Home>Science>Surprising Truth: Birds And Other Predators Fall Victim To Mosquito Bites Too!
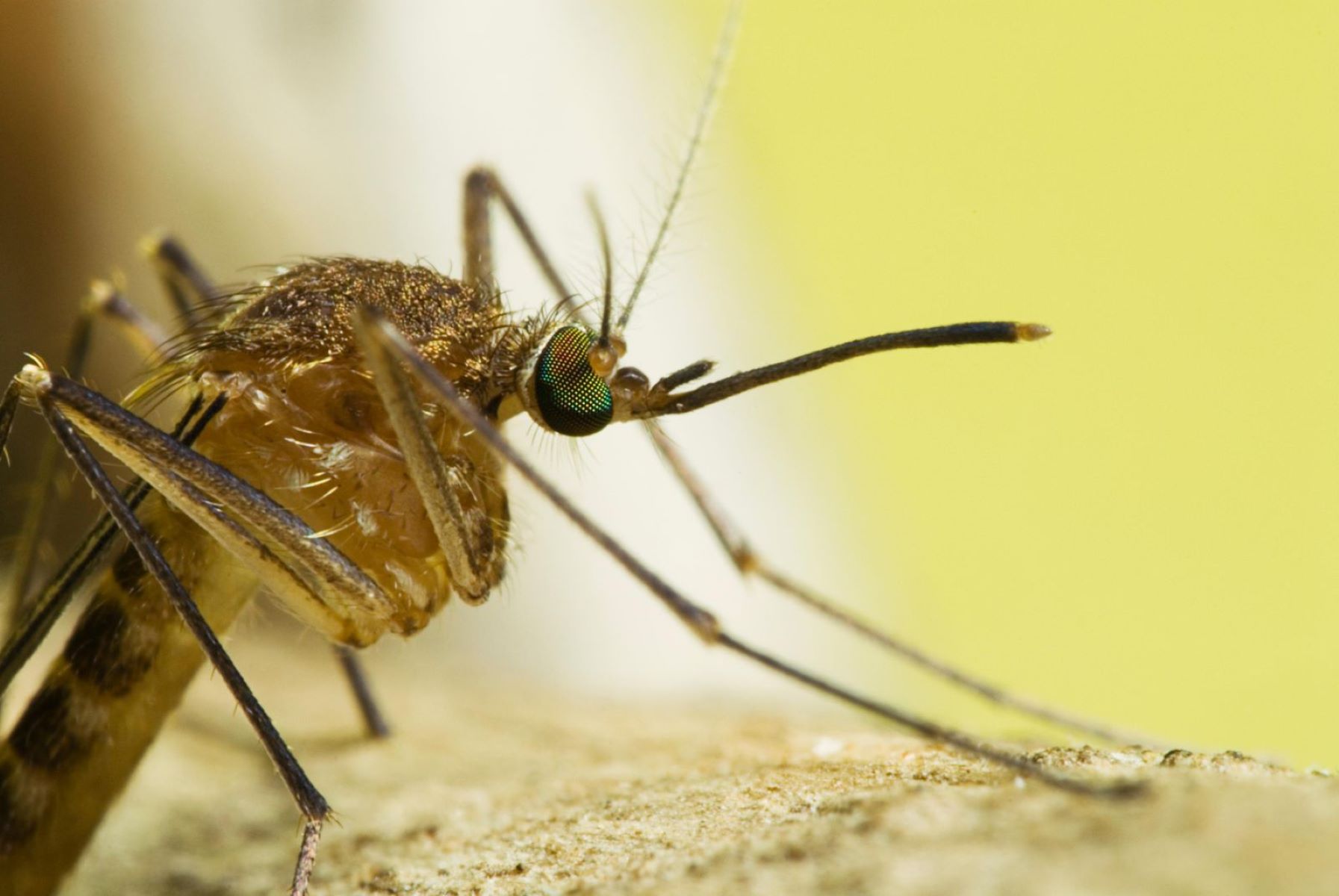


Science
Surprising Truth: Birds And Other Predators Fall Victim To Mosquito Bites Too!
