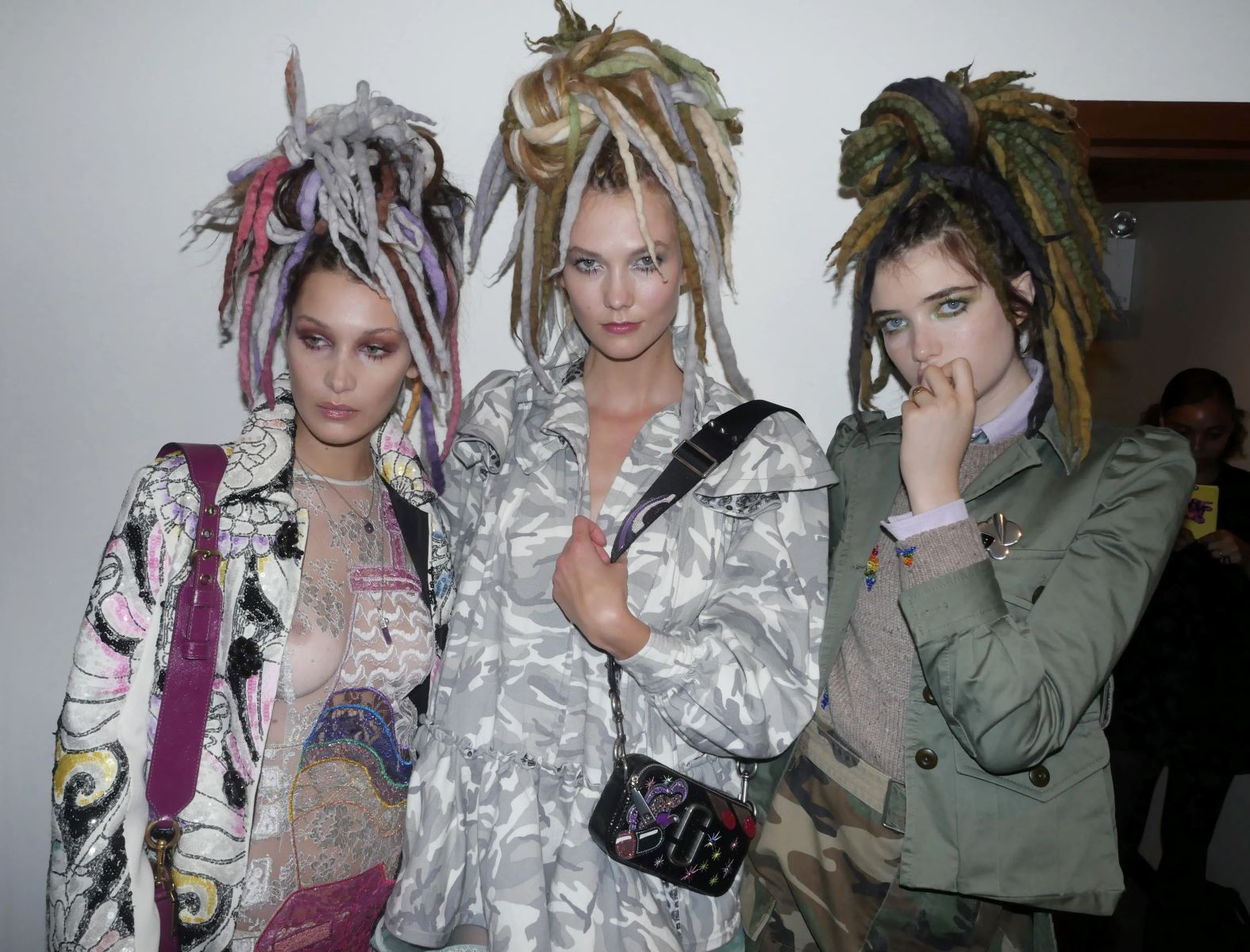
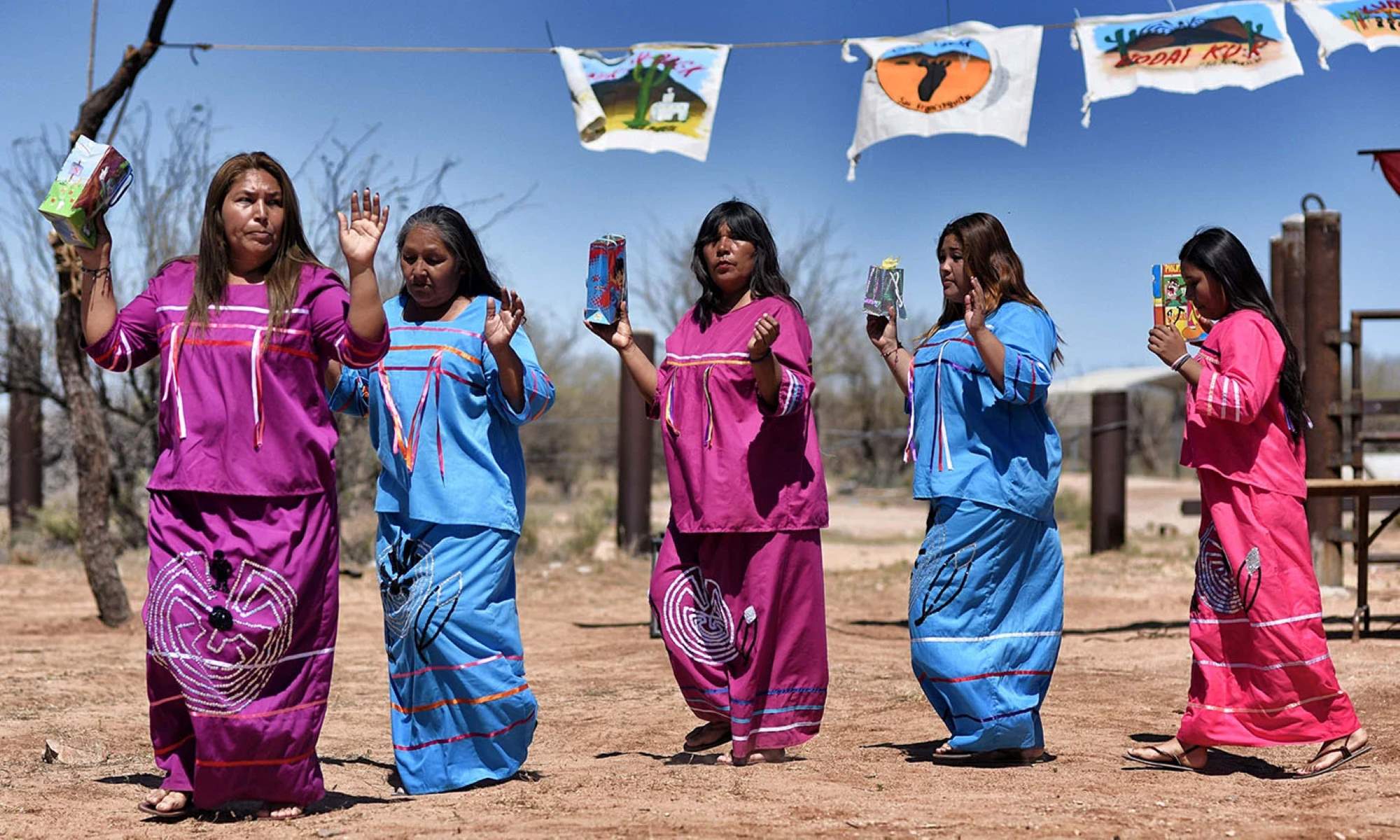
Home>Arts and Culture>The Cultural Appropriation Debate: Exploring The Significance Of Braiding In White People’s Hair Across European Cultures
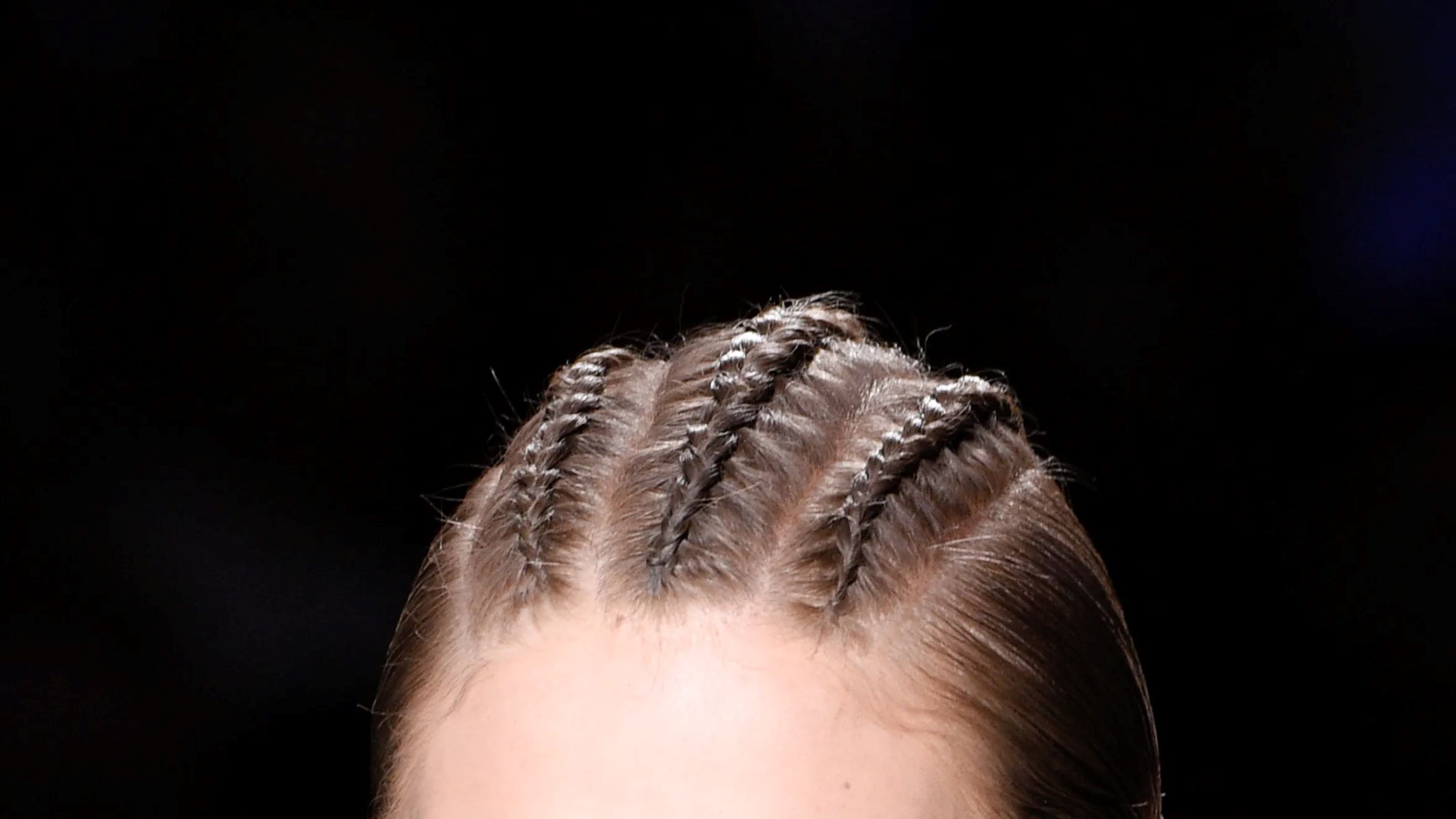


Arts and Culture
The Cultural Appropriation Debate: Exploring The Significance Of Braiding In White People’s Hair Across European Cultures
Published: February 18, 2024
Explore the cultural appropriation debate surrounding braiding in white people's hair across European cultures. Delve into the significance of this practice in the context of arts and culture.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cultural appropriation is a topic that has sparked heated discussions and debates in recent years, particularly in the context of braiding in white people's hair across European cultures. This practice has raised important questions about the intersection of fashion, identity, and cultural significance. As we delve into this complex and nuanced subject, it's essential to approach it with sensitivity and an open mind.
Braiding holds deep cultural significance in many European traditions, and its portrayal in mainstream media and fashion has ignited conversations about the appropriation of these cultural practices. This debate has prompted individuals to critically examine the historical, social, and ethical implications of adopting braiding styles from European cultures.
