Home>Automotive>The Mystery Of Sealed Transmissions: Unveiling Fluid Secrets

Automotive
The Mystery Of Sealed Transmissions: Unveiling Fluid Secrets
Published: January 4, 2024
Uncover the hidden secrets of automotive transmissions with our comprehensive guide to sealed transmission fluids. Learn how to maintain and protect your vehicle's transmission for long-lasting performance. Discover the mysteries of sealed transmissions today!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Regretless.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The transmission system in a vehicle is akin to the heart in a human body, responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Among the various types of transmissions, the sealed transmission has garnered attention due to its unique design and the mystery surrounding its fluid maintenance. This article aims to unravel the enigma of sealed transmissions, shedding light on the significance of transmission fluid and its role in ensuring the smooth operation of these intricate systems.
Sealed transmissions, also known as sealed automatic transmissions, have gained prominence in modern vehicles, particularly those equipped with continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). Unlike traditional transmissions, which allow for fluid level checks and top-ups, sealed transmissions are designed to be maintenance-free, with no dipstick for fluid inspection. This distinctive attribute has sparked curiosity and raised questions about the inner workings of these sealed systems.
As we delve into the world of sealed transmissions, it becomes evident that understanding the role of transmission fluid is pivotal. Transmission fluid serves as a multifaceted agent, facilitating gear shifting, cooling, lubrication, and safeguarding against wear and corrosion within the transmission. The composition and properties of transmission fluid play a crucial role in preserving the integrity and functionality of the transmission system, making it an indispensable component in sealed transmissions.
The significance of transmission fluid extends beyond its basic function, encompassing a diverse range of formulations tailored to meet the specific requirements of various transmission types. From conventional automatic transmission fluid (ATF) to specialized fluids for CVTs and dual-clutch transmissions (DCTs), the automotive industry has witnessed a proliferation of transmission fluid variants, each tailored to optimize performance and longevity.
Moreover, the incorporation of additives further amplifies the complexity of transmission fluid, with specific formulations targeting friction reduction, thermal stability, and anti-wear properties. These additives are meticulously blended to enhance the fluid's performance under diverse operating conditions, underscoring the intricate chemistry involved in formulating transmission fluids for sealed transmissions.