Published: February 6, 2024
Discover the surprising truth about birds and other predators falling victim to mosquito bites. Explore the science behind this unexpected phenomenon and its implications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Mosquitoes, the tiny, buzzing insects that often evoke annoyance and frustration, are widely known for their itchy and irritating bites. However, what may come as a surprise to many is that these blood-sucking pests do not discriminate when it comes to their choice of victims. While humans are commonly aware of the discomfort and potential health risks associated with mosquito bites, it is intriguing to discover that birds and other predators also fall prey to these relentless insects.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of mosquito bites and explore the surprising truth that birds and other predators are also targets of these pesky insects. By understanding the impact of mosquito bites on various creatures, we can gain a deeper insight into the intricate dynamics of ecosystems and the interconnectedness of diverse species.
As we embark on this exploration, it becomes evident that the influence of mosquitoes extends far beyond human experiences, reaching into the realms of wildlife and ecological balance. By shedding light on this lesser-known aspect of mosquito behavior, we can uncover the intricate web of interactions that shape the natural world. Join us as we unravel the surprising truth about mosquito bites and their unexpected victims, shedding new light on the intricate relationships within our ecosystems.
Understanding Mosquito Bites
Mosquito bites, often characterized by red, itchy welts, are the result of a complex biological process. Female mosquitoes, specifically those of the Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex species, require blood to nourish their eggs, making them the primary culprits behind these aggravating bites. When a mosquito lands on the skin and pierces it with its slender mouthparts, it injects saliva containing anticoagulants and proteins to prevent the blood from clotting. This process triggers a localized immune response, leading to the familiar itching and swelling associated with mosquito bites.
The discomfort experienced after a mosquito bite is primarily due to the body's reaction to the foreign substances introduced by the mosquito's saliva. Histamines, a type of immune system chemical, are released in response to the mosquito's saliva, causing the blood vessels to dilate and the surrounding tissue to become inflamed. This immune response is the body's way of defending against potential pathogens carried by the mosquito, but it also leads to the characteristic itching and redness at the bite site.
Interestingly, mosquitoes are attracted to their victims by a combination of factors, including body heat, carbon dioxide, and certain odors emitted by the human body. These factors, along with visual cues, guide the mosquitoes to their targets, making some individuals more prone to mosquito bites than others.
Moreover, the prevalence of mosquito-borne diseases, such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus, underscores the significant impact of these insects on human health. Beyond the immediate discomfort of their bites, mosquitoes pose a considerable threat as vectors for deadly diseases, particularly in regions where these illnesses are endemic.
Understanding the intricacies of mosquito bites is crucial in developing effective strategies for mitigating their impact on human and animal populations. By unraveling the mechanisms behind these bites, researchers and public health officials can work towards innovative solutions to reduce mosquito-borne diseases and alleviate the nuisance caused by these relentless insects.
