety.
5. Aesthetic Appeal: Surgical steel's lustrous and polished surface not only enhances the visual appeal of medical instruments but also facilitates easy cleaning and maintenance, underscoring its suitability for healthcare environments.
Disadvantages of Surgical Steel
1. Weight: Compared to titanium, surgical steel is denser, which may be a consideration in applications where weight reduction is a critical factor, such as orthopedic implants.
2. Cost: While surgical steel is generally cost-effective, the pricing may vary based on specific grades and compositions, potentially impacting its feasibility in certain medical applications.
Advantages of Titanium
1. Lightweight Strength: Titanium's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio makes it particularly advantageous in orthopedic implants, offering structural integrity without adding excessive weight to the patient's body.
2. Biocompatibility: Titanium's seamless integration with biological tissues minimizes the risk of adverse reactions or implant rejection, promoting favorable healing responses and long-term stability within the body.
3. Corrosion Resistance: The stable oxide layer on titanium's surface confers remarkable resistance to corrosion in physiological environments, ensuring the longevity and reliability of titanium implants.
4. Flexibility and Ductility: Titanium's malleability enables the fabrication of intricate implant designs tailored to the unique anatomical requirements of patients, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of medical interventions.
5. Thermal and Biological Inertness: Titanium's inertness ensures that implants do not react adversely to the body's natural processes, providing assurance of their reliability and safety in clinical settings.
Read more: The Surprising Truth About Liquid Calories
Disadvantages of Titanium
1. Cost: Titanium is generally more expensive than surgical steel, which may influence its utilization in certain medical devices and instruments, particularly in cost-sensitive healthcare settings.
2. Difficulty in Fabrication: The unique properties of titanium, including its high melting point and reactivity with other materials, can pose challenges in the fabrication and machining processes, requiring specialized techniques and expertise.
In summary, both surgical steel and titanium offer a range of advantages and disadvantages, necessitating careful consideration of their properties and cost implications in the selection of materials for diverse healthcare needs. By weighing these factors, healthcare professionals and manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize patient outcomes and the efficacy of medical interventions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of surgical steel and titanium reveals the remarkable properties, diverse applications, and nuanced advantages and disadvantages of these exceptional materials in the realm of healthcare. Both materials, with their unique attributes, have significantly contributed to the advancement of medical technology, enabling the development of innovative medical devices, implants, and instruments that uphold the highest standards of patient care and safety.
Surgical steel, celebrated for its corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, strength, and ease of sterilization, remains a versatile and reliable choice for a wide array of medical instruments, devices, and implants. Its enduring aesthetic appeal and cost-effectiveness further underscore its significance in healthcare settings, where precision, durability, and hygienic integrity are paramount.
On the other hand, titanium, with its lightweight strength, exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and inertness, has revolutionized the landscape of medical implants, particularly in orthopedic and dental applications. The material's ability to integrate seamlessly with biological tissues and provide long-term stability within the body has paved the way for transformative advancements in orthopedic interventions and dental restorations, enhancing the quality of life for countless patients.
The comparison between surgical steel and titanium illuminates the distinctive properties and applications of these materials, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals, researchers, and manufacturers. While surgical steel excels in applications requiring robustness, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, titanium shines in scenarios where lightweight strength, biocompatibility, and long-term implant success are critical considerations.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the enduring relevance of surgical steel and titanium underscores their indispensable roles in shaping the future of medical technology. The ongoing pursuit of innovation and excellence in material science holds the promise of further enhancing the properties and applications of these materials, opening new frontiers for the development of advanced medical solutions that prioritize patient well-being and clinical efficacy.
In essence, the surprising truths about surgical steel and titanium unveil a rich tapestry of possibilities, where the convergence of material science and healthcare innovation continues to elevate the standard of care, ushering in a future where the boundaries of medical technology are defined by resilience, biocompatibility, and the relentless pursuit of improved patient outcomes.