Intriguingly, the absence of a dipstick in sealed transmissions poses a challenge in identifying potential fluid-related issues. Recognizing the subtle signs of transmission fluid degradation or malfunction becomes imperative for preserving the longevity of sealed transmissions, prompting a closer examination of the telltale indicators that warrant attention.
The journey to demystify sealed transmissions and unveil the secrets of transmission fluid promises to unravel the intricacies of these enigmatic systems, offering insights into the maintenance and care essential for ensuring their seamless operation. As we embark on this exploration, the veil shrouding sealed transmissions will be lifted, revealing the hidden nuances and essential considerations that underpin their functionality and longevity.
Understanding Sealed Transmissions
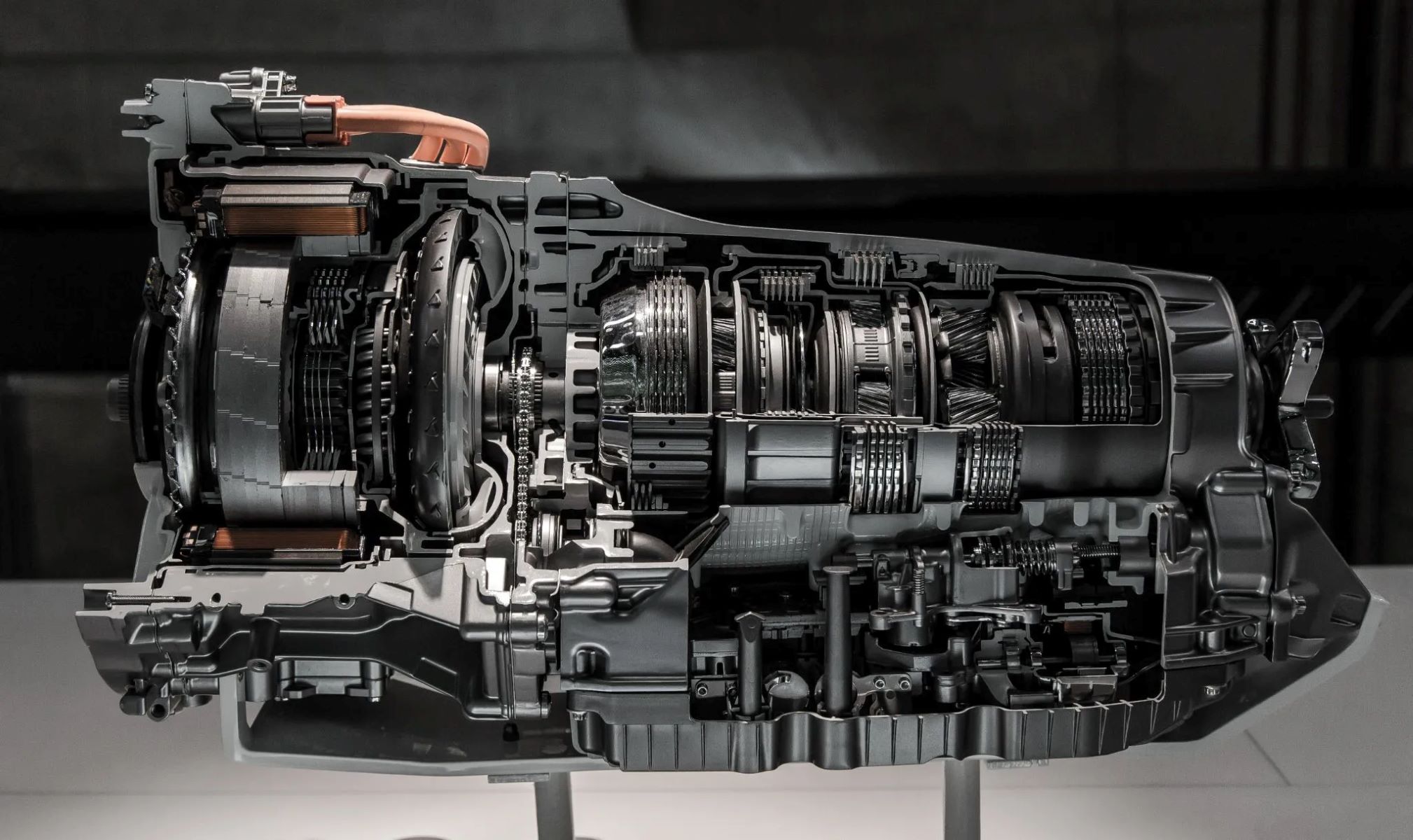
Sealed transmissions, particularly prevalent in modern vehicles featuring continuously variable transmissions (CVTs), represent a departure from traditional transmission systems. Unlike their conventional counterparts, sealed transmissions are designed to operate without the need for regular fluid level checks or top-ups. This unique characteristic stems from their sealed construction, which eliminates the presence of a dipstick for fluid inspection. The absence of a dipstick has sparked intrigue and curiosity, prompting a deeper exploration of the inner workings and maintenance requirements of these intricate systems.
At the core of sealed transmissions lies a complex assembly of components, including hydraulic systems, clutches, and gears, all meticulously engineered to facilitate seamless power transfer from the engine to the wheels. The absence of a dipstick for fluid inspection necessitates a reliance on specialized procedures and equipment for servicing and maintaining sealed transmissions. This distinctive feature has positioned sealed transmissions as a focal point of interest and scrutiny within the realm of automotive engineering and maintenance.
Understanding the operational principles of sealed transmissions is pivotal for appreciating their design intricacies and the implications of their maintenance-free configuration. Sealed transmissions are engineered to encapsulate the transmission fluid within the system, ensuring optimal lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic pressure regulation without the need for external intervention. This self-contained design underscores the meticulous engineering and precision that underpin the functionality of sealed transmissions, emphasizing their role as a cornerstone of modern automotive technology.