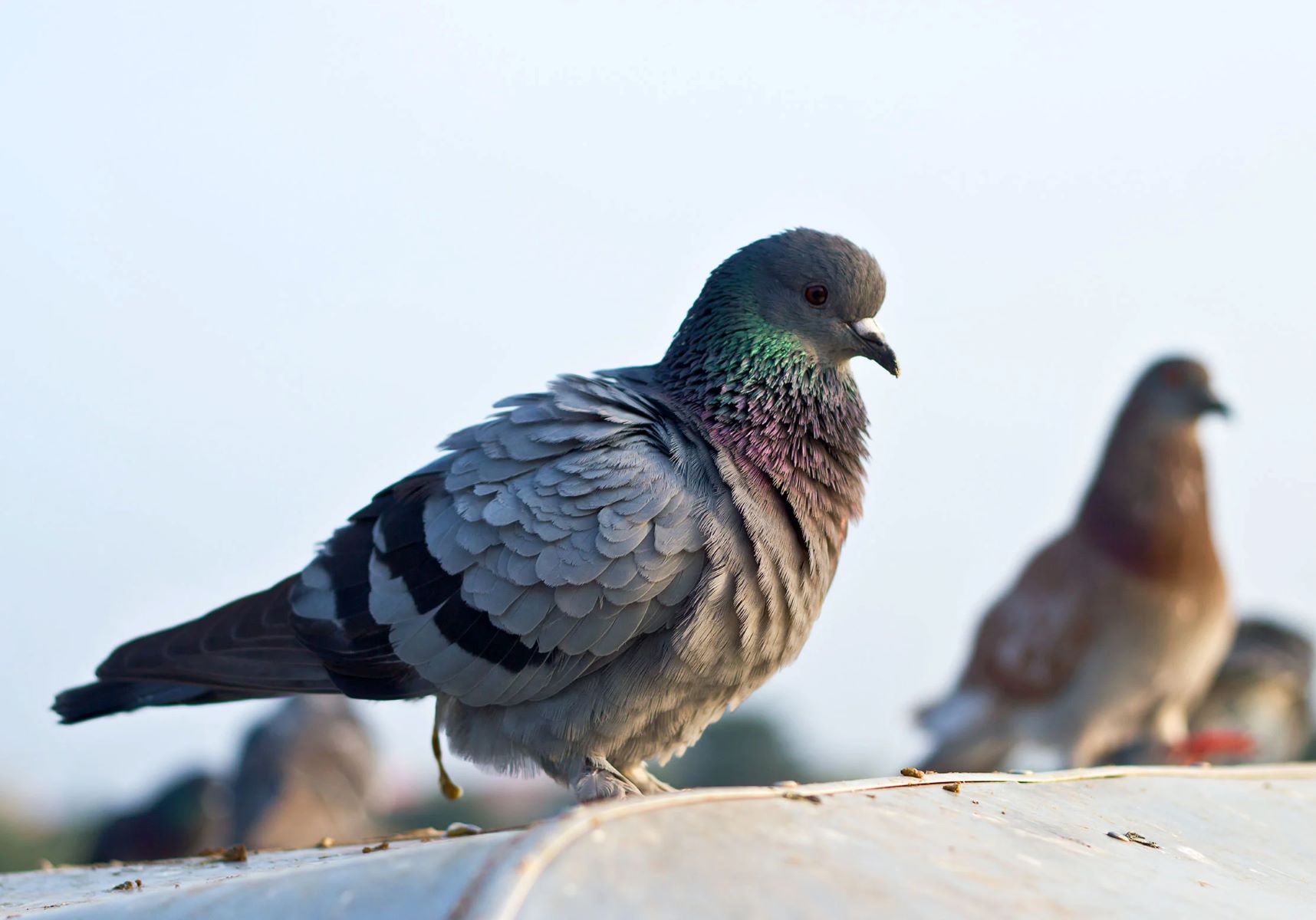
Birds: Surprising Victims of Mosquito Bites
Birds, with their graceful flight and melodic songs, are revered for their captivating presence in the natural world. However, beneath their majestic exterior, these avian creatures face an unexpected adversary: the relentless mosquito. While it may seem improbable that birds, equipped with feathers and agile flight, could fall victim to mosquito bites, the reality unveils a surprising truth.
Mosquitoes, driven by their quest for blood meals to nourish their eggs, target a diverse range of hosts, including birds. These insects exhibit a remarkable ability to locate their avian targets, drawn by the heat and carbon dioxide emitted by birds, along with visual cues and specific odors. As birds roost or forage in their natural habitats, they become susceptible to the persistent advances of mosquitoes, leading to bites that can disrupt their daily activities and overall well-being.
