Education
How To Become A Lineman
Modified: April 1, 2024
Learn about the education and training required to become a lineman and start a rewarding career in the electrical industry. Discover the steps to becoming a skilled professional in this essential field.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Becoming a lineman is a career path that offers a unique blend of physical challenges, technical skills, and a sense of duty to the community. Linemen play a crucial role in ensuring that electricity is safely and reliably delivered to homes, businesses, and public facilities. This profession demands a strong commitment to safety, a willingness to work in various weather conditions, and the ability to troubleshoot complex electrical issues.
Aspiring linemen are drawn to this profession for various reasons. Some are enticed by the opportunity to work outdoors and embrace the physical demands of the job, while others are driven by the desire to contribute to the essential infrastructure that powers modern society. Regardless of the motivation, pursuing a career as a lineman requires dedication, specialized training, and a deep understanding of electrical systems.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the multifaceted journey of becoming a lineman. From understanding the role and responsibilities to the educational requirements, necessary skills, and pathways to employment, this article will provide valuable insights for individuals considering this rewarding career. Whether you are a recent high school graduate exploring vocational options or someone seeking a career change, the information presented here will serve as a roadmap to help you navigate the steps toward becoming a proficient and respected lineman.
Embarking on the path to becoming a lineman is not just about acquiring technical expertise; it is also about embracing a way of life that demands resilience, adaptability, and a commitment to continuous learning. As we delve into the intricacies of this profession, you will gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role that linemen play in powering our communities and ensuring the reliability of electrical infrastructure. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and insight needed to embark on this fulfilling and impactful career journey.
Read more: How To Become A Nascar Driver
Understanding the Role of a Lineman
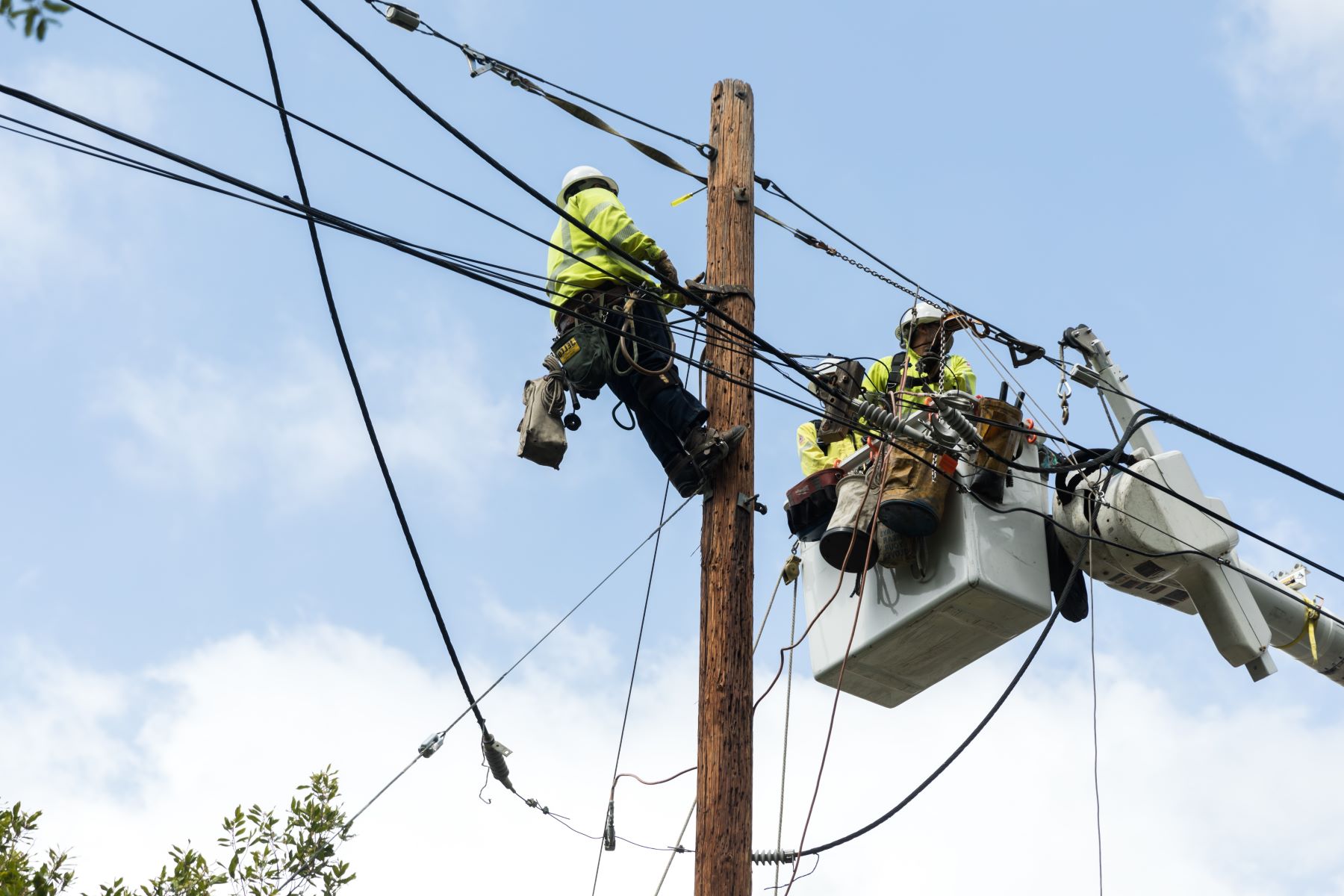
Becoming a lineman entails taking on a multifaceted role that is integral to the functioning of electrical systems. Linemen are responsible for the installation, maintenance, and repair of power lines, ensuring that electricity is transmitted safely and efficiently to homes, businesses, and public facilities. This profession demands a high level of technical expertise, physical agility, and a steadfast commitment to safety protocols.
One of the primary responsibilities of a lineman is to construct and maintain overhead and underground electrical power transmission and distribution lines. This involves working with a variety of equipment, such as bucket trucks, line trucks, and specialized tools, to install and repair power lines at varying heights and in diverse environments. Additionally, linemen are tasked with troubleshooting electrical issues, identifying faults in the system, and implementing effective solutions to restore power in the event of outages or disruptions.