Furthermore, the absence of a dipstick for fluid inspection in sealed transmissions necessitates a proactive approach to maintenance, with specialized tools and procedures employed to assess and address potential fluid-related issues. This distinctive maintenance paradigm underscores the evolution of automotive engineering, highlighting the shift towards advanced, sealed systems that demand specialized expertise and equipment for servicing and upkeep.
In essence, comprehending the intricacies of sealed transmissions unveils the innovative engineering and design considerations that have redefined the landscape of transmission systems in modern vehicles. The unique characteristics and maintenance requirements of sealed transmissions underscore the evolution of automotive technology, encapsulating a fusion of precision engineering, advanced materials, and innovative design philosophies that have culminated in the emergence of these enigmatic, maintenance-free transmission systems.
Importance of Transmission Fluid
Transmission fluid serves as a vital component within the intricate ecosystem of a vehicle's transmission system. Its significance transcends mere lubrication, extending to encompass a myriad of critical functions that are indispensable for the seamless operation and longevity of the transmission.
Lubrication and Cooling
At the core of its importance lies the role of transmission fluid in lubricating the various moving components within the transmission. As the gears, clutches, and bearings interact during gear shifts and power transfer, the fluid forms a protective layer, mitigating friction and wear. This lubricating function is paramount for preserving the integrity of the transmission components, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing the risk of premature wear and damage.
Moreover, transmission fluid plays a pivotal role in dissipating heat generated within the transmission system. As the vehicle operates, the transmission components are subjected to intense friction and heat buildup. Here, the fluid acts as a coolant, absorbing and dispersing the heat, thereby preventing overheating and safeguarding against thermal degradation of the transmission components. This dual function of lubrication and cooling underscores the critical role of transmission fluid in maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the transmission system.
Hydraulic Pressure and Gear Shifting
Another crucial aspect of transmission fluid pertains to its role in facilitating hydraulic pressure within the transmission. In automatic transmissions, the fluid serves as a hydraulic medium, enabling the precise engagement and disengagement of clutches and bands during gear shifts. This hydraulic functionality is instrumental in ensuring seamless gear transitions, contributing to the smooth and efficient operation of the transmission.
Corrosion Prevention and Seal Conditioning
Beyond its primary functions, transmission fluid also acts as a protective agent, guarding against corrosion and rust formation within the transmission. The fluid's chemical composition includes corrosion inhibitors, which shield the internal components from degradation, thereby prolonging the transmission's lifespan and preserving its structural integrity.
Additionally, transmission fluid plays a role in conditioning and maintaining the integrity of the seals and gaskets within the transmission. The fluid's properties help prevent the seals from drying out or becoming brittle, thereby preserving their elasticity and effectiveness in containing the fluid within the transmission system.
In essence, the multifaceted importance of transmission fluid encompasses lubrication, cooling, hydraulic functionality, corrosion prevention, and seal conditioning, collectively contributing to the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the transmission system. Its role as a versatile and indispensable fluid underscores its significance as a cornerstone of automotive engineering, underscoring the intricate symbiosis between fluid dynamics and mechanical precision within the realm of vehicle transmissions.
Types of Transmission Fluid
The diverse landscape of transmission systems in modern vehicles has given rise to a myriad of transmission fluid formulations, each tailored to meet the specific operational requirements and performance characteristics of different transmission types. Understanding the nuances of these fluid variants is pivotal for ensuring optimal transmission functionality and longevity.
Conventional Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF)
Conventional automatic transmission fluid, commonly referred to as ATF, has been a mainstay in traditional automatic transmissions for decades. Formulated to meet the lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic pressure needs of conventional automatic transmissions, ATF exhibits a balanced viscosity profile and additive composition to cater to the demands of gear shifting and power transfer within these systems. The evolution of ATF formulations has seen the incorporation of advanced additives and base oils, enhancing its thermal stability, friction-reducing properties, and wear protection capabilities.