The impact of mosquito bites on birds extends beyond mere annoyance, as these encounters can have significant repercussions. The incessant itching and irritation resulting from mosquito bites can cause distress to birds, affecting their feeding patterns, grooming behaviors, and overall physiological equilibrium. In severe cases, excessive biting by mosquitoes can lead to stress and discomfort, impacting the health and vitality of avian populations.
Furthermore, the potential transmission of mosquito-borne diseases poses a substantial threat to birds. While some bird species have developed natural defenses against certain diseases, others may be vulnerable to infections transmitted by mosquitoes. The spread of avian malaria, West Nile virus, and other mosquito-borne illnesses can pose serious challenges to the health and survival of bird populations, highlighting the far-reaching implications of mosquito bites in the avian world.
The intricate relationship between mosquitoes and birds underscores the interconnectedness of ecosystems. Birds, as integral components of diverse habitats, contribute to the balance and resilience of ecosystems, playing crucial roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and insect control. By recognizing the vulnerability of birds to mosquito bites, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate interactions within natural environments and the profound impact of seemingly minor disturbances.
In light of these revelations, it becomes evident that the impact of mosquito bites extends beyond human experiences, permeating into the lives of avian inhabitants. By acknowledging birds as surprising victims of mosquito bites, we unveil a lesser-known aspect of the complex web of interactions in the natural world, emphasizing the need for comprehensive strategies to safeguard the well-being of diverse species within our ecosystems.
Other Predators: Unexpected Targets of Mosquito Bites
In addition to birds, a myriad of other predators find themselves unexpectedly entangled in the web of mosquito bites. From mammals to reptiles, and even amphibians, these diverse creatures face the persistent nuisance and potential health risks posed by mosquitoes.
Mammalian predators, such as foxes, raccoons, and even domestic pets, are not immune to the relentless pursuit of mosquitoes. These animals, with their fur or hair providing limited protection against mosquito bites, often experience the discomfort and irritation inflicted by these persistent insects. The bites can disrupt their activities, leading to restlessness and potential stress, particularly in cases of repeated exposure to mosquito-infested environments.