The role of a lineman extends beyond the technical aspects of electrical work. Linemen often collaborate closely with engineers, project managers, and other professionals to plan and execute complex electrical projects. They must adhere to stringent safety standards and regulations, utilizing their expertise to mitigate potential hazards and ensure the reliability of electrical infrastructure.
Furthermore, linemen are frequently required to work in challenging conditions, including extreme weather and hazardous environments. Their dedication to maintaining power supply during adverse conditions, such as storms or natural disasters, underscores the critical nature of their role in upholding community safety and well-being.
In essence, the role of a lineman is characterized by a combination of technical proficiency, physical dexterity, and a deep sense of responsibility. By embracing these diverse aspects of the profession, linemen contribute significantly to the functionality and resilience of electrical systems, playing a pivotal role in sustaining the modern way of life.
Aspiring linemen must recognize the dynamic nature of this role, which demands adaptability, problem-solving skills, and a steadfast commitment to upholding the integrity of electrical infrastructure. Understanding the multifaceted responsibilities of a lineman is a crucial first step in embarking on this challenging yet rewarding career path.
Education and Training Requirements
Becoming a proficient lineman requires a combination of formal education, specialized training, and hands-on experience. While a college degree is not mandatory for entry into this field, acquiring the necessary knowledge and skills through targeted educational programs is essential. Aspiring linemen often begin their journey by enrolling in vocational or technical schools that offer comprehensive training in electrical systems, safety protocols, and industry-specific practices.
Vocational programs tailored to the field of electrical power distribution provide students with a solid foundation in electrical theory, circuitry, and the principles of power transmission. These programs typically incorporate practical training, allowing students to gain hands-on experience in working with electrical equipment, conducting installations, and troubleshooting common electrical issues. Additionally, coursework in safety procedures, first aid, and the proper use of personal protective equipment is integral to preparing future linemen for the rigors of the profession.
In addition to formal education, aspiring linemen often pursue apprenticeships or on-the-job training opportunities to further hone their skills and gain practical experience in the field. These hands-on learning experiences provide invaluable insights into the day-to-day responsibilities of a lineman, offering exposure to real-world scenarios and the opportunity to work alongside seasoned professionals.
Furthermore, specialized training in the operation of bucket trucks, line trucks, and other essential equipment is a fundamental aspect of a lineman's education. Proficiency in safely maneuvering and utilizing this equipment is critical to performing tasks at varying heights and in diverse environments, ensuring the efficient installation and maintenance of power lines.
