Home>Health and Wellness>Shocking Discovery: Ticks Found In Human Hair!


Health and Wellness
Shocking Discovery: Ticks Found In Human Hair!
Published: February 12, 2024
Discover the shocking truth about ticks found in human hair and how it impacts health and wellness. Learn how to protect yourself from this surprising health threat.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
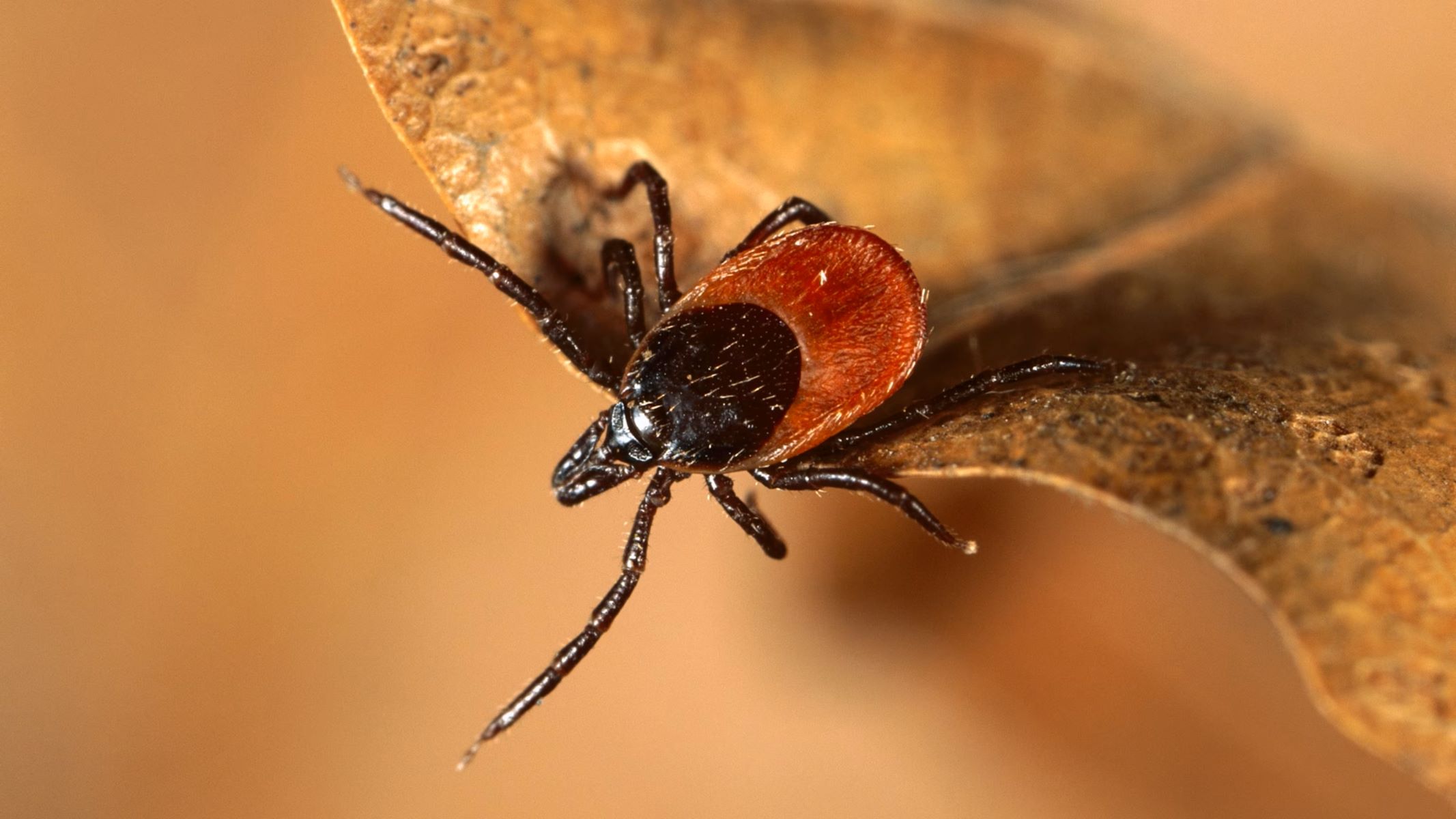
Ticks are tiny, blood-sucking arachnids that have long been associated with lurking in wooded areas and grassy terrains, waiting to latch onto unsuspecting hosts. However, a shocking discovery has recently come to light – ticks have been found in human hair! This unsettling revelation has left many people wondering how these pests end up in the one place they thought was safe from such invaders.