Synthetic Transmission Fluid
Synthetic transmission fluid represents a significant advancement in fluid technology, offering superior performance and longevity compared to conventional ATF. Composed of synthetic base oils and a meticulously engineered additive package, synthetic transmission fluid delivers exceptional thermal stability, oxidation resistance, and shear stability, making it an ideal choice for high-performance and heavy-duty applications. Its ability to withstand extreme operating conditions, including high temperatures and heavy loads, positions synthetic transmission fluid as a preferred option for vehicles that demand uncompromising performance and durability.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) Fluid
The proliferation of vehicles equipped with continuously variable transmissions has led to the development of specialized CVT fluids tailored to the unique operational dynamics of these transmission systems. CVT fluid exhibits distinct frictional properties and viscosity characteristics optimized to accommodate the seamless, stepless gear ratio transitions characteristic of CVTs. Its composition is engineered to ensure precise hydraulic pressure regulation, cooling, and lubrication within the intricate pulley and belt mechanisms of CVTs, thereby preserving their operational efficiency and longevity.
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT) Fluid
Dual-clutch transmissions, known for their rapid gear shifts and enhanced fuel efficiency, rely on specialized DCT fluid to optimize their performance and durability. DCT fluid is designed to accommodate the unique frictional requirements and dual-clutch engagement mechanisms inherent to these transmissions. Its formulation emphasizes rapid heat dissipation, precise clutch engagement, and superior shear stability, catering to the demanding operational parameters of DCTs and ensuring their seamless functionality.
Hybrid Vehicle Transmission Fluid
The advent of hybrid vehicles has spurred the development of transmission fluids tailored to the specific needs of hybrid transmission systems. These fluids are engineered to accommodate the regenerative braking, electric motor assist, and seamless integration of internal combustion and electric power sources characteristic of hybrid vehicles. Their formulation prioritizes thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and compatibility with electrically driven components, ensuring optimal performance and longevity within the unique operational environment of hybrid transmissions.
In essence, the diverse array of transmission fluid variants underscores the intricate interplay between fluid dynamics, material science, and transmission engineering, with each formulation tailored to meet the exacting demands of specific transmission types. The evolution of transmission fluid technology continues to drive advancements in transmission system performance, reliability, and longevity, cementing its status as an indispensable component within the realm of automotive engineering.
The Role of Additives
Additives serve as the cornerstone of transmission fluid formulations, imbuing the fluid with a diverse array of performance-enhancing properties that are instrumental in safeguarding the integrity and functionality of the transmission system. These meticulously engineered compounds, meticulously blended into transmission fluid formulations, play a pivotal role in optimizing the fluid's performance under a broad spectrum of operating conditions.
Friction Reduction
One of the primary roles of additives is to mitigate friction within the transmission system. As the gears, clutches, and bearings interact during gear shifts and power transfer, the additives form a protective boundary, reducing friction and wear. This friction-reducing capability is essential for preserving the longevity of transmission components, ensuring smooth operation, and minimizing the risk of premature wear and damage. The additives' ability to create a durable, low-friction interface between moving parts is instrumental in optimizing the efficiency and reliability of the transmission system.
Thermal Stability
Additives are engineered to bolster the thermal stability of transmission fluid, enabling it to withstand the rigors of high-temperature operating conditions. As the transmission components are subjected to intense heat during operation, the additives act as thermal stabilizers, preventing fluid degradation and maintaining its viscosity and lubricating properties. This thermal stability is critical for preserving the fluid's functionality and ensuring consistent performance, even under demanding thermal loads.
Oxidation Resistance
The additives incorporated into transmission fluid formulations exhibit robust oxidation resistance, shielding the fluid from degradation due to exposure to oxygen and high temperatures. This oxidation resistance prevents the formation of sludge and varnish within the transmission, preserving the cleanliness and integrity of the internal components. By inhibiting oxidation, the additives contribute to the longevity of the fluid and the transmission system, ensuring sustained performance and protection against detrimental oxidative effects.
Wear Protection
Another essential role of additives is to provide wear protection for the transmission components. The additives form a resilient, protective film on metal surfaces, guarding against wear and corrosion. This wear protection capability is crucial for extending the lifespan of transmission components, preserving their precision-engineered surfaces, and minimizing the risk of mechanical degradation. By mitigating wear, the additives contribute to the overall durability and reliability of the transmission system.