In this article, we will explore the multifaceted layers of the cultural appropriation debate as it pertains to the significance of braiding in white people's hair across various European cultures. By delving into the historical roots, social impact, and contemporary discourse surrounding this practice, we aim to shed light on the complexities and sensitivities associated with cultural exchange and representation.
As we navigate through this exploration, it's important to approach the subject with empathy and a willingness to understand diverse perspectives. By engaging in this dialogue, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural richness and diversity that braiding represents within European traditions. Let's embark on this journey with an open heart and a commitment to fostering understanding and respect for the cultural heritage woven into the art of braiding.
Defining Cultural Appropriation
Cultural appropriation is a concept that encompasses the adoption, use, or exploitation of elements from one culture by individuals or groups belonging to another culture, often without proper understanding or respect for the original cultural significance. This phenomenon is deeply rooted in power dynamics, historical context, and the commodification of cultural practices.
At its core, cultural appropriation involves the borrowing or imitation of cultural elements, such as symbols, rituals, fashion, music, or art, from marginalized or oppressed communities by those in positions of privilege or power. This appropriation often occurs without acknowledgment, permission, or understanding of the cultural context from which these elements originate.
One of the key aspects of cultural appropriation is the imbalance of power and the potential harm it can inflict on the source culture. It can lead to the trivialization, distortion, or misrepresentation of sacred or deeply meaningful cultural practices, perpetuating harmful stereotypes and erasing the historical and social significance of these traditions.
Moreover, cultural appropriation often occurs within a framework of unequal power dynamics, where dominant cultures selectively adopt elements of marginalized cultures for aesthetic or commercial purposes, while the originators of these cultural practices continue to face discrimination and marginalization.
It's important to note that cultural exchange and appreciation, when approached with respect, understanding, and mutual consent, differ from cultural appropriation. Genuine cultural exchange involves a reciprocal and respectful sharing of traditions, where individuals from different cultures engage in a meaningful dialogue and collaboration, honoring the origins and significance of the practices being exchanged.
In the context of braiding in white people's hair across European cultures, the discussion of cultural appropriation becomes particularly relevant. The act of adopting braiding styles without acknowledging their cultural roots and significance raises important questions about the ethical and social implications of this practice.