It is important to note that the field of electrical power distribution is constantly evolving, with advancements in technology and industry standards shaping the skill set required of linemen. As such, ongoing professional development and training are essential for staying abreast of industry developments and enhancing proficiency in new methodologies and equipment.
Ultimately, the education and training requirements for aspiring linemen encompass a blend of formal instruction, practical experience, and a commitment to continuous learning. By immersing themselves in comprehensive educational programs and seeking opportunities for hands-on training, individuals can lay a solid foundation for a successful career as a skilled and knowledgeable lineman.
Physical and Mental Skills Needed
Becoming a proficient lineman necessitates a unique combination of physical prowess, mental acuity, and unwavering resilience. The demanding nature of the profession requires individuals to possess a diverse set of skills that enable them to navigate the challenges inherent in working with electrical power distribution systems.
Physical Agility and Endurance
The role of a lineman demands exceptional physical agility and endurance. Working at varying heights, often in challenging weather conditions, requires a high level of physical fitness and dexterity. Linemen must be adept at maneuvering on poles, towers, and other elevated structures while carrying out installations, maintenance, and repairs. Additionally, the ability to lift and maneuver heavy equipment and materials is essential to the successful execution of tasks in the field.
Read more: How To Become Valedictorian
Mental Fortitude and Focus
The mental demands of being a lineman are equally significant. The ability to remain focused and composed in high-pressure situations is crucial, especially when troubleshooting complex electrical issues or responding to power outages. Linemen must possess strong problem-solving skills, enabling them to analyze electrical systems, identify faults, and implement effective solutions in a timely manner. Moreover, the capacity to adhere to stringent safety protocols and regulations while working in hazardous environments underscores the importance of mental fortitude in this profession.
Adaptability and Resilience
The dynamic nature of the role requires linemen to be adaptable and resilient in the face of adversity. They must be prepared to work in diverse environments, including extreme weather conditions and challenging terrains, without compromising on safety or efficiency. The ability to adapt to unexpected circumstances and rapidly changing work conditions is a hallmark of a skilled lineman, reflecting their commitment to upholding the reliability of electrical infrastructure.
Teamwork and Communication
Effective teamwork and clear communication are essential skills for linemen, as they often collaborate with colleagues and other professionals to execute projects and resolve electrical issues. The capacity to work harmoniously in a team, communicate clearly and concisely, and coordinate tasks efficiently contributes to the overall safety and success of electrical projects.
In essence, the physical and mental skills needed to excel as a lineman encompass a blend of physical agility, mental acuity, adaptability, and effective communication. By cultivating these skills, aspiring linemen can position themselves for a successful and fulfilling career in the vital field of electrical power distribution.
Gaining Experience and Apprenticeships
Gaining practical experience and participating in apprenticeship programs are pivotal steps in the journey toward becoming a proficient lineman. While formal education provides a foundational understanding of electrical systems and industry practices, hands-on experience in real-world settings is invaluable for honing skills, gaining industry insights, and cultivating a deep appreciation for the intricacies of the profession.
Apprenticeships serve as a bridge between classroom learning and on-the-job proficiency, offering aspiring linemen the opportunity to work alongside seasoned professionals and acquire firsthand knowledge of the day-to-day responsibilities in the field. These programs typically combine structured classroom instruction with practical training, allowing apprentices to apply theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios while under the guidance of experienced mentors.
Participating in an apprenticeship program provides numerous benefits, including the opportunity to develop a comprehensive understanding of electrical power distribution, refine technical skills, and gain exposure to diverse work environments. Apprentices learn to navigate the complexities of electrical systems, troubleshoot issues, and execute installations and maintenance tasks with precision and efficiency.
Moreover, apprenticeships foster a culture of continuous learning and mentorship, enabling aspiring linemen to glean valuable insights from seasoned professionals who impart their expertise, best practices, and industry-specific knowledge. This collaborative learning environment not only accelerates skill development but also instills a strong sense of camaraderie and professional growth within the aspiring lineman community.
Furthermore, apprenticeships often serve as a pathway to securing employment within reputable electrical utility companies or contracting firms. The hands-on experience gained during the apprenticeship period enhances the marketability of aspiring linemen, positioning them as competent and skilled professionals ready to contribute to the vital work of maintaining and enhancing electrical infrastructure.