Anti-Foaming Properties
Additives are tailored to impart anti-foaming properties to transmission fluid, preventing the formation of foam or air entrainment during operation. This anti-foaming capability ensures the consistent hydraulic performance of the fluid, preventing air pockets from compromising the transmission's functionality. By mitigating foam formation, the additives uphold the fluid's hydraulic integrity, contributing to the seamless operation of the transmission system.
In essence, the role of additives in transmission fluid formulations encompasses friction reduction, thermal stability, oxidation resistance, wear protection, and anti-foaming properties. These multifaceted capabilities underscore the pivotal role of additives in optimizing the performance, longevity, and reliability of transmission systems, showcasing the intricate chemistry and engineering expertise that underpin the formulation of transmission fluid for modern vehicles.
Signs of Transmission Fluid Issues
Identifying potential issues related to transmission fluid is crucial for preserving the optimal performance and longevity of the transmission system. Recognizing the subtle signs of fluid degradation or malfunction can serve as an early warning mechanism, prompting timely intervention and maintenance to mitigate potential damage. Here are the key indicators that warrant attention:
-
Discolored Fluid: Transmission fluid should exhibit a translucent, reddish hue in the case of conventional ATF or a distinct color characteristic of the specific fluid type. Discoloration, such as a dark or cloudy appearance, may indicate contamination or thermal breakdown, signaling the need for fluid inspection and potential replacement.
-
Burnt Odor: A burnt or acrid odor emanating from the transmission fluid signifies overheating and thermal degradation. This pungent odor is indicative of fluid breakdown due to excessive heat, necessitating immediate attention to prevent consequential damage to the transmission components.
-
Leaking Fluid: The presence of transmission fluid puddles or drips beneath the vehicle indicates a potential leak in the transmission system. Fluid leaks can lead to a drop in fluid levels, compromising lubrication and hydraulic functionality, thereby necessitating prompt identification and rectification of the source of the leak.
-
Slipping Gears: A noticeable hesitation or delay in gear engagement, accompanied by a sensation of slipping or erratic gear shifts, may signify insufficient fluid pressure or deteriorated fluid properties. This symptom warrants a thorough assessment of the transmission fluid and hydraulic systems to address potential causes of gear slippage.
-
Unusual Noise: An increase in transmission-related noise, such as whining, clunking, or grinding during gear shifts or operation, may indicate inadequate lubrication or mechanical stress within the transmission. This auditory anomaly necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of the transmission fluid's condition and its potential impact on the internal components.
-
Erratic Shifting: Inconsistent or abrupt gear shifts, including harsh transitions or delayed responses, can be attributed to compromised fluid properties or hydraulic irregularities. Monitoring and addressing these shifting irregularities are essential to prevent further transmission issues and ensure smooth operation.
-
Transmission Overheating: Elevated transmission temperatures, as indicated by dashboard warning lights or temperature gauges, signal potential fluid-related issues. Overheating can accelerate fluid degradation and compromise the transmission's functionality, necessitating prompt inspection and remedial measures.
-
Visible Particles or Debris: Inspecting the transmission fluid for the presence of metallic particles, debris, or sludge during fluid checks may indicate internal component wear or contamination. The identification of foreign particles warrants a comprehensive assessment of the transmission system to address potential sources of contamination or mechanical degradation.
By remaining vigilant for these telltale signs of transmission fluid issues, vehicle owners and maintenance professionals can proactively address potential concerns, safeguarding the integrity and performance of the transmission system. Timely fluid inspection, maintenance, and, if necessary, fluid replacement can mitigate the risk of extensive transmission damage, ensuring the sustained reliability and functionality of this critical automotive component.
Unveiling the Mystery: Secrets of Sealed Transmissions
The enigmatic realm of sealed transmissions has long captivated automotive enthusiasts and maintenance professionals alike, shrouded in intrigue and curiosity due to its distinctive maintenance-free design. Unraveling the secrets of sealed transmissions unveils a tapestry of engineering ingenuity, technological evolution, and meticulous attention to detail that underpin their functionality and longevity.