As we continue to explore the complexities of cultural appropriation and its impact on European cultures, it's crucial to approach this subject with empathy, open-mindedness, and a commitment to understanding the diverse perspectives and experiences surrounding this contentious issue.
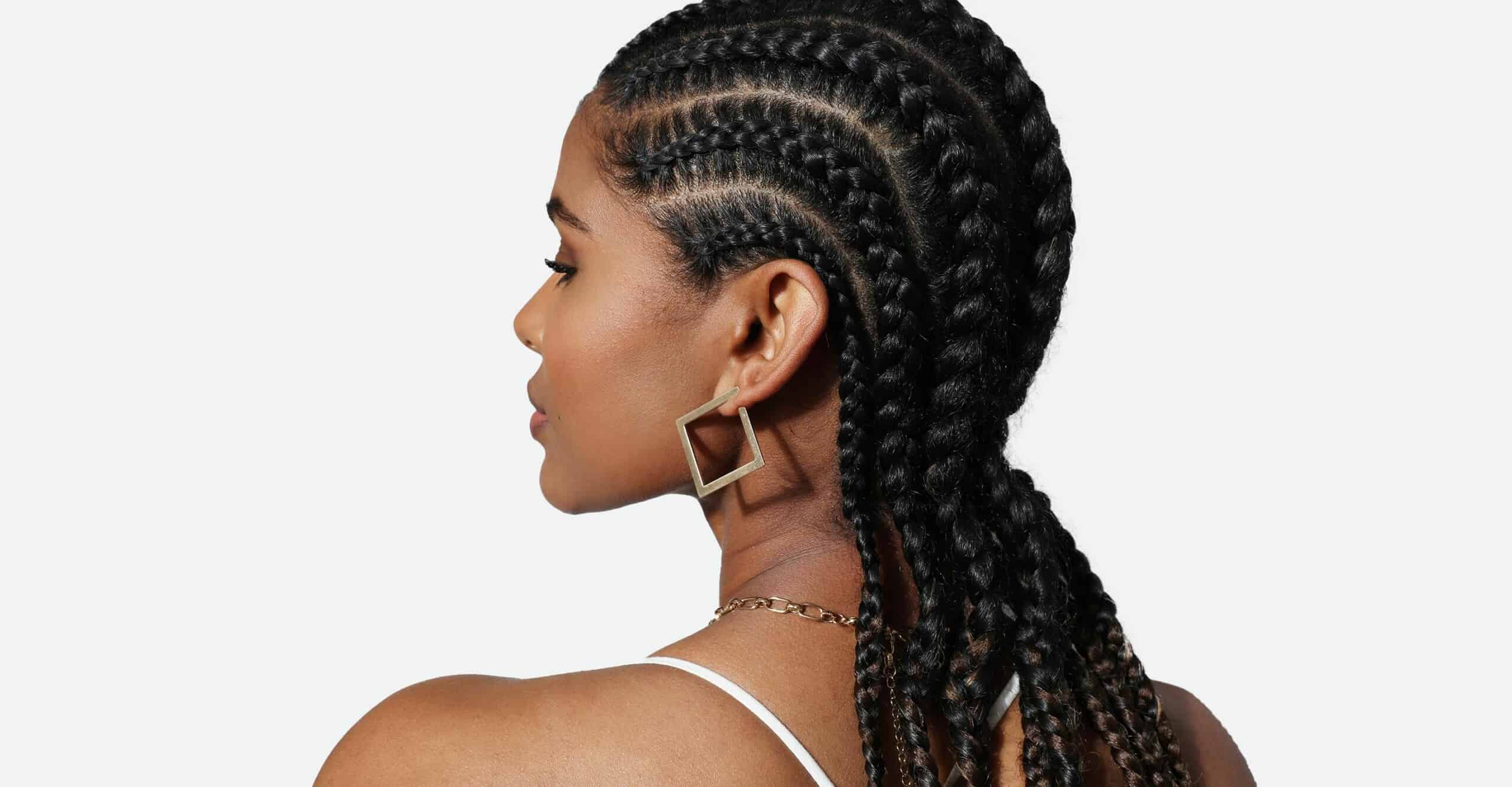
The Significance of Braiding in European Cultures
Braiding holds profound cultural significance across various European traditions, serving as a tangible expression of heritage, identity, and community. In many European cultures, braiding has been intertwined with rituals, symbolism, and social customs for centuries, embodying a rich tapestry of cultural heritage.
Symbolism and Tradition
Braiding in European cultures often carries symbolic meanings that reflect the values and beliefs of specific communities. For example, in Scandinavian cultures, intricate braided hairstyles were emblematic of familial ties and kinship, with distinct braiding patterns signifying familial lineage and social status. Similarly, in Celtic traditions, braiding symbolized interconnectedness and the eternal cycle of life, reflecting the interconnected nature of existence.
Rituals and Rites of Passage
Braiding has been an integral part of various rituals and rites of passage in European cultures. In many communities, the act of braiding holds deep significance during significant life events, such as weddings, coming-of-age ceremonies, and religious celebrations. The intricate braiding techniques passed down through generations serve as a means of preserving cultural heritage and transmitting ancestral wisdom.
Cultural Identity and Heritage
Braiding serves as a visual representation of cultural identity and heritage within European communities. The distinct braiding styles and patterns are often reflective of regional traditions, historical influences, and indigenous craftsmanship. Through braiding, individuals honor their cultural roots and celebrate the diversity of European heritage, fostering a sense of pride and connection to their ancestral lineage.
Artistic Expression and Creativity
Within European cultures, braiding is celebrated as a form of artistic expression and creativity. The intricate weaving of hair into elaborate patterns and designs showcases the skill and artistry of braiders, who often draw inspiration from nature, folklore, and traditional motifs. Braiding serves as a canvas for storytelling and artistic innovation, allowing individuals to express their unique creativity while upholding cultural traditions.
Community and Solidarity
Braiding has historically served as a communal activity, bringing individuals together to bond, share stories, and strengthen social ties. In many European cultures, the act of braiding fosters a sense of solidarity and unity within communities, creating opportunities for intergenerational exchange and the preservation of cultural knowledge.