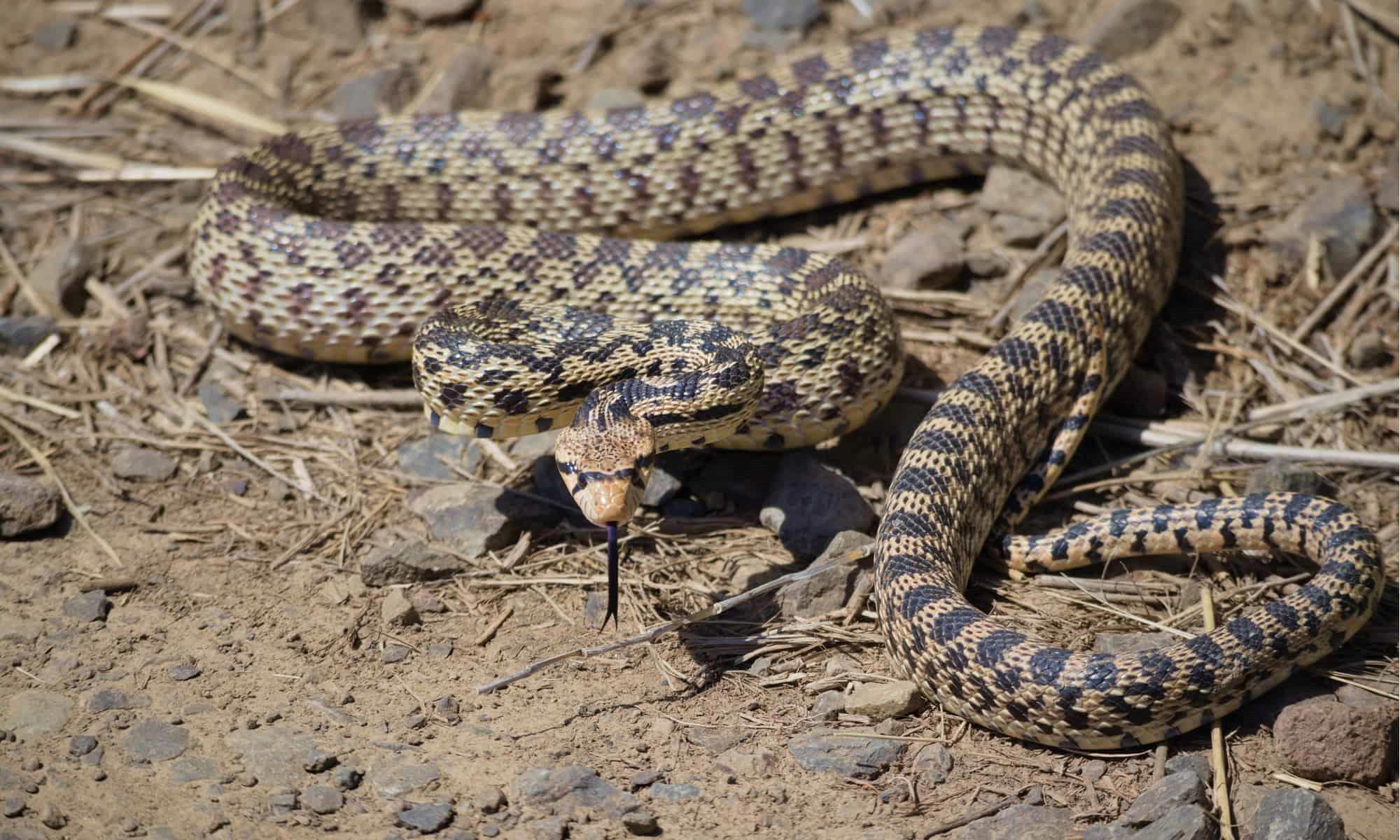
Reptiles, including snakes and lizards, also fall prey to the probing bites of mosquitoes. Despite their scaly exteriors, these cold-blooded predators are susceptible to the relentless advances of mosquitoes, which can disrupt their basking and foraging behaviors. The potential transmission of mosquito-borne diseases further amplifies the impact on reptilian predators, posing additional threats to their well-being and survival.
Amphibians, known for their permeable skin and semi-aquatic lifestyles, face unique challenges when confronted with mosquito bites. Frogs, toads, and other amphibious predators are vulnerable to the irritating bites of mosquitoes, which can interfere with their vital activities, such as feeding and breeding. The susceptibility of amphibians to mosquito-borne diseases adds another layer of complexity to the impact of these bites on their populations, underscoring the far-reaching consequences for these vital members of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
The unexpected targeting of these diverse predators by mosquitoes sheds light on the pervasive nature of mosquito bites across various animal species. As integral components of ecological communities, these predators play crucial roles in regulating prey populations, shaping food webs, and contributing to the overall balance of ecosystems. The disruption caused by mosquito bites can reverberate through these intricate networks, affecting the health and dynamics of predator-prey interactions and the stability of natural habitats.
By recognizing the unexpected targets of mosquito bites, we gain a deeper understanding of the intricate relationships within ecosystems and the interconnectedness of diverse species. This insight underscores the need for comprehensive approaches to mitigate the impact of mosquito bites on a wide range of predators, safeguarding the resilience and vitality of ecosystems as a whole.
Impact on Ecosystems
The impact of mosquito bites extends far beyond individual discomfort, reaching into the intricate fabric of ecosystems. As mosquitoes target a diverse array of hosts, including birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians, the repercussions of their relentless pursuit reverberate through the interconnected web of life.