The presence of ticks in human hair poses a significant health concern, as these parasites are known carriers of various diseases, including Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Understanding the biology of ticks, how they find their way into human hair, the potential health risks they pose, and effective preventive measures is crucial in safeguarding our well-being.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate world of ticks, shedding light on their biology, the factors that lead to their presence in human hair, the potential health risks associated with tick infestation, and most importantly, practical strategies to prevent these bloodthirsty pests from taking up residence in our locks. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the truth about ticks and equip ourselves with the knowledge necessary to protect our hair and health from these stealthy invaders.
The Biology of Ticks
Ticks, belonging to the arachnid family, are parasitic organisms that thrive by feeding on the blood of various hosts, including mammals, birds, and reptiles. These ectoparasites have a remarkable ability to adapt to diverse environments, enabling them to survive in a wide range of habitats, from dense forests to urban parks. Understanding the biological features and life cycle of ticks is essential in comprehending their capability to infest human hair and the associated health risks.
Life Cycle
Ticks undergo a complex life cycle consisting of four stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. The life cycle duration varies among species and can range from several months to several years. Ticks require blood meals at each stage to progress to the next phase of their life cycle. This reliance on blood sustains their growth, development, and reproduction.
Feeding Behavior
Ticks are hematophagous, meaning they feed exclusively on blood. They possess specialized mouthparts that enable them to pierce the skin of their host and extract blood. Once attached, ticks engorge themselves with blood, expanding in size as they feed. This blood meal is crucial for the tick's survival and reproduction.
Host Detection
Ticks rely on sensory organs to detect potential hosts. They can perceive stimuli such as body heat, carbon dioxide, and odor, allowing them to locate and attach to a suitable host. This remarkable ability to detect hosts contributes to their ability to infest human hair, as they can sense the presence of a potential blood meal.
Adaptability
Ticks are highly adaptable creatures, capable of surviving in various climates and habitats. Some species thrive in wooded areas, while others inhabit grasslands or urban environments. This adaptability enables ticks to infiltrate human habitats, increasing the likelihood of encountering these parasites in unexpected places, such as human hair.
Understanding the intricate biology of ticks provides valuable insights into their behavior, feeding habits, and adaptability. This knowledge forms the foundation for developing effective strategies to prevent tick infestation and mitigate the associated health risks. By unraveling the biological intricacies of ticks, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge necessary to safeguard against these resilient parasites.
How Ticks End Up in Human Hair
Ticks have a remarkable ability to infiltrate unexpected places, including human hair, due to several factors that contribute to their presence in this seemingly unlikely location. Understanding how ticks end up in human hair is essential in implementing preventive measures to avoid infestation. Here are the primary reasons behind this unsettling phenomenon:
-
Seeking Warmth and Shelter: Ticks are constantly in search of warm and sheltered environments to ensure their survival and reproduction. Human hair provides an ideal refuge for ticks, offering warmth and protection from external threats. When questing for a blood meal, ticks may inadvertently encounter human hair and perceive it as a suitable shelter, leading to their presence in this unexpected location.
-
Host Detection Mechanisms: Ticks possess sensory organs that enable them to detect potential hosts based on stimuli such as body heat, carbon dioxide, and odor. This remarkable ability allows ticks to locate and attach to hosts, including humans. In some instances, ticks may mistake human hair for a potential host, leading to their presence in the hair.