In essence, the significance of braiding in European cultures transcends mere aesthetics, encompassing a profound tapestry of symbolism, tradition, identity, and artistic expression. As we navigate the complexities of the cultural appropriation debate, it is crucial to recognize and honor the deep-rooted significance of braiding within European heritage.
The History of Braiding in White People's Hair
The history of braiding in white people's hair is a multifaceted tapestry that intertwines with diverse cultural narratives, social customs, and historical influences. Across various European cultures, braiding has been an enduring tradition, with its roots tracing back to ancient civilizations and indigenous practices.
In ancient Greece, intricate braided hairstyles adorned the heads of both men and women, serving as a symbol of status, elegance, and artistic expression. The art of braiding, known as "plaiting," was intricately woven into the fabric of Greek society, reflecting the aesthetic sensibilities and cultural values of the time. These elaborate braiding techniques were often accompanied by adornments such as ribbons, beads, and gold filigree, further accentuating the intricate beauty of the braided styles.
Similarly, in medieval Europe, braiding held significant cultural and social connotations. Noblewomen adorned their hair with elaborate braided designs, symbolizing their lineage, marital status, and societal standing. Braiding was intricately woven into courtly rituals and ceremonies, serving as a visual marker of aristocratic identity and refinement.
During the Renaissance period, braiding continued to evolve as a prominent feature of European fashion and cultural expression. Intricate braided hairstyles adorned with jewels, pearls, and ornate accessories became emblematic of wealth, sophistication, and artistic flair. The artistry of braiding extended beyond mere adornment, reflecting the fusion of artistic creativity and cultural symbolism.
In more recent history, the 1960s and 1970s witnessed a resurgence of interest in braiding among white communities, influenced by the cultural movements of the time. Inspired by the bohemian ethos and the embrace of diverse cultural influences, individuals sought to incorporate braiding into their personal style as a form of self-expression and solidarity with global cultural traditions.
The history of braiding in white people's hair reflects a rich tapestry of artistic evolution, cultural exchange, and social symbolism. As we navigate the complexities of the cultural appropriation debate, it is essential to acknowledge the historical legacy of braiding within European cultures and the enduring impact of these traditions on contemporary expressions of beauty and identity.
The Debate Surrounding Cultural Appropriation and Braiding
The debate surrounding cultural appropriation and braiding in white people's hair across European cultures has ignited impassioned discussions within academic, social, and artistic circles. At the heart of this debate lies a complex interplay of historical, social, and ethical considerations, prompting individuals to critically examine the implications of adopting braiding styles from European traditions.
Proponents of cultural appropriation argue that the act of incorporating braiding into mainstream fashion and beauty practices represents a celebration of cultural diversity and a form of artistic expression. They emphasize the fluidity of cultural exchange, asserting that the sharing of traditions fosters cross-cultural understanding and appreciation. From this perspective, the adoption of braiding in white people's hair is viewed as a homage to the intricate artistry and cultural heritage embedded within European braiding traditions.
Conversely, critics of cultural appropriation raise concerns about the potential erasure of the historical and social significance of braiding within European cultures. They highlight the power dynamics at play, emphasizing that the commodification of braiding by dominant cultures may perpetuate harmful stereotypes and dilute the authentic cultural narratives associated with these traditions. Furthermore, critics underscore the importance of acknowledging the origins and cultural context of braiding, advocating for respectful engagement with the traditions of marginalized communities.
The debate also delves into questions of agency, representation, and ethical responsibility. Advocates for cultural appropriation argue that individuals should have the freedom to express themselves through diverse cultural influences, transcending rigid boundaries of cultural ownership. They emphasize the transformative nature of cultural exchange, where the fusion of diverse influences leads to innovative and inclusive forms of self-expression.
On the other hand, opponents of cultural appropriation stress the need for ethical engagement with cultural practices, emphasizing the importance of informed consent, respect for cultural origins, and the amplification of marginalized voices. They advocate for a nuanced approach to cultural exchange, one that acknowledges the historical legacies of colonialism, imperialism, and cultural exploitation, and seeks to redress power imbalances through equitable representation and collaboration.
As the debate surrounding cultural appropriation and braiding continues to unfold, it underscores the complexities and sensitivities inherent in the intersection of fashion, identity, and cultural heritage. By engaging in this dialogue with empathy and critical reflection, individuals can contribute to a more nuanced understanding of the ethical and social implications of adopting braiding styles from European cultures.