In essence, gaining experience through apprenticeships is a pivotal phase in the journey toward becoming a proficient lineman. The combination of practical training, mentorship, and exposure to real-world challenges equips aspiring linemen with the skills, knowledge, and confidence needed to excel in this dynamic and essential profession. By embracing apprenticeship opportunities, individuals can lay a solid foundation for a successful and impactful career as a respected and proficient lineman.
Read more: How To Become Swat
Obtaining Necessary Certifications and Licenses
Obtaining the necessary certifications and licenses is a critical step in the journey of becoming a proficient lineman. These credentials not only validate the expertise and competence of individuals in the field of electrical power distribution but also serve as essential prerequisites for securing employment and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Aspiring linemen must navigate a structured process to obtain the relevant certifications and licenses, demonstrating their commitment to upholding safety standards, adhering to industry best practices, and contributing to the reliability of electrical infrastructure.
One of the primary certifications sought by aspiring linemen is the Journeyman Lineman Certification. This credential signifies a high level of proficiency in the installation, maintenance, and repair of electrical power distribution systems. To attain this certification, individuals typically undergo a comprehensive assessment of their technical skills, safety knowledge, and understanding of industry regulations. Achieving Journeyman Lineman Certification not only validates the expertise of individuals but also enhances their marketability and credibility within the field.
In addition to the Journeyman Lineman Certification, linemen often pursue specialized certifications in areas such as pole climbing, bucket truck operation, and first aid/CPR. These certifications underscore the commitment of linemen to maintaining a high standard of safety and proficiency in executing essential tasks. They demonstrate a dedication to honing specific skills and staying abreast of industry best practices, further solidifying the expertise and reliability of linemen in the eyes of employers and clients.
Furthermore, obtaining the requisite licenses is integral to legally practicing as a lineman. Licensing requirements vary by state and locality, necessitating a thorough understanding of the specific mandates governing the profession in a given area. Linemen must diligently fulfill the licensing criteria, which may include completing formal training programs, accruing a specified number of work hours, and passing rigorous examinations that assess their knowledge of electrical systems, safety protocols, and industry regulations.
The process of obtaining necessary certifications and licenses demands a steadfast commitment to continuous learning, adherence to safety standards, and a dedication to professional excellence. By acquiring these credentials, aspiring linemen not only validate their expertise but also demonstrate their unwavering commitment to upholding the integrity and reliability of electrical infrastructure. These certifications and licenses serve as a testament to the proficiency and dedication of linemen, positioning them as indispensable contributors to the essential work of powering our communities.
Finding Employment Opportunities
Securing employment as a lineman involves navigating a dynamic landscape of opportunities within the electrical utility industry, contracting firms, and municipal or government entities. The demand for skilled linemen remains robust, driven by the ongoing need to maintain, expand, and modernize electrical infrastructure to meet the evolving energy needs of communities. Aspiring linemen can explore various avenues to find employment opportunities and embark on a fulfilling career in the field of electrical power distribution.
One of the primary channels for finding employment as a lineman is through electrical utility companies. These entities are responsible for the transmission and distribution of electricity to homes, businesses, and public facilities, making them key employers of skilled linemen. Electrical utility companies often offer diverse roles, including positions for apprentice linemen, journeyman linemen, and lead lineman, providing opportunities for individuals at different stages of their career journey.
Contracting firms specializing in electrical construction and maintenance also serve as prominent sources of employment for linemen. These firms undertake a wide range of projects, including the installation of power lines, maintenance of electrical infrastructure, and response to power outages. As such, they actively seek skilled linemen to contribute to their projects, offering opportunities for individuals to apply their expertise in diverse settings and projects.
Municipal and government entities, including public works departments and municipal utilities, frequently seek linemen to support the maintenance and expansion of local electrical systems. These entities play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and safety of electrical infrastructure within communities, presenting opportunities for linemen to contribute to essential public service initiatives.
Moreover, networking within the industry and actively engaging with professional organizations can open doors to employment opportunities for aspiring linemen. Attending industry events, participating in career fairs, and connecting with established professionals can provide valuable insights and potential leads for securing employment within the field of electrical power distribution.
Additionally, leveraging online job platforms, industry-specific websites, and professional networking platforms can facilitate the exploration of available job openings and the submission of applications for lineman positions. These platforms serve as valuable resources for identifying employment opportunities, connecting with potential employers, and showcasing the skills and qualifications of aspiring linemen.