-
Activities in Tick-Infested Areas: Engaging in outdoor activities in tick-infested areas significantly increases the risk of encountering ticks. When individuals venture into wooded or grassy areas where ticks are prevalent, these parasites may attach themselves to clothing or skin and eventually find their way into the hair. Additionally, pets that roam in tick-infested environments can inadvertently bring ticks into the household, increasing the likelihood of tick infestation in human hair.
-
Interaction with Infested Animals: Close interaction with infested animals, such as pets or wildlife, can facilitate the transfer of ticks to humans. When animals carry ticks in their fur, these parasites can easily transfer to human hair during close contact. This scenario underscores the importance of regular tick checks for both humans and pets after spending time in areas where ticks are prevalent.
-
Tick Attachment Behavior: Ticks exhibit a behavior known as questing, where they perch on vegetation or objects and extend their forelegs, waiting to latch onto passing hosts. In outdoor settings, ticks may latch onto clothing, hats, or scarves, and subsequently transfer to human hair. This behavior increases the likelihood of ticks ending up in human hair, especially after outdoor activities in tick-prone areas.
Understanding the mechanisms that lead to ticks ending up in human hair empowers individuals to take proactive measures to minimize the risk of infestation. By being mindful of these factors and implementing preventive strategies, such as thorough tick checks and protective clothing, individuals can reduce the likelihood of encountering ticks in their hair and mitigate the associated health risks.
Health Risks Associated with Tick Infestation in Human Hair
The discovery of ticks in human hair poses significant health risks, as these blood-sucking parasites are known carriers of various diseases. When ticks infest human hair, they present a unique set of health concerns that can have profound implications for individuals affected by this unsettling phenomenon.
-
Disease Transmission: Ticks are notorious vectors of disease, capable of transmitting a range of pathogens to their hosts through their bites. The presence of ticks in human hair increases the risk of disease transmission, as these parasites may remain undetected for extended periods, allowing them to feed and potentially transmit infectious agents. The most notable disease associated with ticks is Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which can lead to a range of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, and joint pain if left untreated. Additionally, ticks can transmit other serious illnesses such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis, and anaplasmosis, posing a substantial threat to the health of individuals with tick infestation in their hair.
-
Skin Irritation and Allergic Reactions: The presence of ticks in human hair can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Tick bites can elicit local inflammatory responses, resulting in redness, itching, and swelling at the site of attachment. Individuals with sensitive skin or allergies may experience heightened reactions to tick bites, exacerbating the discomfort and potentially triggering allergic symptoms. Furthermore, the sensation of ticks crawling in the hair can induce anxiety and distress, impacting the overall well-being of affected individuals.
-
Secondary Infections: Prolonged tick infestation in human hair can increase the risk of secondary infections at the bite sites. When ticks feed on the scalp or other areas of the hair, the skin may become susceptible to bacterial infections, particularly if the affected individual scratches or irritates the bite sites. Secondary infections can exacerbate the initial discomfort caused by tick infestation and may require medical intervention to address the resulting complications.
-
Psychological Impact: Beyond the physical health risks, the presence of ticks in human hair can have a profound psychological impact on affected individuals. The distress and anxiety stemming from the awareness of tick infestation in a highly personal area, such as the hair, can lead to heightened stress and emotional strain. This psychological burden can significantly affect the mental well-being of individuals, highlighting the multifaceted impact of tick infestation on overall health.
In light of these health risks, addressing tick infestation in human hair is essential to safeguard the well-being of individuals and prevent the potential consequences associated with tick-borne diseases, skin irritation, secondary infections, and psychological distress. Implementing effective preventive measures and promptly addressing tick infestation is paramount in mitigating these health risks and promoting overall health and well-being.
Preventing Tick Infestation in Human Hair
Preventing tick infestation in human hair is paramount in safeguarding against the potential health risks associated with tick bites and disease transmission. By implementing proactive measures and adopting vigilant practices, individuals can minimize the risk of encountering ticks in their hair and protect their well-being. Here are effective strategies to prevent tick infestation in human hair:
-
Protective Clothing: When venturing into tick-prone areas, wearing protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes can act as a physical barrier, reducing the likelihood of ticks coming into contact with the skin and hair. Tucking pants into socks and wearing a hat can further minimize the risk of ticks latching onto hair and clothing.