The ongoing discourse surrounding cultural appropriation and braiding serves as a catalyst for introspection, fostering a deeper appreciation for the diverse narratives and lived experiences embedded within the art of braiding. It is through this introspective lens that individuals can navigate the complexities of cultural exchange with respect, empathy, and a commitment to honoring the cultural heritage woven into the intricate art of braiding.
Exploring the Impact of Cultural Appropriation on European Cultures
The impact of cultural appropriation on European cultures is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that reverberates across historical, social, and artistic landscapes. As the debate surrounding the adoption of braiding in white people's hair from European traditions unfolds, it is essential to critically examine the implications of cultural appropriation on the integrity and representation of European cultural heritage.
One significant impact of cultural appropriation is the potential distortion and misrepresentation of European braiding traditions. When braiding styles are adopted without an understanding of their cultural significance, there is a risk of diluting the authentic narratives and symbolism embedded within these traditions. This can lead to the erasure of the historical and social contexts that have shaped European braiding practices, perpetuating a superficial and commodified portrayal of these cultural expressions.
Furthermore, cultural appropriation can contribute to the perpetuation of harmful stereotypes and the marginalization of European cultural narratives. By selectively adopting elements of European traditions for aesthetic or commercial purposes, without acknowledging their origins and significance, there is a risk of reinforcing reductive and exoticized portrayals of European cultures. This can overshadow the diverse and nuanced heritage of braiding within European communities, perpetuating a skewed and incomplete representation of these traditions.
Moreover, the impact of cultural appropriation extends to questions of power dynamics and ethical responsibility. The commodification of braiding by dominant cultures may exacerbate existing inequalities and historical imbalances, further marginalizing the voices and agency of European communities. This imbalance of power underscores the need for a more equitable and respectful approach to engaging with European cultural practices, one that amplifies diverse narratives and fosters inclusive representations.
On a broader societal level, cultural appropriation can influence perceptions of beauty, identity, and cultural belonging within European communities. The portrayal of braiding in mainstream media and fashion as a trend divorced from its cultural roots can shape perceptions of what is deemed fashionable or desirable, potentially overshadowing the authentic significance of braiding within European cultural contexts. This can impact the self-esteem and cultural pride of individuals within European communities, as their traditions are commodified and detached from their original cultural meanings.
In essence, the impact of cultural appropriation on European cultures underscores the need for a nuanced and empathetic approach to engaging with diverse cultural traditions. By critically examining the implications of adopting braiding styles from European heritage, individuals can contribute to a more inclusive and respectful representation of these cultural practices, fostering a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of European cultural heritage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate surrounding the cultural appropriation of braiding in white people's hair across European cultures encapsulates a complex interplay of historical, social, and ethical considerations. The significance of braiding within European traditions is deeply rooted in symbolism, tradition, and artistic expression, reflecting a profound tapestry of cultural heritage. However, the adoption of braiding styles from European cultures has sparked impassioned discussions about the ethical implications of cultural exchange and representation.
As we navigate this discourse, it is crucial to approach the subject with empathy, open-mindedness, and a commitment to understanding diverse perspectives. The historical legacy of braiding within European cultures underscores the enduring impact of these traditions on contemporary expressions of beauty and identity. It is imperative to recognize and honor the deep-rooted significance of braiding, while critically examining the implications of cultural appropriation on the integrity and representation of European cultural heritage.
The ongoing discourse surrounding cultural appropriation and braiding serves as a catalyst for introspection, fostering a deeper appreciation for the diverse narratives and lived experiences embedded within the art of braiding. By engaging in this dialogue with respect and critical reflection, individuals can contribute to a more nuanced understanding of the ethical and social implications of adopting braiding styles from European cultures.
Ultimately, the exploration of cultural appropriation and braiding in white people's hair across European cultures invites us to navigate the complexities of cultural exchange with empathy, respect, and a commitment to honoring the cultural heritage woven into the intricate art of braiding. It is through this introspective lens that individuals can contribute to a more inclusive and respectful representation of these cultural practices, fostering a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of European cultural heritage.