In essence, finding employment opportunities as a lineman involves proactive engagement with industry stakeholders, leveraging professional networks, and exploring diverse avenues within the electrical utility sector, contracting firms, and municipal entities. By actively pursuing these opportunities, aspiring linemen can embark on a rewarding career path characterized by meaningful contributions to the reliability and functionality of electrical infrastructure.
Advancing in the Field
Advancing in the field of electrical power distribution offers linemen the opportunity to elevate their expertise, take on leadership roles, and contribute to the advancement of industry practices. As linemen gain experience and proficiency in their craft, they may seek avenues for professional growth and career advancement that align with their aspirations and long-term goals.
One of the primary pathways for advancing in the field is pursuing advanced certifications and specialized training. Beyond the foundational certifications required for entry into the profession, linemen can pursue advanced credentials that demonstrate mastery of specific skills or specialized areas within electrical power distribution. These certifications, such as Advanced Journeyman Lineman or specialized training in advanced electrical systems, equip linemen with the expertise needed to take on more complex projects and leadership roles within their organizations.
Moreover, aspiring linemen can explore opportunities for career advancement within electrical utility companies, contracting firms, and municipal entities. As they demonstrate proficiency, leadership potential, and a commitment to excellence, linemen may be considered for supervisory or managerial positions, where they can oversee teams, manage projects, and contribute to strategic initiatives aimed at enhancing electrical infrastructure.
Another avenue for advancement involves staying abreast of industry trends, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Linemen can engage in continuous learning and professional development to expand their knowledge base, adapt to evolving industry standards, and leverage emerging technologies to optimize electrical systems. By embracing a proactive approach to staying informed and updated, linemen position themselves as valuable assets within the field, capable of driving innovation and efficiency.
Furthermore, mentorship and knowledge sharing play a pivotal role in advancing in the field. Experienced linemen can take on mentorship roles, guiding and nurturing the next generation of aspiring linemen. By imparting their wisdom, best practices, and industry insights, seasoned professionals contribute to the collective growth and advancement of the field, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and knowledge exchange.
In essence, advancing in the field of electrical power distribution encompasses a multifaceted journey of skill enhancement, leadership development, and industry engagement. By pursuing advanced certifications, seeking career progression opportunities, staying informed about industry developments, and embracing mentorship, linemen can chart a course toward professional advancement and make enduring contributions to the vitality and reliability of electrical infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey to becoming a proficient lineman is characterized by a blend of technical expertise, physical agility, and unwavering commitment to safety and reliability. Aspiring linemen embark on a path that demands continuous learning, hands-on experience, and a deep understanding of electrical power distribution systems. From the foundational education and training requirements to the acquisition of necessary certifications and licenses, the pursuit of a career as a lineman is marked by dedication, resilience, and a profound sense of responsibility.
The role of a lineman extends beyond the technical aspects of electrical work; it embodies a commitment to upholding the integrity of electrical infrastructure, ensuring the uninterrupted flow of power to communities, and responding to challenges with agility and expertise. The physical and mental skills required of linemen underscore the multifaceted nature of the profession, emphasizing the need for adaptability, teamwork, and a steadfast focus on safety and efficiency.
Gaining practical experience through apprenticeships and actively seeking employment opportunities within electrical utility companies, contracting firms, and municipal entities are pivotal steps in the journey of aspiring linemen. These experiences not only hone technical skills but also foster a deep appreciation for the vital role that linemen play in powering our communities and upholding the reliability of electrical infrastructure.
As linemen progress in their careers, the pursuit of advanced certifications, career advancement opportunities, and a commitment to continuous learning positions them as indispensable contributors to the field of electrical power distribution. By embracing mentorship, staying informed about industry trends, and leveraging emerging technologies, linemen can make enduring contributions to the vitality and efficiency of electrical infrastructure.
In essence, the journey of becoming a lineman is a testament to the dedication, expertise, and unwavering commitment of individuals who play a pivotal role in sustaining the modern way of life. The resilience, adaptability, and technical proficiency demonstrated by linemen underscore their indispensable contribution to the reliability and functionality of electrical systems, making this career path both challenging and deeply rewarding. Aspiring linemen who embark on this journey are poised to make a lasting impact on the essential infrastructure that powers our communities, ensuring the safety, resilience, and continuity of electrical power distribution for generations to come.