-
Tick Repellents: Applying EPA-approved tick repellents containing DEET or permethrin to exposed skin and clothing can effectively deter ticks. Additionally, treating outdoor gear and clothing with permethrin can provide long-lasting protection against tick exposure.
-
Regular Tick Checks: Conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities is crucial in detecting and removing ticks before they have the opportunity to infest the hair. Paying close attention to the scalp, hairline, and behind the ears is essential, as ticks may seek refuge in these areas.
-
Pet Care: Regularly inspecting pets for ticks and implementing preventive measures such as tick collars or topical treatments can reduce the likelihood of ticks being brought into the household and potentially infesting human hair.
-
Landscaping and Habitat Modification: Maintaining well-groomed yards, minimizing brush and leaf litter, and creating barriers such as gravel or wood chips between lawns and wooded areas can help reduce tick habitats near residential properties, lowering the risk of tick encounters.
-
Showering and Clothing Change: Promptly showering and changing into clean clothing after spending time in tick-prone environments can help remove any unattached ticks and prevent them from reaching the hair.
-
Professional Pest Control: Seeking professional pest control services to address tick infestations in outdoor areas surrounding the home can effectively reduce the tick population, lowering the risk of encountering ticks in the hair.
-
Educational Awareness: Raising awareness about tick prevention and proper tick removal techniques within communities and educational institutions can empower individuals to take proactive measures to prevent tick infestation in human hair and minimize the associated health risks.
By integrating these preventive strategies into daily routines and outdoor activities, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of tick infestation in their hair, mitigating the potential health risks and promoting a safer and healthier living environment. Vigilance, education, and proactive measures form the cornerstone of effective tick prevention, ensuring that individuals can enjoy outdoor activities while minimizing the threat of tick-borne illnesses and infestations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the discovery of ticks in human hair has unveiled a concerning reality that underscores the importance of understanding tick biology, infestation mechanisms, associated health risks, and preventive strategies. Ticks, with their remarkable adaptability and host-seeking abilities, have demonstrated their capability to infiltrate unexpected locations, including human hair. This revelation has prompted a critical reevaluation of personal protection measures and environmental management practices to mitigate the risks posed by these resilient parasites.
The health risks associated with tick infestation in human hair are multifaceted, encompassing the transmission of tick-borne diseases, skin irritation, potential secondary infections, and psychological distress. The presence of ticks in the hair not only poses immediate health concerns but also elicits anxiety and emotional strain, highlighting the broader impact on overall well-being. Addressing these risks necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates personal protective measures, environmental management, and community awareness initiatives to effectively combat tick infestation.
Effective prevention of tick infestation in human hair hinges on proactive measures, including the use of protective clothing, tick repellents, regular tick checks, pet care, habitat modification, and educational awareness. By embracing these strategies, individuals can reduce the likelihood of encountering ticks in their hair and minimize the associated health risks. Furthermore, fostering a culture of vigilance and knowledge-sharing within communities and educational institutions can empower individuals to take proactive steps in safeguarding against tick infestation, fostering a collective effort to promote public health and well-being.
As we navigate the intricate landscape of tick prevention and management, it is imperative to recognize the interconnected nature of human and environmental health. By adopting a holistic approach that encompasses personal protection, environmental stewardship, and community engagement, we can create a resilient defense against tick infestation, fostering a safer and healthier living environment for all.
In essence, the revelation of ticks in human hair serves as a poignant reminder of the need for ongoing vigilance, education, and collaborative action to mitigate the risks posed by these resilient parasites. By leveraging our understanding of tick biology and infestation dynamics, we can cultivate a culture of prevention and resilience, fortifying our defenses against the potential health impacts of tick infestation in human hair. Through collective efforts and informed practices, we can navigate this challenge with resilience and determination, fostering a future where the threat of tick infestation in human hair is minimized, and the well-being of individuals is safeguarded.