Mosquitoes, as vectors of disease, pose a significant threat to the health and stability of ecosystems. The transmission of mosquito-borne illnesses, such as West Nile virus, avian malaria, and various encephalitis viruses, can have profound effects on wildlife populations. Birds, in particular, are susceptible to these diseases, with outbreaks leading to declines in avian populations and disruptions in the ecological balance. The loss of key bird species can cascade through ecosystems, impacting insect control, seed dispersal, and pollination, thereby influencing the overall structure and function of natural habitats.
Furthermore, the stress and discomfort inflicted by mosquito bites on predators, such as mammals, reptiles, and amphibians, can disrupt their behaviors and physiological well-being. Restless movements, altered feeding patterns, and compromised immune responses are among the consequences of persistent mosquito bites, affecting the ability of predators to regulate prey populations and maintain ecological equilibrium. This disruption can reverberate through food webs, influencing the abundance and distribution of species within ecosystems.
In aquatic environments, the impact of mosquito bites on amphibians can be particularly pronounced. Frogs, toads, and other amphibious predators, with their permeable skin, face heightened vulnerability to mosquito-borne diseases and the physical irritation caused by bites. The resulting stress and compromised health can affect their reproductive success, population dynamics, and roles in nutrient cycling, ultimately shaping the resilience of aquatic ecosystems.
Moreover, the influence of mosquito bites on wildlife intersects with human activities and land use. As human-altered landscapes encroach upon natural habitats, the interactions between mosquitoes and wildlife are further complicated. Fragmentation of habitats, altered water dynamics, and the introduction of non-native species can influence the distribution and abundance of mosquitoes and their wildlife hosts, potentially exacerbating the impact on ecosystems.
By recognizing the multifaceted impact of mosquito bites on ecosystems, from disease transmission to disruptions in predator-prey dynamics, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships that underpin the resilience and functioning of natural environments. Comprehensive strategies for mitigating the impact of mosquito bites on wildlife, coupled with efforts to conserve diverse habitats and minimize human-wildlife conflicts, are essential for maintaining the integrity and biodiversity of ecosystems.
Read more: Snail Bites: The Shocking Truth Revealed!
Conclusion
The intricate world of mosquito bites transcends the familiar realm of human experiences, encompassing a surprising array of victims, including birds and other predators. As we unravel the unexpected impact of mosquito bites on diverse wildlife, a deeper understanding emerges of the interconnectedness and fragility of ecosystems.
The revelation that birds, with their aerial prowess and captivating presence, are susceptible to the relentless advances of mosquitoes underscores the pervasive nature of these blood-seeking insects. The disruption caused by mosquito bites can affect the vital activities and overall well-being of avian populations, highlighting the need for comprehensive approaches to safeguard the health and resilience of these iconic creatures.
Moreover, the unexpected targeting of mammals, reptiles, and amphibians by mosquitoes sheds light on the far-reaching consequences of these bites across various animal species. The disruption of predator-prey dynamics, the potential transmission of mosquito-borne diseases, and the stress inflicted on diverse wildlife emphasize the profound implications of mosquito bites on the intricate web of life.
The impact of mosquito bites extends beyond individual discomfort, permeating into the fabric of ecosystems. From disease transmission to the disruption of ecological interactions, the repercussions of mosquito bites reverberate through natural habitats, shaping the balance and resilience of diverse ecosystems.
As we confront the surprising truth that birds and other predators fall victim to mosquito bites, a call to action emerges. It becomes imperative to develop holistic strategies that encompass wildlife conservation, disease management, and habitat preservation. By safeguarding the well-being of diverse species and the integrity of natural ecosystems, we can mitigate the far-reaching impact of mosquito bites and nurture the intricate relationships that sustain the rich tapestry of life on our planet.
In this journey of discovery, the surprising truth about mosquito bites serves as a poignant reminder of the delicate balance that underpins the natural world. By embracing a harmonious coexistence with the diverse creatures that share our planet, we can aspire to cultivate a future where the pervasive influence of mosquito bites does not overshadow the resilience and vitality of ecosystems.