At the heart of the mystery lies the absence of a dipstick for fluid inspection, a defining characteristic that sets sealed transmissions apart from their traditional counterparts. This absence, while seemingly enigmatic, reflects a paradigm shift in automotive engineering, heralding the advent of self-contained, maintenance-free transmission systems that operate within exacting parameters without the need for routine fluid level checks or top-ups.
The sealed nature of these transmissions underscores a holistic approach to fluid containment and preservation, encapsulating the transmission fluid within the system's confines, safeguarding it from external contaminants and environmental factors. This self-contained ecosystem embodies a symphony of precision engineering, material science, and fluid dynamics, harmonizing to ensure optimal lubrication, cooling, and hydraulic functionality without external intervention.
Moreover, the maintenance-free configuration of sealed transmissions necessitates a proactive approach to fluid management, with specialized equipment and procedures employed for fluid inspection and potential replenishment. This distinctive maintenance paradigm underscores the evolution of automotive technology, highlighting the transition towards advanced, sealed systems that demand specialized expertise and resources for servicing and upkeep.
The unveiling of sealed transmissions' secrets illuminates a narrative of innovation and sophistication, showcasing the fusion of cutting-edge engineering principles, advanced materials, and meticulous design considerations that have culminated in the emergence of these enigmatic, maintenance-free transmission systems. This revelation serves as a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence within the automotive industry, where sealed transmissions stand as a testament to the ceaseless quest for precision, reliability, and technological advancement.
In essence, the unveiling of sealed transmissions' secrets transcends mere technical elucidation, offering a glimpse into the intricate interplay of engineering prowess, design innovation, and the relentless pursuit of automotive excellence that defines these enigmatic systems. This unveiling serves as a testament to the enduring spirit of innovation and excellence that propels the automotive industry forward, shaping the landscape of vehicle technology and redefining the boundaries of performance, reliability, and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of sealed transmissions and the secrets of transmission fluid has provided a captivating glimpse into the intricate world of automotive engineering and maintenance. The enigmatic nature of sealed transmissions, characterized by their maintenance-free design and absence of a dipstick for fluid inspection, underscores a paradigm shift in transmission system technology. This evolution reflects a convergence of precision engineering, material science, and fluid dynamics, culminating in the emergence of these self-contained, enigmatic transmission systems.
The significance of transmission fluid, with its multifaceted role in lubrication, cooling, hydraulic functionality, and corrosion prevention, has been underscored as a cornerstone of transmission system integrity. The diverse array of transmission fluid variants, ranging from conventional ATF to specialized formulations for CVTs, DCTs, and hybrid transmissions, exemplifies the meticulous tailoring of fluid compositions to meet the exacting demands of diverse transmission types.
Furthermore, the pivotal role of additives in enhancing transmission fluid performance, encompassing friction reduction, thermal stability, oxidation resistance, wear protection, and anti-foaming properties, has highlighted the intricate chemistry and engineering expertise that underpin the formulation of transmission fluid for modern vehicles.
The identification of telltale signs of transmission fluid issues, such as discoloration, burnt odor, leaking fluid, slipping gears, unusual noise, erratic shifting, transmission overheating, and visible particles or debris, serves as a proactive mechanism for preserving the integrity and functionality of the transmission system.
The revelation of sealed transmissions' secrets has unveiled a narrative of innovation and sophistication, showcasing the fusion of cutting-edge engineering principles, advanced materials, and meticulous design considerations that have culminated in the emergence of these enigmatic, maintenance-free transmission systems. This unveiling serves as a testament to the relentless pursuit of excellence within the automotive industry, where sealed transmissions stand as a testament to the ceaseless quest for precision, reliability, and technological advancement.
In essence, the exploration of sealed transmissions and the secrets of transmission fluid has unraveled a captivating tapestry of engineering ingenuity, technological evolution, and meticulous attention to detail that underpin the functionality and longevity of these enigmatic automotive components. This journey serves as a testament to the enduring spirit of innovation and excellence that propels the automotive industry forward, shaping the landscape of vehicle technology and redefining the boundaries of performance, reliability, and longevity.